Shop for Plans
Shop for your own coverage
Plans through your employer
Learn about the medical, dental, pharmacy, behavioral, and voluntary benefits your employer may offer.
Learn
Living or working abroad?
Animal and Human Bites
Overview
Animal and human bites may cause puncture wounds, cuts, scrapes, or crushing injuries. Most animal and human bites cause minor injuries. Home treatment is usually all that is needed to care for the wound.
Animal bites
Most animal bites occur in school-age children. The face, hands, arms, and legs are the most common sites for animal bites. Be sure to teach children to be careful around animals and that an animal could hurt them. Young children should always be supervised around animals.
- Dog bites occur more than any other animal bite. They happen most often in the summer months. The dog is usually known to the person. Most injuries result from the dog being teased or bothered while eating or sleeping. Boys are bitten about twice as often as girls. The arms, head, and neck are the most likely areas to be bitten in children.
- Cat bites usually cause deeper puncture wounds than dog bites. They have a high risk of bacterial infection because they can be hard to clean well.
- Exotic pet bites, such as from rats, mice, or gerbils, may carry illnesses. But
rabies usually isn't a concern. The bites from some pets, such as iguanas, are at risk for infection. But they don't carry other serious risks. - Livestock bites, such as from horses, cows, and sheep, can cause crushing injuries. These animals have powerful jaws. Infection,
tetanus , and rabies are possible risks. - Wild animal bites may occur while hunting, camping, or hiking. Infection, tetanus, and rabies are possible risks. Bats, raccoons, skunks, foxes, and coyotes are the animals most likely to have rabies in the U.S. and Canada. Small mammals, such as mice and squirrels, almost never have rabies.
Human bites
Adult bites that cause a wound to the hand can be serious. A clenched fist striking another person in the mouth and teeth can cut or puncture the skin over the knuckles. This is commonly called a "fight bite." Tissues under the skin may be damaged, and an infection can develop.
Bites from children are:
- Usually not very deep.
- Not as forceful as adult bites.
- Not too likely to become infected.
- Not damaging to tissue under the skin.
Check Your Symptoms
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Symptoms of infection may include:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness in or around the area.
- Red streaks leading from the area.
- Pus draining from the area.
- A fever.
Pain in adults and older children
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that you can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt your normal activities and your sleep, but you can tolerate it for hours or days. Moderate can also mean pain that comes and goes even if it's severe when it's there.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): You notice the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt your sleep or activities.
Pain in children under 3 years
It can be hard to tell how much pain a baby or toddler is in.
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the baby cannot sleep, cannot get comfortable, and cries constantly no matter what you do. The baby may kick, make fists, or grimace.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The baby is very fussy, clings to you a lot, and may have trouble sleeping but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The baby is a little fussy and clings to you a little but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
With severe bleeding, any of these may be true:
- Blood is pumping from the wound.
- The bleeding does not stop or slow down with pressure.
- Blood is quickly soaking through bandage after bandage.
With moderate bleeding, any of these may be true:
- The bleeding slows or stops with pressure but starts again if you remove the pressure.
- The blood may soak through a few bandages, but it is not fast or out of control.
With mild bleeding, any of these may be true:
- The bleeding stops on its own or with pressure.
- The bleeding stops or slows to an ooze or trickle after 15 minutes of pressure. It may ooze or trickle for up to 45 minutes.
Symptoms of difficulty breathing can range from mild to severe. For example:
- You may feel a little out of breath but still be able to talk (mild difficulty breathing), or you may be so out of breath that you cannot talk at all (severe difficulty breathing).
- It may be getting hard to breathe with activity (mild difficulty breathing), or you may have to work very hard to breathe even when you're at rest (severe difficulty breathing).
Usually found in dirt and soil, tetanus bacteria typically enter the body through a wound. Wounds may include a bite, a cut, a puncture, a burn, a scrape, insect bites, or any injury that may cause broken skin. Tetanus can also happen with other infections, like dental infections. It can happen during a surgery or pregnancy and delivery.
A wound can be so small, you may not notice you have one. Or a skin blister could break and become an open wound. If there is any delay in finding or cleaning a wound, there is an increased risk for skin infection and a chance for tetanus to get in the wound. A tetanus infection can start 3 to 21 days after the bacteria enter the wound. Be especially careful about wounds on your fingers and toes.
Many people may not know when they got their last tetanus shot. So it's a good idea to call your doctor to see if you need one.
Make sure to stay up to date on your tetanus shots. A tetanus shot is recommended:
- For a dirty wound that has things like dirt, saliva, or feces in it, if you haven't had a tetanus shot in the past 5 years.
- For a clean wound, if you haven't had a tetanus shot in the past 10 years.
Rabies may be a concern after an animal bite if:
- The animal that bit you was acting strangely or foaming at the mouth.
- The animal attacked you for no clear reason.
- The animal cannot be watched for signs of rabies.
- You were bitten while you were in a foreign country or in the wilderness.
To clean a wound well:
- Wash your hands first.
- Remove large pieces of dirt or debris from the wound with cleaned tweezers. Do not push the tweezers deeply into the wound.
- Hold the wound under cool running water. If you have a sprayer in your sink, you can use it to help remove dirt and other debris from the wound.
- Scrub gently with water, a mild soap, and a washcloth.
- If some dirt or other debris is still in the wound, clean it again.
- If the wound starts to bleed, put direct, steady pressure on it.
If a chemical has caused a wound or burn, follow the instructions on the chemical's container or call Poison Control (1-800-222-1222) to find out what to do. Most chemicals should be rinsed off with lots of water, but with some chemicals, water may make the burn worse.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system's ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in adults are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and HIV/AIDS.
- Long-term alcohol and drug problems.
- Steroid medicines, which may be used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Other medicines used to treat autoimmune disease.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Not having a spleen.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Put direct, steady pressure on the wound until help arrives. Keep the area raised if you can.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Self-Care
Minor animal and human bites usually can be treated at home. Some bites cause only bruising (contusions) at the bite site, but they don't break the skin. These bites usually don't get infected.
Try these tips for caring for a bite.
-
Stop the bleeding .Apply direct pressure to the wound.
- Clean the bite as soon as you can.
This may reduce the chance of infection and scarring.
- Wash the wound for 5 minutes with large amounts of clean water.
- Don't use rubbing alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, iodine, or Mercurochrome. These products can harm the tissue and slow healing.
- Check to see if other tissues have been injured.
These tissues include blood vessels, nerves, tendons, ligaments, joints, bones, or internal organs.
- Apply a bandage, if needed.
Most bites heal well and may not need a bandage. But you may need to protect the bite from dirt and irritation. Be sure to clean the bite thoroughly before you bandage it. This can reduce the risk of infection under the bandage.
- Choose the bandage carefully. There are many products available. Don't use liquid skin bandages or moisture-enhancing bandages unless your doctor tells you to. These types of dressings may seal in bacteria that could cause an infection.
- If you use a cloth-like bandage, apply a clean bandage when your bandage gets wet or dirty. If a bandage is stuck to a scab, soak it in warm water. This will soften the scab and make the bandage easier to remove. If available, use a nonstick dressing. There are many bandage products you can buy. Be sure to read the product label for correct use.
- Watch for
signs of infection . If an infection forms under a bandage, you may need to see your doctor. - Petroleum jelly, such as Vaseline, will keep the bandage from sticking to the wound. Apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly to the wound.
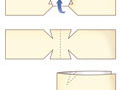
- Use an adhesive strip to hold the edges of a wound together. The strip should always go across a wound to hold the edges together, not lengthwise. You can
make a butterfly bandage at home or buy one to help hold the skin edges together.
- Treat pain.
An ice or cold pack may help reduce swelling and bruising. Never apply ice directly to a wound or the skin. This could cause tissue damage.
Prop up the injured area on pillows while you apply ice and anytime you sit or lie down. Try to keep the area at or above the level of your heart. This can reduce swelling.
If you are concerned that the injury is more serious, you may need to be checked by a doctor to see if you need stitches or a tetanus shot or to find out if you were exposed to rabies.
Call animal control
After an animal bite, notify animal control authorities. Even if the law in your area doesn't require you to report animal bites, you may wish to call animal control to report the bite. They can help you find out if the animal that bit you:
- Has been properly vaccinated.
- Needs to be observed for signs of illness. A healthy pet that has bitten someone should be confined and observed for 10 days to see whether it develops symptoms of rabies.
- Is a rabies carrier in your area and whether you need to be vaccinated to prevent
rabies . - Is a danger to others.
If you can't find a phone number for animal control, contact the police for the number.
Need for a tetanus shot
To decide if you need a tetanus shot after a wound, first decide if the object that caused the wound was dirty or clean. An object is dirty if it has dirt, soil, spit, or feces on it. A clean object does not have dirt, soil, spit, or feces on it.
You will need a tetanus shot if:
- Your wound was caused by something that was clean and your last tetanus shot was longer than 10 years ago.
- Your wound was caused by something that was dirty and your last tetanus shot was longer than 5 years ago.
- You are not sure if your wound was caused by something clean or dirty and your last tetanus shot was longer than 5 years ago.
- You are not sure when you had your last tetanus shot.
- You did not get the first series of tetanus shots (primary vaccination series).
If you need a tetanus shot, call your doctor to arrange for a shot.
Some people may need tetanus
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- New or worse signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, swelling, pus, or a fever.
- New loss of function near the wound.
- Decreased blood flow, such as cool, pale skin near the wound.
- Pain gets worse.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Learn more
Over-the-counter medicines
-
Acetaminophen -
Aspirin for Pain, Fever, and Inflammation -
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) -
Quick Tips: Safely Giving Over-the-Counter Medicines to Children
More self-care
-
Care for a Skin Wound
Current as of: October 1, 2025
Author:
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.
Related Links
Page Footer
I want to...
Audiences
Secure Member Sites
The Cigna Group Information
Disclaimer
Individual and family medical and dental insurance plans are insured by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (CHLIC), Cigna HealthCare of Arizona, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Illinois, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Georgia, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of North Carolina, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of South Carolina, Inc., and Cigna HealthCare of Texas, Inc. Group health insurance and health benefit plans are insured or administered by CHLIC, Connecticut General Life Insurance Company (CGLIC), or their affiliates (see
All insurance policies and group benefit plans contain exclusions and limitations. For availability, costs and complete details of coverage, contact a licensed agent or Cigna sales representative. This website is not intended for residents of New Mexico.