How It Is Done
CVS is usually done by a perinatologist. It may be done in the doctor's office or the hospital. An overnight stay in the hospital usually is not needed.
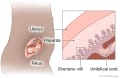
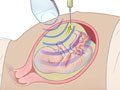
CVS may be done either through the belly (transabdominal) or through the cervix (transcervical). The choice may depend on the position of the fetus and the placenta.
Through the belly (transabdominal)
You will lie on your back on an exam table with your belly bare.
Ultrasound will be used to help your doctor guide the needle to the placenta. Gel will be rubbed on your belly. An ultrasound device (transducer) will be moved over your belly. It gives off and picks up sound waves. The sound waves are sent to a computer to make a picture of your uterus, your baby, and the placenta on a screen. The doctor can also use ultrasound to check your baby's heart rate.
Your skin where the needle will be put in is cleaned with an antiseptic and may be numbed with a medicine. Your doctor then puts a long, thin needle through your belly and uterus to the placenta. The needle is used to collect a sample of the chorionic villus cells.
After the sample is collected, the doctor may listen to your baby's heart and check your blood pressure, pulse, and breathing.
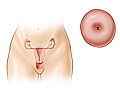
Through the cervix (transcervical)
You will take off your clothes below the waist. You will have a paper or cloth covering around your waist. You will lie on your back on an exam table with your knees bent and feet and legs supported by footrests.
Your doctor will put a special tool with curved sides (speculum) into your vagina. The speculum helps to open the vagina a little bit. This lets the doctor see the inside of the vagina and the cervix. The cervix will be cleaned with an antiseptic.
Your doctor will use ultrasound to guide a thin tube (catheter) through your cervix to the placenta. Gel will be rubbed on your belly. An ultrasound device (transducer) will be moved over your belly. It gives off and picks up sound waves. The sound waves are sent to a computer to make a picture of your uterus, your baby, and the placenta. The doctor can also use ultrasound to check your baby's heart rate.
When the catheter is in the right place, a sample of chorionic villus cells will be collected.
After the sample is collected, the doctor may listen to your baby's heart and check your blood pressure, pulse, and breathing.
How long the test takes
The test will take about 30 minutes. Getting the sample takes only a few minutes.