Shop for Plans
Shop for your own coverage
Plans through your employer
Learn about the medical, dental, pharmacy, behavioral, and voluntary benefits your employer may offer.
Learn
Living or working abroad?
Back Problems and Injuries
Overview
Most people will have a minor back problem at one time or another. Our body movements usually don't cause problems. But sometimes symptoms can develop from everyday wear and tear, overuse, or injury. Back problems and injuries often occur during sports or recreation activities, work-related tasks, or home projects.
Back pain can cause problems anywhere from the neck to the tailbone (coccyx). The back includes:
- The bones and joints of the spine (
vertebrae ). - The
discs that separate the vertebrae and absorb shock as you move. - The muscles and
ligaments that hold the spine together.
Back injuries are the most common cause of back pain. Injuries often occur when you use your back muscles in activities that you don't do very often. This can be things like lifting a heavy object or doing yard work. Minor injuries also may occur if you trip, fall a short distance, or twist your spine too much. A severe back injury may be caused by a car crash, a fall from a high place, a direct blow to the back or the top of the head, a high-energy fall onto the buttocks, or a penetrating injury such as a stab wound.
Back pain is often caused by an injury to one or more of the structures of the back. But it may have another cause. Some people are more likely to have back pain than others. Things that increase your risk for back pain and injury include getting older, having a family history of back pain, sitting too long, lifting or pulling heavy objects, and having a degenerative disease such as
Slumping or slouching alone may not cause low back pain. But after the back has been strained or injured, bad posture can make pain worse. "Good posture" generally means that your ears, shoulders, and hips are in a straight line. If this posture causes pain, you may have another condition such as a problem with a disc or bones in your back.
Low back pain may occur in children and teens. It's often caused by overuse or repeated activities like carrying a backpack. But children and teens are less likely to see a doctor for low back pain. Most back problems occur in adults ages 20 to 50. But back problems in children younger than 20 and adults older than 50 are more likely to have a serious cause.
Sudden (acute) injuries
Pain from an injury may be sudden and severe. Bruising and swelling may occur soon after the injury. Pain from an acute injury usually doesn't last longer than 6 weeks. Acute injuries include:
- An injury to the ligaments or muscles in the back. Examples of this are a
sprain or astrain . - A fracture or dislocation of the spine. It can cause a spinal cord injury that may lead to lifelong paralysis. It's important to immobilize the injured person and then move him or her the right way to reduce the risk of lifelong paralysis.
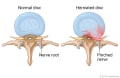
- A torn or ruptured disc. If the tear is large enough, the jellylike material inside the disc may leak out (
herniate ) and press against a nerve. - An injury that causes the compression of nerves in the lower back (
cauda equina syndrome ).
Overuse injuries
You may not remember a specific injury, especially if your symptoms began slowly or during everyday activities. These injuries occur most often from a wrong movement or posture when you lift, stand, walk, sit, or even sleep. Symptoms can include pain, muscle spasms, and stiffness. The pain often goes away within 4 weeks without any treatment.
Conditions that may cause back problems
- Conditions that weaken the spine. These include
ankylosing spondylitis ,osteoarthritis ,osteoporosis ,spinal stenosis , andPaget's disease . They are most common in older adults. In rare cases, tumors or infections can form in or around the spine. - Some medical conditions that can cause pain to spread to the back from other parts of the body (referred pain). Many health problems that can cause back pain have nothing to do with the bones, joints, muscles, or ligaments of the back.
- Spinal deformities. These include
scoliosis ,kyphosis (Scheuermann's disease) , andspondylolisthesis . -
Chronic pain syndrome caused by a past injury or degenerative disease with aging.
Treatment
Most back pain will get better and go away by itself in 1 to 4 weeks. Home treatment will often help relieve back pain that's caused by minor injuries. It's usually a good idea to keep doing your regular activities while your back is healing. Avoid heavy lifting and activities that seem to make your back problems worse.
Other treatments for a back problem or injury may include first aid, physical therapy, manipulative therapy (such as chiropractic), and medicine. In some cases, surgery is needed. Treatment depends on:
- The location and type of injury, and how bad it is.
- Your age, health condition, and activities (such as work, sports, or hobbies).
Check Your Symptoms
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Bladder or bowel trouble can include:
- Trouble emptying your bladder.
- Leaking urine.
- Blood in your urine.
- Not being able to have a bowel movement.
- Leaking stool.
Pain in adults and older children
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that you can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt your normal activities and your sleep, but you can tolerate it for hours or days. Moderate can also mean pain that comes and goes even if it's severe when it's there.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): You notice the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt your sleep or activities.
Pain in children under 3 years
It can be hard to tell how much pain a baby or toddler is in.
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the baby cannot sleep, cannot get comfortable, and cries constantly no matter what you do. The baby may kick, make fists, or grimace.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The baby is very fussy, clings to you a lot, and may have trouble sleeping but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The baby is a little fussy and clings to you a little but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
Pain in children 3 years and older
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the child can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain. No one can tolerate severe pain for more than a few hours.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt the child's normal activities and sleep, but the child can tolerate it for hours or days.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The child notices and may complain of the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt his or her sleep or activities.
Major trauma is any event that can cause very serious injury, such as:
- A fall from more than 10 ft (3.1 m)[more than 5 ft (1.5 m) for children under 2 years and adults over 65].
- A car crash in which any vehicle involved was going more than 20 miles (32 km) per hour.
- Any event that causes severe bleeding that you cannot control.
- Any event forceful enough to badly break a large bone (like an arm bone or leg bone).
With severe bleeding, any of these may be true:
- Blood is pumping from the wound.
- The bleeding does not stop or slow down with pressure.
- Blood is quickly soaking through bandage after bandage.
With moderate bleeding, any of these may be true:
- The bleeding slows or stops with pressure but starts again if you remove the pressure.
- The blood may soak through a few bandages, but it is not fast or out of control.
With mild bleeding, any of these may be true:
- The bleeding stops on its own or with pressure.
- The bleeding stops or slows to an ooze or trickle after 15 minutes of pressure. It may ooze or trickle for up to 45 minutes.
Urinary tract infections may occur in the bladder or kidneys. Symptoms may include:
- Pain or burning when you urinate.
- A frequent need to urinate without being able to pass much urine.
- Pain in the flank, which is either side of the back just below the rib cage and above the waist.
- Blood in the urine.
- Fever.
Shock is a life-threatening condition that may quickly occur after a sudden illness or injury.
Adults and older children often have several symptoms of shock. These include:
- Passing out (losing consciousness).
- Feeling very dizzy or lightheaded, like you may pass out.
- Feeling very weak or having trouble standing.
- Not feeling alert or able to think clearly. You may be confused, restless, fearful, or unable to respond to questions.
Shock is a life-threatening condition that may occur quickly after a sudden illness or injury.
Babies and young children often have several symptoms of shock. These include:
- Passing out (losing consciousness).
- Being very sleepy or hard to wake up.
- Not responding when being touched or talked to.
- Breathing much faster than usual.
- Acting confused. The child may not know where he or she is.
Symptoms of a heart attack may include:
- Chest pain or pressure, or a strange feeling in the chest.
- Sweating.
- Shortness of breath.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Pain, pressure, or a strange feeling in the back, neck, jaw, or upper belly, or in one or both shoulders or arms.
- Lightheadedness or sudden weakness.
- A fast or irregular heartbeat.
For men and women, the most common symptom is chest pain or pressure. But women are somewhat more likely than men to have other symptoms like shortness of breath, tiredness, nausea, and back or jaw pain.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Make an Appointment
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks, or contact your telehealth provider.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor or telehealth provider. You may need care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Do not move the person unless there is an immediate threat to the person's life, such as a fire. If you have to move the person, keep the head and neck supported and in a straight line at all times. If the person has had a diving accident and is still in the water, float the person face up in the water.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Put direct, steady pressure on the wound until help arrives. Keep the area raised if you can.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
After you call 911, the operator may tell you to chew 1 adult-strength (325 mg) or 2 to 4 low-dose (81 mg) aspirin. Wait for an ambulance. Do not try to drive yourself.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Self-Care
First aid for possible spinal injury
The possibility of a spinal injury must be considered anytime an accident involves the head, face, neck, or back. Permanent paralysis may be avoided if the injured person is kept from moving (immobilized) and is transported correctly.
Do not move the person.
If you think the person may have a spinal injury, do not move them unless there is an immediate threat to their life, such as a fire. If there is immediate danger, keep the person's head and neck supported and in a straight line while you move them to a safe place.
Do not remove the person from the water if they were in a diving accident. Float the person face up in the water until help arrives.
Call emergency services.
Call 911 or other emergency services to transport the injured person if you think they may have a spinal injury. This will reduce the risk of more injury to the spinal cord.
Try the following tips to help relieve back pain, swelling, and stiffness.
- Return to normal activities.
Return to your normal daily activities and work as soon as you can. You may need to make changes to or limit some work tasks.
- Stay out of bed.
Avoid bed rest. Bed rest doesn't work well for back pain. And it may cause you to heal more slowly.
- Try using heat or ice.
- Use a heating pad on a low or medium setting for 15 to 20 minutes every 2 to 3 hours. Try a warm shower in place of one session. You can also buy single-use heat wraps that last up to 8 hours.
- You can also use an ice pack for 10 to 15 minutes every 2 to 3 hours.
- Change positions every 30 minutes.
- Rub the area.
Gently massage or rub the area to help relieve pain and to encourage blood flow. Don't massage the affected area if it causes pain.
- Watch your posture.
Avoid sitting up in bed, sitting on soft couches, and twisting or sitting in other positions that make your symptoms worse.
- Change sleep positions.
Try one of the these sleep positions if you have trouble sleeping at night:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and supported by large pillows. Or lie on the floor with your legs on the seat of a sofa or chair.
- Lie on your side with your knees and hips bent and a pillow between your legs.
- Lie on your stomach if it doesn't make your pain worse.
- Start to exercise.
Back pain often gets better when you slowly increase your physical activity.
Begin moderate aerobic exercise. Take short walks (3 to 5 minutes every 3 hours) on level surfaces as soon as you can. This can help keep your muscles strong. Avoid hills and stairs. Walk only distances that you can manage without pain, especially pain in your legs.
After 2 to 3 days:
- Keep doing daily walks. But increase the walks to 5 to 10 minutes 3 to 4 times a day.
- Try swimming, which is good for your back. It may be painful right after a back injury. But lap swimming or kicking with swim fins often helps prevent back pain from coming back.
- Take a yoga class.
Add to your exercise program every week to make more progress.
- Do
pelvic tilt exercises .These gently move the spine and stretch the lower back. Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Slowly tighten your stomach muscles and press your lower back against the floor. Hold the position for 6 seconds. Don't hold your breath. Slowly relax.
- Don't smoke or use other tobacco products.
Smoking slows healing because it decreases blood supply and delays tissue repair.
Tailbone injury
Things you can do at home to treat a back injury—such as being active and getting exercise—can also help you care for a tailbone (coccyx) injury. Here are some more things you can try for a tailbone injury.
- Take a warm
sitz bath .Do this for 20 minutes, 3 to 4 times a day after the first 48 to 72 hours. This can be soothing to the tailbone area. Sitting in a hot tub or warm bath may also feel good, as long as you don't sit directly on your tailbone.
- Watch where you sit.
Don't sit on hard, unpadded surfaces.
- Use a special pillow.
Sit on a C-shaped pillow with the open space under your tailbone. This can take pressure off the tailbone area.
- Avoid constipation.
Straining to have a bowel movement will increase tailbone pain.
- Don't smoke or use other tobacco products.
Smoking slows healing because it decreases blood supply and delays tissue repair.
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- One or both legs become weak or numb.
- Loss of bowel or bladder control.
- Back pain does not improve, or it gets worse.
- A fever.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Learn more
Over-the-counter medicines
-
Acetaminophen -
Aspirin for Pain, Fever, and Inflammation -
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) -
Quick Tips: Safely Giving Over-the-Counter Medicines to Children
More self-care
-
Low Back Pain: Exercises to Reduce Pain -
Good Posture for a Healthy Back -
Stress and Back Pain -
Using Cold and Heat Therapies
Current as of: July 24, 2025
Author:
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.
Related Links
Page Footer
I want to...
Audiences
Secure Member Sites
The Cigna Group Information
Disclaimer
Individual and family medical and dental insurance plans are insured by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (CHLIC), Cigna HealthCare of Arizona, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Illinois, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Georgia, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of North Carolina, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of South Carolina, Inc., and Cigna HealthCare of Texas, Inc. Group health insurance and health benefit plans are insured or administered by CHLIC, Connecticut General Life Insurance Company (CGLIC), or their affiliates (see
All insurance policies and group benefit plans contain exclusions and limitations. For availability, costs and complete details of coverage, contact a licensed agent or Cigna sales representative. This website is not intended for residents of New Mexico.