How It Is Done
A needle or bronchoscopic biopsy can be done without staying in the hospital. You may need to stay in the hospital if you have a video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) biopsy or an open biopsy.
You may be asked to remove dentures, eyeglasses or contact lenses, hearing aids, a wig, makeup, and jewelry before the biopsy. You will empty your bladder before the biopsy. You will need to take off all or most of your clothes. (You may be allowed to keep on your underwear if it does not interfere with the biopsy.) You will be given a cloth or paper covering to use during the biopsy. To keep you comfortable, you may get medicines through an intravenous (I.V.) needle in a vein.
A chest X-ray is usually taken after a lung biopsy to look for any problems related to the biopsy.
Bronchoscopic biopsy
A bronchoscopic biopsy is done by a doctor who specializes in lung problems (pulmonologist or a thoracic surgeon). A thin, lighted tool called a bronchoscope is inserted through the mouth or nose and into the airway. The doctor uses the bronchoscope to remove a lung tissue sample.
Needle biopsy
Your doctor will use a CT scan, ultrasound, or fluoroscopy to guide the biopsy needle. The place where your doctor inserts the needle is cleaned first with an antiseptic solution and draped with sterile towels. Your doctor will give you a numbing medicine to keep you from feeling any pain when the needle is inserted into your chest.
Your doctor will then make a small puncture in your skin and ask you to hold your breath while the biopsy needle is inserted into your lung. It is very important to avoid coughing or moving while the needle is in your chest.
After the lung tissue sample is taken, the needle is removed and a bandage is placed over the puncture site. Your care team will position you so that the needle puncture site can seal up. You will need to stay in this position for at least an hour.
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) biopsy or open biopsy
A VATS or open biopsy is done by a chest (thoracic) surgeon or a general surgeon. You will be kept comfortable and safe by your anesthesia provider. You will be asleep during the surgery.
You will be given a sedative in your I.V. to help you relax about an hour before the biopsy.
An incision is made between the ribs over the area of lung where the tissue sample is to be collected. A scope called a thoracoscope is used in VATS and is passed through this incision to view the surface of the lung and to remove a sample of lung tissue. A larger incision will be made if an open biopsy is needed to remove a tissue sample.
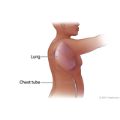
After the tissue sample is collected, your doctor will insert a drainage tube (chest tube) into the area and close the incision with stitches. One end of the tube will be in the space next to your lung. The other end will be sticking out of your chest and connected to a collection container. The chest tube helps re-expand your lung. The chest tubes will be removed when the drainage from your chest has stopped and no air is leaking from your chest incision, usually in a few days. Your stitches will be removed in 7 to 14 days.
VATS uses smaller incisions and takes less time to recover from than an open biopsy.
How long the test takes
Bronchoscopy and a needle biopsy usually take 30 to 60 minutes. You will be in the recovery room 1 to 2 hours.
A video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) biopsy or open biopsy takes 1 to 2 hours. Then you will be taken to the recovery room for about an hour. Then you will be taken to a hospital room if you need to stay overnight or longer.