Treatment Option Overview
There are different types of treatment for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia.
Different types of treatments are available for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). You and your cancer care team will work together to decide your treatment plan, which may include more than one type of treatment. Many factors will be considered, such as the stage of the cancer, your overall health, and your preferences. Your plan will include information about your cancer, the goals of treatment, your treatment options and the possible side effects, and the expected length of treatment.
Talking with your cancer care team before treatment begins about what to expect will be helpful. You'll want to learn what you need to do before treatment begins, how you'll feel while going through it, and what kind of help you will need. To learn more, visit Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Treatment.
The following types of treatment are used:
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells.
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy blocks the enzyme tyrosine kinase that causes stem cells to develop into more white blood cells (blasts) than the body needs.
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors used to treat CML include:
- asciminib
- imatinib mesylate
- dasatinib
- nilotinib
- bosutinib
Having bariatric surgery may block some absorption of oral tyrosine kinase inhibitors, limiting their effectiveness.
Learn more about Targeted Therapy to Treat Cancer and Drugs Approved for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body (systemic chemotherapy).
Learn more about Chemotherapy to Treat Cancer and Drugs Approved for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a treatment that uses the patient's immune system to fight cancer. Substances made by the body or made in a laboratory are used to boost, direct, or restore the body's natural defenses against cancer. Interferon is a type of immunotherapy used to treat CML. It affects the division of cancer cells and can slow tumor growth.
Learn more about Immunotherapy to Treat Cancer and Drugs Approved for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.
High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant (SCT)
High doses of chemotherapy are given to kill cancer cells. Healthy cells, including blood -forming cells, are also destroyed by the cancer treatment. stem cell transplant is a treatment to replace the blood-forming cells. Stem cells (immature blood cells) are removed from the blood or bone marrow of the patient or a donor and are frozen and stored. After the patient completes chemotherapy, the stored stem cells are thawed and given back to the patient through an infusion. These reinfused stem cells grow into (and restore) the body's blood cells.
Learn more about Stem Cell Transplants in Cancer Treatment.
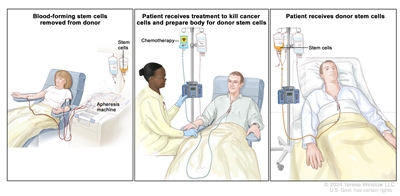
Donor stem cell transplant. (Step 1): Four to five days before donor stem cell collection, the donor receives a medicine to increase the number of stem cells circulating through their bloodstream (not shown). The blood-forming stem cells are then collected from the donor through a large vein in their arm. The blood flows through an apheresis machine that removes the stem cells. The rest of the blood is returned to the donor through a vein in their other arm. (Step 2): The patient receives chemotherapy to kill cancer cells and prepare their body for the donor stem cells. The patient may also receive radiation therapy (not shown). (Step 3): The patient receives an infusion of the donor stem cells.
Donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI)
Donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) is a cancer treatment that may be used after stem cell transplant. Lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) from the stem cell transplant donor are removed from the donor's blood and may be frozen for storage. The donor's lymphocytes are thawed if they were frozen and then given to the patient through one or more infusions. The lymphocytes see the patient's cancer cells as not belonging to the body and attack them.
Surgery
Splenectomy is surgery to remove the spleen.
New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
For some people, joining a clinical trial may be an option. There are different types of clinical trials for people with cancer. For example, a treatment trial tests new treatments or new ways of using current treatments. Supportive care and palliative care trials look at ways to improve quality of life, especially for those who have side effects from cancer and its treatment.
You can use the clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials accepting participants. The search allows you to filter trials based on the type of cancer, your age, and where the trials are being done. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Learn more about clinical trials, including how to find and join one, at Clinical Trials Information for Patients and Caregivers.
Treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia may cause side effects.
For information about side effects caused by treatment for cancer, visit our Side Effects page.
Follow-up care may be needed.
As you go through treatment, you will have follow-up tests or check-ups. Some tests that were done to diagnose or stage the cancer may be repeated to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred (come back).