Types of treatment for childhood thyroid cancer
Who treats children with thyroid cancer?
A pediatric oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating children with cancer, oversees treatment of thyroid cancer. The pediatric oncologist works with other health care providers who are experts in treating children with cancer and who specialize in certain areas of medicine. Other specialists may include:
- pediatrician
- pediatric surgeon
- radiation oncologist
- pathologist
- pediatric nurse specialist
- social worker
- rehabilitation specialist
- psychologist
- child-life specialist
There are different types of treatment for children and adolescents with thyroid cancer. You and your child's cancer care team will work together to decide treatment. Many factors will be considered, such as your child's overall health and whether the tumor is newly diagnosed or has come back.
Your child's treatment plan will include information about the cancer, the goals of treatment, treatment options, and the possible side effects. It will be helpful to talk with your child's cancer care team before treatment begins about what to expect. For help every step of the way, see our booklet, Children with Cancer: A Guide for Parents.
Treatment for thyroid cancer might include:
Surgery
Surgery is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer. One of the following procedures may be used:
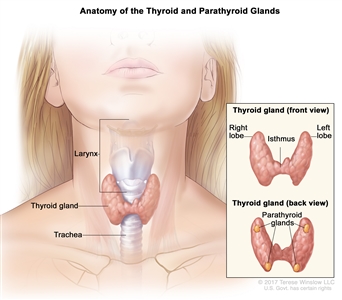
- Total thyroidectomy is the removal of the whole thyroid. Lymph nodes near the cancer may also be removed and checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.
- Near-total thyroidectomy is the removal of all but a very small part of the thyroid. Lymph nodes near the cancer may also be removed and checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.
In children, a total thyroidectomy is usually done.
Learn more about Surgery to Treat Cancer.
Radioactive iodine therapy
Follicular and papillary thyroid cancers are sometimes treated with radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy. RAI therapy may be given to children after surgery to kill any thyroid cancer cells that were not removed or to children whose tumor cannot be removed by surgery. RAI is taken by mouth and collects in any remaining thyroid tissue, including thyroid cancer cells that have spread to other places in the body. Because only thyroid tissue takes up iodine, the RAI destroys thyroid tissue and thyroid cancer cells without harming other tissue. Before a full treatment dose of RAI is given, a small test dose is given to see if the tumor takes up the iodine.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs or other substances to block the action of specific enzymes, proteins, and other molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. Targeted therapies used to treat thyroid cancer include:
- entrectinib
- larotrectinib
- selpercatinib
- vandetanib
Learn more about Targeted Therapy to Treat Cancer.
Clinical trials
Joining a clinical trial may be an option. There are different types of clinical trials for childhood cancer. For example, a treatment trial tests new treatments or new ways of using existing treatments. Supportive care and palliative care trials look at ways to improve quality of life, especially for those who have side effects from cancer and its treatment.
You can use the clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. The search allows you to filter trials based on the type of cancer, your child's age, and where the trials are being done.
Learn more at Clinical Trials Information for Patients and Caregivers.
Treatment of newly diagnosed childhood papillary and follicular thyroid cancer
Treatment of papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma in children may include:
- Surgery to remove all or most of the thyroid gland and sometimes lymph nodes near the thyroid gland. Radioactive iodine therapy may also be given if any thyroid cancer cells remain after surgery. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is given to make up for the lost thyroid hormone.
- Radioactive iodine therapy alone may be given to children whose tumor cannot be removed by surgery. HRT is given to make up for the lost thyroid hormone.
Treatment of newly diagnosed childhood medullary thyroid cancer
Treatment of medullary thyroid cancer in children may include:
- surgery to remove the cancer
- targeted therapy (selpercatinib or vandetanib) for cancer that has continued to grow during treatment or has spread to other parts of the body
Treatment of progressive or recurrent childhood thyroid cancer
Treatment of progressive or recurrent papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma in children may include:
- radioactive iodine therapy
- targeted therapy (entrectinib, larotrectinib, or selpercatinib)
If the cancer comes back after treatment, your child's doctor will talk with you about what to expect and possible next steps. There might be treatment options that may shrink the cancer or control its growth. If there are no treatments, your child can receive care to control symptoms from cancer so they can be as comfortable as possible.