Skip to main navigation
Skip to main content
Skip to footer
For
Medicare
For
Providers
For
Brokers
For
Employers
Español
For Individuals & Families:
For Individuals & Families
Medical
Dental
Other Supplemental
Explore coverage through work
How to Buy Health Insurance
Types of Dental Insurance
Open Enrollment vs. Special Enrollment
See all topics
Shop for international insurance plans
Member Guide
Find a Doctor
Log in to myCigna
Home
Knowledge Center
Wellness Library
Sonohysterogram
Sonohysterogram
Test Overview
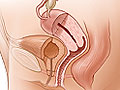
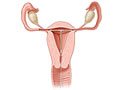
A sonohysterography test uses ultrasound to look at the inside of your uterus. A salt (saline) solution is put in the uterus for a clearer image.
Ultrasound images from this test can help find the cause of bleeding or problems getting pregnant.
If a contrast fluid is used, your doctor will look at the fallopian tubes too. This is called hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography.
Why It Is Done
Why It Is Done
A sonohysterography test may be done if other tests don't show enough detail. A clearer view of the uterus can help to:
- Look for the cause of abnormal vaginal bleeding.
- Look for the cause of fertility problems or repeated miscarriages.
- Find problems in the uterus, such as an abnormal shape or structure.
- Look for an injury, polyps, fibroids, or scars.
A hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography test is a similar test. It can check the fallopian tubes for blockage.
How To Prepare
How To Prepare
Schedule your test for when you won't be having your period. Your doctor may suggest that the test be done soon after your period ends and before your ovary releases an egg (ovulates). This timing allows your doctor to see the inside of your uterus better. It also avoids doing the test when you could be pregnant.
Your doctor may have you take an over-the-counter pain medicine, such as ibuprofen, about an hour before your test. This can help with cramps you might get during or after the test.
You may want to bring a sanitary pad. Some of the fluid may leak out after the test. You also may have some slight bleeding.
How It Is Done
How It Is Done
How is a sonohysterography test done?
A sonohysterography test can be done in a doctor's office, a hospital, or a clinic.
Before the test, you empty your bladder. You then take off your clothes below the waist. You are given a gown or drape to cover up with during the test.
For the test, you sit on the edge of a padded table. Then you lie back with your feet and legs supported by footrests.
This test is done in several steps.
- Transvaginal ultrasound. A thin ultrasound wand with gel on it is gently placed into your vagina. It will slowly be moved to take pictures from different angles. Then it is removed.
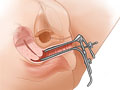
- Catheter placement. Next, your doctor places a tool called a speculum into your vagina. The speculum opens the vagina a little bit. This allows your doctor to see the cervix. Then a flexible tube (catheter) is put in the cervix or through the cervix into the uterus.
- Transvaginal ultrasound while the uterus is filled with fluid. The doctor then removes the speculum and places the ultrasound wand again. Onscreen, the ultrasound image shows the inside of your uterus while saline solution is put into the uterus. Ultrasound images are taken and reviewed.
After the test, the ultrasound wand and then the tube are removed. Most of the saline solution will leak from your cervix and vagina.
If you're having a hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography test, a contrast fluid will be passed through the catheter into the uterus. The contrast fluid allows your doctor to see the fallopian tubes. If those tubes are open, the fluid will pass through the uterus and into the fallopian tubes. Ultrasound images are taken and reviewed.
How long the test takes
The test will take about 15 to 30 minutes.
How It Feels
How It Feels
You may feel some pressure as the transducer is put into your vagina. You may feel some cramping (like menstrual cramps) from the fluid being put into your uterus.
Risks
Risks
There is a small chance of pelvic infection after a sonohysterography test.
Results
Results
Sonohysterography test results
|
Normal:
|
The shape of the uterus is normal.
|
|
No objects (such as an intrauterine device, or IUD), or growths (such as fibroids or polyps) are seen in the uterus.
|
|
Abnormal:
|
The uterus may have an abnormal shape or structure.
|
|
The uterus may have abnormal growths or masses, such as scar tissue.
|
|
The uterus may show tissue (called a septum) that divides the uterus.
|
Hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography test results
|
Normal:
|
The fallopian tubes are not scarred or damaged. The contrast fluid flows freely from the uterus and through the fallopian tubes and then spills normally into the belly.
|
|
Abnormal:
|
Fallopian tubes may be scarred, malformed, or blocked so that the contrast fluid does not flow through the tubes and spill into the belly. Blocked fallopian tubes may be caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), endometriosis, or a previous ectopic pregnancy.
|
Current as of: May 5, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.
Related Links
Medical Tests: Questions to Ask the Doctor
<cipublic-spinner variant="large"><span>Loading…</span></cipublic-spinner>