Shop for Plans
Shop for your own coverage
Plans through your employer
Learn about the medical, dental, pharmacy, behavioral, and voluntary benefits your employer may offer.
Learn
Living or working abroad?
Childhood Medulloblastoma and Other Central Nervous System Embryonal Tumors Treatment (PDQ®): Treatment - Patient Information [NCI]
General Information About Childhood Medulloblastoma and Other Central Nervous System Embryonal Tumors
Medulloblastoma and other central nervous system (CNS) embryonal tumors may begin in embryonic (fetal) cells that remain in the brain after birth.
Medulloblastoma is a fast-growing tumor that forms in the cerebellum (the lower, back part of the brain). Medulloblastoma is the most common type of CNS embryonal tumor. CNS embryonal tumors are uncontrolled growths of cells in the brain. These tumors form in cells that are left over from fetal development, called embryonal cells. Pineoblastoma is a fast-growing type of brain tumor that forms in or around a tiny organ near the center of the brain called the pineal gland.
These tumors may be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). Benign brain tumors grow and press on nearby areas of the brain but rarely spread to other parts of the brain. Malignant brain tumors are likely to grow quickly and spread into other parts of the brain. They may also spread to other parts of the body, but this is rare. When a tumor grows into and presses on an area of the brain or spreads to other parts of the brain, it may stop that part of the brain from working the way it should. Both benign and malignant brain tumors can cause serious signs or symptoms and need treatment.
Most medulloblastomas, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastomas in children are malignant. These tumors tend to spread through the cerebrospinal fluid to other parts of the brain and spinal cord.
Although cancer is rare in children, brain tumors are the second most common type of childhood cancer, after leukemia. This summary is about the treatment of primary brain tumors (tumors that begin in the brain).

Anatomy of the inside of the brain, showing the pineal and pituitary glands, optic nerve, ventricles (with cerebrospinal fluid shown in blue), and other parts of the brain.
There are different types of CNS embryonal tumors.
The different types of CNS embryonal tumors include:
| Medulloblastomas
Most CNS embryonal tumors are medulloblastomas. Medulloblastomas are fast-growing tumors that form in brain cells in the cerebellum. The cerebellum is at the lower back part of the brain between the cerebrum and the brain stem. The cerebellum controls movement, balance, and posture. It is rare for medulloblastomas to spread to the bone, bone marrow, lung, or other parts of the body. |
| Other types of CNS embryonal tumors (nonmedulloblastoma)
Other types of CNS embryonal tumors are fast-growing tumors and may form in brain cells anywhere in the brain, including the cerebrum, brain stem, or spinal cord. The cerebrum is at the top of the head and is the largest part of the brain. The cerebrum controls thinking, learning, problem-solving, emotions, speech, reading, writing, and voluntary movement. It is rare for these tumors to spread to the bone, bone marrow, lung, or other parts of the body. There are many types of CNS embryonal (nonmedulloblastoma) tumors:
|
CNS atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor is also a type of embryonal tumor, but it is treated differently than other childhood CNS embryonal tumors. Learn more at
Pineoblastoma forms in cells of the pineal gland.
The pineal gland is a tiny organ in the center of the brain. The gland makes melatonin, a substance that helps control our sleep cycle. Pineoblastoma are usually malignant fast-growing tumors with cells that look very different from normal pineal gland cells. Pineoblastomas are not a type of CNS embryonal tumor but treatment for them is similar to treatment for CNS embryonal tumors.
Pineoblastoma is linked with inherited changes in the retinoblastoma (RB1) gene. A child with the inherited form of retinoblastoma (cancer that forms in the tissues of the retina) has an increased risk of pineoblastoma. When retinoblastoma forms at the same time as a tumor in or near the pineal gland, it is called trilateral retinoblastoma. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) testing in children with retinoblastoma may detect pineoblastoma at an early stage when it can be treated successfully. It is rare for pineoblastoma to spread to the bone, bone marrow, lung, or other parts of the body.
Certain genetic conditions increase the risk of childhood medulloblastoma.
Childhood medulloblastoma is caused by certain changes to the way brain cells function, especially how they grow and divide into new cells. Often, the exact cause of the cell changes is unknown. Learn more about how cancer develops at
A risk factor is anything that increases the chance of getting a disease. Not every child with one or more of these risk factors will develop medulloblastoma. And it will develop in some children who don't have a known risk factor.
The risk for medulloblastoma is increased in people who have any of the following inherited diseases:
- Turcot syndrome
- Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
- Nevoid basal cell carcinoma (Gorlin) syndrome
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Fanconi anemia
Talk with your child's doctor if you think your child may be at risk.
Genetic counseling may be done for children with medulloblastoma or pineoblastoma.
It may not be clear from the family medical history whether a child with a brain tumor has an inherited condition that increased their risk. Genetic counselors and other specially trained health professionals can discuss your child's diagnosis and the family's medical history to understand:
- your options for ELP1, APC, SUFU, PTCH1, TP53, PALB2, or BRCA2 gene testing if your child has medulloblastoma
- your options for RB1 or DICER1 gene testing if your child has pineoblastoma
- the risk of other cancers for your child
- the risk of cancer for your child's siblings
- the risks and benefits of learning genetic information
Genetic counselors can also help you cope with your child's genetic testing results, including how to discuss the results with family members.
Learn more about
Symptoms of medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastoma depend on the child's age and where the tumor is.
Children may not have symptoms of medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, or pineoblastoma until the tumor has grown bigger. It's important to check with your child's doctor if your child has:
- loss of balance, trouble walking, lack of coordination, or slow speech
- a headache, especially in the morning, or headache that goes away after vomiting
- general weakness
- weakness on one side of the face
- unusual sleepiness or change in energy level
- seizures
- double vision or other eye problems
- nausea and vomiting
Infants and young children with these tumors may be irritable or grow slowly. Also they may not eat well or meet developmental milestones such as sitting, walking, and talking in sentences. These tumors may also cause an increase in the size of an infant's head.
These symptoms may be caused by problems other than medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, or pineoblastoma. The only way to know is to see your child's doctor.
Tests that examine the brain and spinal cord are used to diagnose childhood medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastoma.
If your child has symptoms that suggest medulloblastoma, another type of CNS embryonal tumor, or pineoblastoma, the doctor will need to find out if these are due to cancer or another problem. They will ask about your child's personal and family health history and do a physical exam. Depending on the results, they may recommend other tests. If your child is diagnosed with medulloblastoma, another type of CNS embryonal tumor, or pineoblastoma, the results of these tests will help you and your child's doctor plan treatment.
The tests used to diagnose medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastoma may include:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the brain and spinal cord with gadolinium is a procedure that uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the brain and spinal cord. A substance called gadolinium is injected into a vein. The gadolinium collects around the cancer cells so they show up brighter in the picture. This procedure is also called nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI). Sometimes magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is done during the MRI scan to look at the chemicals in brain tissue.
- CT scan (CAT scan) uses a computer linked to an x-ray machine to make a series of detailed pictures inside the body from different angles. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography. Learn more about
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans and Cancer . - Lumbar puncture is a procedure used to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the spinal column. This is done by placing a needle between two bones in the spine and into the lining around the spinal cord to remove a sample of CSF. The sample of CSF is checked under a microscope for signs of tumor cells. The sample may also be checked for the amounts of protein and glucose. A higher-than-normal amount of protein or lower-than-normal amount of glucose may be a sign of a tumor. This procedure is also called an LP or spinal tap.
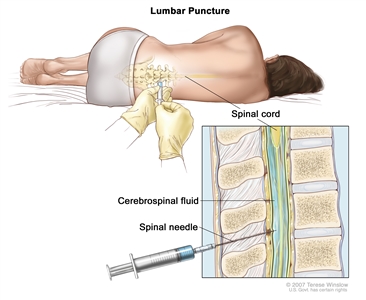
Lumbar puncture. A patient lies in a curled position on a table. After a small area on the lower back is numbed, a spinal needle (a long, thin needle) is inserted into the lower part of the spinal column to remove cerebrospinal fluid (CSF, shown in blue). The fluid may be sent to a laboratory for testing.
A biopsy may be done to be sure of the diagnosis.
If doctors think your child may have medulloblastoma, another type of CNS embryonal tumor, or pineoblastoma, a biopsy may be done. The biopsy is done by removing part of the skull and using a needle to remove a sample of tissue. Sometimes, a computer-guided needle is used to remove the tissue sample. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. If cancer cells are found, the doctor may remove as much tumor as safely possible during the same surgery. The piece of skull is usually put back in place after the procedure.
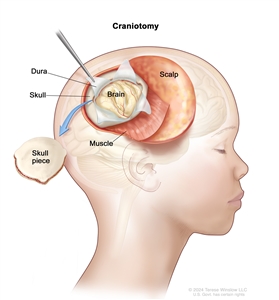
Craniotomy. An opening is made in the skull and a piece of the skull is removed to show part of the brain.
The following tests may be done on the sample of tissue that is removed:
- Immunohistochemistry is a laboratory test that uses antibodies to check for certain antigens (markers) in a sample of a patient's tissue. The antibodies are usually linked to an enzyme or a fluorescent dye. After the antibodies bind to a specific antigen in the tissue sample, the enzyme or dye is activated, and the antigen can then be seen under a microscope. This type of test is used to help diagnose cancer and to help tell one type of cancer from another type of cancer.
- Molecular testing checks for certain genes, proteins, or other molecules in a sample of tissue, blood, or bone marrow. Molecular tests also check for certain changes in a gene or chromosome that may cause or affect the chance of developing medulloblastoma, another type of embryonal tumor, or pineoblastoma. A molecular test may be used to help plan treatment, find out how well treatment is working, or make a prognosis. Children with medulloblastoma, another type of embryonal tumor, or pineoblastoma may be eligible for molecular testing through the Molecular Characterization Initiative.
The Molecular Characterization Initiative offers free molecular testing to children, adolescents, and young adults with certain types of newly diagnosed cancer. The program is offered through NCI's Childhood Cancer Data Initiative. To learn more, visit
About the Molecular Characterization Initiative .
Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
If your child has been diagnosed with medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumor, or pineoblastoma, you likely have questions about how serious the cancer is and your child's chances of survival. The likely outcome or course of a disease is called prognosis.
The prognosis and treatment options depend on:
- the type of tumor and where it is in the brain
- whether the cancer has spread within the brain and spinal cord when the tumor is found
- the age of the child when the tumor is found
- how much of the tumor remains after surgery
- whether there are certain changes in the chromosomes, genes, or brain cells
- whether the tumor has just been diagnosed or has recurred (come back)
No two people are alike, and responses to treatment can vary greatly. Your child's cancer care team is in the best position to talk with you about your child's prognosis.
You may want to get a second opinion.
You may want to get a second opinion to confirm your child's diagnosis and treatment plan. If you seek a second opinion, you will need to get important medical test results and reports from the first doctor to share with the second doctor. The second doctor will review the genetic test results, pathology report, slides, and scans. This doctor may agree with the first doctor, suggest changes to the treatment plan, or provide more information about your child's tumor.
To learn more about choosing a doctor and getting a second opinion, see
Staging Childhood Medulloblastoma, Other Central Nervous System Embryonal Tumors, and Pineoblastoma
Medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastoma in children are treated based on the tumor type and the child's age.
Cancer stage describes the extent of cancer in the body, such as the size of the tumor, whether it has spread, and how far it has spread from where it first formed. There is no staging system used for childhood medulloblastoma, other central nervous system (CNS) embryonal tumors, or pineoblastoma, but the tests and procedures done to diagnose the cancer are also used to help plan treatment.
Treatment of other CNS embryonal tumors and pineoblastoma in children is based on the child's age. Children aged 3 years and younger may be given different treatment than children older than 3 years.
Treatment of medulloblastoma in children older than 3 years also depends on whether the tumor is average risk or high risk.
Average risk
Medulloblastomas are called average risk when all of the following are true:
- The tumor was completely removed by surgery or there was only a very small amount remaining.
- The cancer has not spread to other parts of the body.
High risk
Medulloblastomas are called high risk if any of the following are true:
- Some of the tumor was not removed by surgery.
- The cancer has spread to other parts of the brain or spinal cord or to other parts of the body.
In general, cancer is more likely to recur (come back) after treatment in patients with a high-risk tumor.
The results of the tests and procedures done to diagnose medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastoma in children are used to plan cancer treatment.
If your child is diagnosed with medulloblastoma, another type of CNS embryonal tumor, or pineoblastoma, they will be referred to a pediatric oncologist /neuro-oncologist. This is a doctor who specializes in staging and treating childhood cancers. They will recommend tests to determine the extent (stage) of cancer. Some of the tests used to diagnose the cancer are repeated after surgery. This is to find out how much tumor remains after surgery and to see if the cancer has spread from the brain to the spine or other parts of the body. It is important to know if the cancer has spread in order to plan the best treatment. Learn more about diagnostic tests in the
The following tests may be used to find out if the cancer has spread beyond the brain and spinal cord:
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are procedures in which a sample of bone marrow and bone is removed from the hipbone or breastbone using a special needle. A pathologist views the sample under a microscope to look for signs of cancer. A bone marrow aspiration and biopsy are only done when there are signs the cancer has spread to the bone marrow.
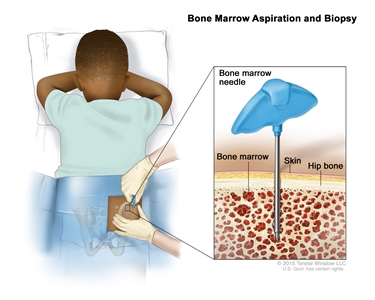
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. After a small area of skin is numbed, a bone marrow needle is inserted into the child's hip bone. Samples of blood, bone, and bone marrow are removed for examination under a microscope. - Bone scan is a procedure to check if there are rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, in the bone. A very small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive material collects in the bones with cancer and is detected by a scanner. A bone scan is only done when there are signs or symptoms that the cancer has spread to the bone.
Sometimes childhood medulloblastoma and other central nervous system embryonal tumors come back after treatment.
Childhood medulloblastoma and other types of CNS embryonal tumors most often recur (come back) within 3 years after treatment but may come back many years later. Recurrent childhood medulloblastoma and other CNS embryonal tumors may come back in the same place as the original tumor and/or in a different place in the brain or spinal cord.
Treatment Option Overview
There are different types of treatment for children who have medulloblastoma and other central nervous system (CNS) embryonal tumors.
There are different types of treatment for children and adolescents with medulloblastoma, other types of CNS embryonal tumors, or pineoblastoma. You and your child's cancer care team will work together to decide treatment. Many factors will be considered, such as your child's overall health and whether the tumor is newly diagnosed or has come back.
Children who have medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastoma should have their treatment planned by a team of health care providers who are experts in treating brain tumors in children.
A pediatric oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating children with cancer, oversees treatment of medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastoma. The pediatric oncologist works with other pediatric health care providers who are experts in treating children with brain tumors and who specialize in certain areas of medicine. Other specialists may include:
- pediatrician
- neurosurgeon
- neurologist
- neuropathologist
- neuroradiologist
- rehabilitation specialist
- radiation oncologist
- psychologist
Your child's treatment plan will include information about the cancer, the goals of treatment, treatment options, and the possible side effects. It will be helpful to talk with your child's cancer care team before treatment begins about what to expect. For help every step of the way, see our downloadable booklet,
The following types of treatment may be used:
Surgery
Surgery is used to diagnose and treat childhood medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastoma as described in the
After the doctor removes all the cancer that can be seen at the time of the surgery, some patients may be given chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both to kill any cancer cells that are left. Treatment given after the surgery, to lower the risk that the cancer will come back, is called adjuvant therapy.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. Medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, or pineoblastoma in children may be treated with external beam radiation therapy. External beam radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the area of the body with cancer.
Certain ways of giving external radiation therapy can help keep radiation from damaging nearby healthy tissue. These types of radiation therapy include:
- Conformal radiation therapy uses a computer to make a 3-dimensional (3-D) picture of the tumor and shapes the radiation beams to fit the tumor. This allows a high dose of radiation to reach the tumor and causes less damage to nearby healthy tissue.
- Stereotactic radiation therapy uses a machine that aims radiation directly at the tumor, causing less damage to nearby healthy tissue. The total dose of radiation is divided into several smaller doses given over several days. A rigid head frame is attached to the skull to keep the head still during this radiation treatment. This procedure is also called stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotaxic radiation therapy.
Because radiation therapy can affect growth and brain development in young children, especially children who are 3 years or younger, chemotherapy may be given to delay or reduce the need for radiation therapy.
Radiation therapy to the brain can also affect growth and development in children older than 3 years. For this reason, clinical trials are studying new ways of giving radiation that may have fewer side effects than standard methods.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (also called chemo) uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. Chemotherapy may be given alone or with other types of treatment, such as radiation therapy.
To treat medulloblastoma, other CNS embryonal tumors, and pineoblastoma, chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein. When given this way, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy that may be used alone or in combination includes:
- carboplatin
- cisplatin
- cyclophosphamide
- etoposide
- irinotecan
- lomustine
- methotrexate
- temozolomide
- thiotepa
- topotecan
- vincristine
Other chemotherapy drugs not listed here may also be used.
Learn more about
High-dose chemotherapy with autologous stem cell rescue
High doses of chemotherapy are given to kill cancer cells. This cancer treatment destroys healthy cells, including blood-forming cells. Stem cell transplant is a treatment to replace the blood-forming cells. Stem cells (immature blood cells) are removed from the blood or bone marrow of the patient and are frozen and stored. After the patient completes chemotherapy, the stored stem cells are thawed and given back to the patient through an infusion. These reinfused stem cells grow into (and restore) the body's blood cells.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs or other substances to block the action of specific enzymes, proteins, or other molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Vismodegib may be used to treat recurrent medulloblastoma in children who have finished growing.
Targeted therapy is also being studied for the treatment of childhood medulloblastoma and other CNS embryonal tumors that have recurred (come back) after treatment.
Learn more about
New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice.
Use our
Learn more at
Treatment of Childhood Medulloblastoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the
Younger children with medulloblastoma
Treatment of newly diagnosed medulloblastoma in children aged 3 years and younger includes:
- Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible, followed by chemotherapy.
Other treatments that may be given after surgery include:
- High-dose systemic and intraventricular chemotherapy.
- High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue.
- Chemotherapy with or without radiation therapy to the area where the tumor was removed.
Children older than 3 years with average-risk medulloblastoma
Treatment of newly diagnosed average-risk medulloblastoma in children older than 3 years includes:
- Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This is followed by radiation therapy to the brain and spinal cord. Chemotherapy may also be given during and after radiation therapy.
- Surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, and high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue.
Children older than 3 years with high-risk medulloblastoma
Treatment of newly diagnosed high-risk medulloblastoma in children older than 3 years includes:
- Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This is followed by a larger dose of radiation therapy to the brain and spinal cord than the dose given for average-risk medulloblastoma. Chemotherapy is also given during and after radiation therapy.
- Surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, and high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue.
Treatment of Other CNS Embryonal (nonmedulloblastoma) Tumors in Children
For information about the treatments listed below, see the
Children aged 3 years and younger with nonmedulloblastoma, nonmedulloepithelioma embryonal tumors
Treatment of newly diagnosed nonmedulloblastoma, nonmedulloepithelioma embryonal tumors in children 3 years or younger includes:
- Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible, followed by chemotherapy.
Children older than 3 years with nonmedulloblastoma, nonmedulloepithelioma embryonal tumors
Treatment of newly diagnosed nonmedulloblastoma, nonmedulloepithelioma embryonal tumors in children older than 3 years includes:
- Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This is followed by radiation therapy to the brain and spinal cord. Chemotherapy is also given during and after radiation therapy.
Children with embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes or medulloepithelioma
Treatment of newly diagnosed embryonal tumor with multilayered rosettes (ETMR) or medulloepithelioma may include:
- Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This is followed by chemotherapy. Radiation therapy may also be given.
- Surgery to remove the tumor, followed by high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue.
Children with CNS neuroblastoma
Treatment of newly diagnosed CNS neuroblastoma may include:
- Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This is followed by radiation therapy to the brain and spinal cord. Chemotherapy may also be given.
Treatment of Childhood Pineoblastoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the
Children aged 3 years and younger
Treatment of newly diagnosed pineoblastoma in children aged 3 years and younger includes:
- Biopsy to diagnose pineoblastoma and surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. Chemotherapy is usually given after surgery.
- Surgery followed by high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell rescue.
- If the tumor responds to chemotherapy, radiation therapy is given when the child is older.
Children older than 3 years
Treatment of newly diagnosed pineoblastoma in children older than 3 years includes:
- Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible. This is followed by radiation therapy to the brain and spinal cord and chemotherapy.
Treatment of Recurrent Childhood Medulloblastoma and Other Central Nervous System Embryonal Tumors
For information about the treatments listed below, see the
Treatment for recurrent childhood medulloblastoma and other CNS embryonal tumors may include:
- Biopsy to diagnose medulloblastoma and other CNS embryonal tumors. Surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible may be done.
- For children who previously received radiation therapy and chemotherapy, treatment may include repeat radiation at the site where the cancer started and where the tumor has spread. Stereotactic radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy may also be used.
- For infants and young children who previously received chemotherapy only and have a local recurrence, treatment may be chemotherapy with radiation therapy to the tumor and the area close to it. Surgery to remove the tumor may also be done.
- For patients who previously received radiation therapy, high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell rescue may be used. It is not known whether this treatment improves survival.
- Targeted therapy with a signal transduction inhibitor (vismodegib) for patients whose cancer has certain changes in the genes.
Use our
Side Effects
The tumor and the treatment may cause symptoms that continue after treatment ends.
Signs or symptoms caused by the tumor may begin before the cancer is diagnosed and continue for months or years. It is important to talk with your child's doctors about signs or symptoms caused by the tumor that may continue after treatment.
Cancer treatments can cause side effects. Which side effects your child might have depends on the type of treatment they receive, the dose, and how their body reacts. Talk with your child's treatment team about which side effects to look for and ways to manage them.
To learn more about side effects that begin during treatment for cancer, visit
Problems from cancer treatment that begin 6 months or later after treatment and continue for months or years are called late effects. Late effects of cancer treatment may include:
- Physical problems that affect:
- bone and muscle growth and development
- thyroid, heart, or hearing function
- Changes in mood, feelings, thinking, learning, or memory
- Second cancers (new types of cancer), such as thyroid or other brain tumors
Children diagnosed with medulloblastoma may have certain problems after surgery or radiation therapy, such as changes in the ability to think, learn, and pay attention. Also, cerebellar mutism syndrome may occur after surgery. Signs of this syndrome include:
- delayed ability to speak
- trouble swallowing and eating
- loss of balance, trouble walking, and worsening handwriting
- loss of muscle tone
- mood swings and changes in personality
Some late effects may be treated or controlled. It is important to talk with your child's doctors about the effects cancer treatment can have on your child and the types of symptoms to expect after cancer treatment has ended. Learn more about
Follow-Up Care
Some of the tests that were done to diagnose the cancer or to find out the stage of the cancer may be repeated to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests. This is sometimes called re-staging. Learn more about these tests in the
Some of the imaging tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your child's condition has changed or if the brain tumor has recurred (come back). If the imaging tests show abnormal tissue in the brain, a biopsy may also be done to find out if the tissue is made up of dead tumor cells or if new cancer cells are growing. These tests are sometimes called follow-up tests or check-ups.
Coping With Cancer
When a child has cancer, every member of the family needs support. Taking care of yourself during this difficult time is also important. Reach out to your child's treatment team and to people in your family and community for support. To learn more, see
Related Resources
For more information about childhood medulloblastoma and other central nervous system embryonal tumor, see:
-
Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium (PBTC)
For more childhood cancer information and other general cancer resources, visit:
-
About Cancer -
Childhood Cancers -
CureSearch for Children's Cancer -
Late Effects of Treatment for Childhood Cancer -
Adolescents and Young Adults with Cancer -
Children with Cancer: A Guide for Parents -
Cancer in Children and Adolescents -
Cancer Staging -
Coping with Cancer -
Questions to Ask Your Doctor about Cancer -
For Survivors, Caregivers, and Advocates
About This PDQ Summary
About PDQ
Physician Data Query (PDQ) is the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) comprehensive cancer information database. The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language. The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in
PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). NIH is the federal government's center of biomedical research. The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH.
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of childhood medulloblastoma and other central nervous system embryonal tumors. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Reviewers and Updates
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Updated") is the date of the most recent change.
The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the
Clinical Trial Information
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another. Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients. During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard." Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Clinical trials can be found online at
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as "NCI's PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: [include excerpt from the summary]."
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Childhood Medulloblastoma and Other Central Nervous System Embryonal Tumors Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at:
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our
Last Revised: 2024-12-02
If you want to know more about cancer and how it is treated, or if you wish to know about clinical trials for your type of cancer, you can call the NCI's Cancer Information Service at 1-800-422-6237, toll free. A trained information specialist can talk with you and answer your questions.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the
Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Ignite Healthwise, LLC.
Page Footer
I want to...
Audiences
Secure Member Sites
The Cigna Group Information
Disclaimer
Individual and family medical and dental insurance plans are insured by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (CHLIC), Cigna HealthCare of Arizona, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Illinois, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Georgia, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of North Carolina, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of South Carolina, Inc., and Cigna HealthCare of Texas, Inc. Group health insurance and health benefit plans are insured or administered by CHLIC, Connecticut General Life Insurance Company (CGLIC), or their affiliates (see
All insurance policies and group benefit plans contain exclusions and limitations. For availability, costs and complete details of coverage, contact a licensed agent or Cigna sales representative. This website is not intended for residents of New Mexico.