Shop for Plans
Shop for your own coverage
Plans through your employer
Learn about the medical, dental, pharmacy, behavioral, and voluntary benefits your employer may offer.
Learn
Living or working abroad?
Colon Cancer Treatment (PDQ®): Treatment - Health Professional Information [NCI]
General Information About Colon Cancer
Cancer of the colon is a highly treatable and often curable disease when localized to the bowel. Surgery is the primary form of treatment and results in cure in approximately 50% of patients. However, recurrence following surgery is a major problem and is often the ultimate cause of death.
Incidence and Mortality
Worldwide, colorectal cancer is the third most common form of cancer. In 2022, there were an estimated 1.93 million new cases of colorectal cancer and 903,859 deaths.[
Estimated new cases and deaths from colon and rectal cancer in the United States in 2025:[
- New cases of colon cancer: 107,320.
- New cases of rectal cancer: 46,950.
- Deaths: 52,900 (colon and rectal cancers combined).
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors can occur in the colon. For more information, see
Anatomy
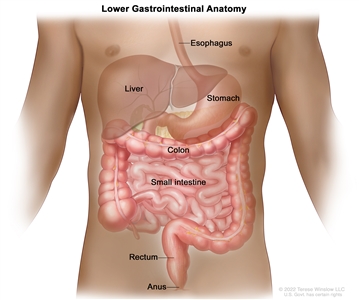
Anatomy of the lower gastrointestinal (digestive) system.
Risk Factors
Increasing age is the most important risk factor for most cancers. Other risk factors for colorectal cancer include the following:
- Family history of colorectal cancer in a first-degree relative.[
3 ] - Personal history of colorectal adenomas, colorectal cancer, or ovarian cancer.[
4 ,5 ,6 ] - Hereditary conditions, including familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer [HNPCC]).[
7 ] - Personal history of long-standing chronic ulcerative colitis or Crohn colitis.[
8 ] - Excessive alcohol use.[
9 ] - Cigarette smoking.[
10 ] - Race and ethnicity: African American.[
11 ,12 ] - Obesity.[
13 ]
Screening
Screening for colon cancer should be a part of routine care for all adults aged 50 years and older, especially for those with first-degree relatives with colorectal cancer. This recommendation is based on the frequency of the disease, ability to identify high-risk groups, slow growth of primary lesions, better survival of patients with early-stage lesions, and relative simplicity and accuracy of screening tests. For more information, see
Prognostic Factors
The prognosis of patients with colon cancer is clearly related to:
- The degree of penetration of the tumor through the bowel wall.
- The presence or absence of nodal involvement.
- The presence or absence of distant metastases.
These three characteristics form the basis for all staging systems developed for this disease.
Other prognostic factors for colon cancer include:
- Bowel obstruction and bowel perforation are indicators of poor prognosis.[
14 ] - Elevated pretreatment serum levels of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) have a negative prognostic significance.[
15 ]
Many other prognostic markers have been evaluated retrospectively for patients with colon cancer, though most, including allelic loss of chromosome 18q or thymidylate synthase expression, have not been prospectively validated.[
Treatment decisions depend on factors such as physician and patient preferences and the stage of the disease, rather than the age of the patient.[
Racial differences in overall survival (OS) after adjuvant therapy have been observed, without differences in disease-free survival, suggesting that comorbid conditions play a role in survival outcome in different patient populations.[
Follow-Up and Survivorship
Limited data and no high-level evidence are available to guide patients and physicians about surveillance and management of patients after surgical resection and adjuvant therapy. The American Society of Clinical Oncology and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommend specific surveillance and follow-up strategies.[
Following treatment of colon cancer, periodic evaluations may lead to the earlier identification and management of recurrent disease.[
CEA is a serum glycoprotein frequently used in the management of patients with colon cancer. A review of the use of this tumor marker suggests:[
- A CEA level is not a valuable screening test for colorectal cancer because of the large number of false-positive and false-negative reports.
- Postoperative CEA testing should be restricted to patients who would be candidates for resection of liver or lung metastases.
- Routine use of CEA levels alone for monitoring response to treatment is not recommended.
The optimal regimen and frequency of follow-up examinations are not well defined because the impact on patient survival is not clear and the quality of data is poor.[
Factors Associated With Recurrence
Diet and exercise
Although cohort studies have suggested that a diet or exercise regimen may improve outcomes, no prospective randomized trials have confirmed these findings. The cohort studies contained multiple opportunities for unintended bias, and caution is needed when using the data from them.
Two prospective observational studies were performed with patients enrolled in the Cancer and Leukemia Group B CALGB-89803 trial (NCT00003835), an adjuvant chemotherapy trial for patients with stage III colon cancer.[
A meta-analysis of seven prospective cohort studies evaluating physical activity before and after a diagnosis of colorectal cancer demonstrated that patients who participated in any amount of physical activity before diagnosis had an RR of 0.75 (95% CI, 0.65–0.87; P < .001) for colorectal cancer-specific mortality, compared with patients who did not participate in any physical activity.[
Aspirin
A prospective cohort study examined the use of aspirin after a colorectal cancer diagnosis.[
References:
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al.: Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 74 (3): 229-263, 2024.
- American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts and Figures 2025. American Cancer Society, 2025.
Available online . Last accessed January 16, 2025. - Johns LE, Houlston RS: A systematic review and meta-analysis of familial colorectal cancer risk. Am J Gastroenterol 96 (10): 2992-3003, 2001.
- Imperiale TF, Juluri R, Sherer EA, et al.: A risk index for advanced neoplasia on the second surveillance colonoscopy in patients with previous adenomatous polyps. Gastrointest Endosc 80 (3): 471-8, 2014.
- Singh H, Nugent Z, Demers A, et al.: Risk of colorectal cancer after diagnosis of endometrial cancer: a population-based study. J Clin Oncol 31 (16): 2010-5, 2013.
- Srinivasan R, Yang YX, Rubin SC, et al.: Risk of colorectal cancer in women with a prior diagnosis of gynecologic malignancy. J Clin Gastroenterol 41 (3): 291-6, 2007.
- Mork ME, You YN, Ying J, et al.: High Prevalence of Hereditary Cancer Syndromes in Adolescents and Young Adults With Colorectal Cancer. J Clin Oncol 33 (31): 3544-9, 2015.
- Laukoetter MG, Mennigen R, Hannig CM, et al.: Intestinal cancer risk in Crohn's disease: a meta-analysis. J Gastrointest Surg 15 (4): 576-83, 2011.
- Fedirko V, Tramacere I, Bagnardi V, et al.: Alcohol drinking and colorectal cancer risk: an overall and dose-response meta-analysis of published studies. Ann Oncol 22 (9): 1958-72, 2011.
- Liang PS, Chen TY, Giovannucci E: Cigarette smoking and colorectal cancer incidence and mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cancer 124 (10): 2406-15, 2009.
- Laiyemo AO, Doubeni C, Pinsky PF, et al.: Race and colorectal cancer disparities: health-care utilization vs different cancer susceptibilities. J Natl Cancer Inst 102 (8): 538-46, 2010.
- Lansdorp-Vogelaar I, Kuntz KM, Knudsen AB, et al.: Contribution of screening and survival differences to racial disparities in colorectal cancer rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 21 (5): 728-36, 2012.
- Ma Y, Yang Y, Wang F, et al.: Obesity and risk of colorectal cancer: a systematic review of prospective studies. PLoS One 8 (1): e53916, 2013.
- Steinberg SM, Barkin JS, Kaplan RS, et al.: Prognostic indicators of colon tumors. The Gastrointestinal Tumor Study Group experience. Cancer 57 (9): 1866-70, 1986.
- Filella X, Molina R, Grau JJ, et al.: Prognostic value of CA 19.9 levels in colorectal cancer. Ann Surg 216 (1): 55-9, 1992.
- McLeod HL, Murray GI: Tumour markers of prognosis in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 79 (2): 191-203, 1999.
- Jen J, Kim H, Piantadosi S, et al.: Allelic loss of chromosome 18q and prognosis in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 331 (4): 213-21, 1994.
- Lanza G, Matteuzzi M, Gafá R, et al.: Chromosome 18q allelic loss and prognosis in stage II and III colon cancer. Int J Cancer 79 (4): 390-5, 1998.
- Griffin MR, Bergstralh EJ, Coffey RJ, et al.: Predictors of survival after curative resection of carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Cancer 60 (9): 2318-24, 1987.
- Johnston PG, Fisher ER, Rockette HE, et al.: The role of thymidylate synthase expression in prognosis and outcome of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 12 (12): 2640-7, 1994.
- Shibata D, Reale MA, Lavin P, et al.: The DCC protein and prognosis in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 335 (23): 1727-32, 1996.
- Bauer KD, Lincoln ST, Vera-Roman JM, et al.: Prognostic implications of proliferative activity and DNA aneuploidy in colonic adenocarcinomas. Lab Invest 57 (3): 329-35, 1987.
- Bauer KD, Bagwell CB, Giaretti W, et al.: Consensus review of the clinical utility of DNA flow cytometry in colorectal cancer. Cytometry 14 (5): 486-91, 1993.
- Sun XF, Carstensen JM, Zhang H, et al.: Prognostic significance of cytoplasmic p53 oncoprotein in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Lancet 340 (8832): 1369-73, 1992.
- Roth JA: p53 prognostication: paradigm or paradox? Clin Cancer Res 5 (11): 3345, 1999.
- Gryfe R, Kim H, Hsieh ET, et al.: Tumor microsatellite instability and clinical outcome in young patients with colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 342 (2): 69-77, 2000.
- Watson P, Lin KM, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, et al.: Colorectal carcinoma survival among hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal carcinoma family members. Cancer 83 (2): 259-66, 1998.
- Iwashyna TJ, Lamont EB: Effectiveness of adjuvant fluorouracil in clinical practice: a population-based cohort study of elderly patients with stage III colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 20 (19): 3992-8, 2002.
- Chiara S, Nobile MT, Vincenti M, et al.: Advanced colorectal cancer in the elderly: results of consecutive trials with 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 42 (4): 336-40, 1998.
- Popescu RA, Norman A, Ross PJ, et al.: Adjuvant or palliative chemotherapy for colorectal cancer in patients 70 years or older. J Clin Oncol 17 (8): 2412-8, 1999.
- Dignam JJ, Colangelo L, Tian W, et al.: Outcomes among African-Americans and Caucasians in colon cancer adjuvant therapy trials: findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project. J Natl Cancer Inst 91 (22): 1933-40, 1999.
- Meyerhardt JA, Mangu PB, Flynn PJ, et al.: Follow-up care, surveillance protocol, and secondary prevention measures for survivors of colorectal cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline endorsement. J Clin Oncol 31 (35): 4465-70, 2013.
- Benson AB, Bekaii-Saab T, Chan E, et al.: Localized colon cancer, version 3.2013: featured updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 11 (5): 519-28, 2013.
- Martin EW, Minton JP, Carey LC: CEA-directed second-look surgery in the asymptomatic patient after primary resection of colorectal carcinoma. Ann Surg 202 (3): 310-7, 1985.
- Bruinvels DJ, Stiggelbout AM, Kievit J, et al.: Follow-up of patients with colorectal cancer. A meta-analysis. Ann Surg 219 (2): 174-82, 1994.
- Lautenbach E, Forde KA, Neugut AI: Benefits of colonoscopic surveillance after curative resection of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg 220 (2): 206-11, 1994.
- Khoury DA, Opelka FG, Beck DE, et al.: Colon surveillance after colorectal cancer surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (3): 252-6, 1996.
- Safi F, Link KH, Beger HG: Is follow-up of colorectal cancer patients worthwhile? Dis Colon Rectum 36 (7): 636-43; discussion 643-4, 1993.
- Moertel CG, Fleming TR, Macdonald JS, et al.: An evaluation of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) test for monitoring patients with resected colon cancer. JAMA 270 (8): 943-7, 1993.
- Rosen M, Chan L, Beart RW, et al.: Follow-up of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Dis Colon Rectum 41 (9): 1116-26, 1998.
- Desch CE, Benson AB, Smith TJ, et al.: Recommended colorectal cancer surveillance guidelines by the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol 17 (4): 1312, 1999.
- Benson AB, Desch CE, Flynn PJ, et al.: 2000 update of American Society of Clinical Oncology colorectal cancer surveillance guidelines. J Clin Oncol 18 (20): 3586-8, 2000.
- Clinical practice guidelines for the use of tumor markers in breast and colorectal cancer. Adopted on May 17, 1996 by the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol 14 (10): 2843-77, 1996.
- Meyerhardt JA, Niedzwiecki D, Hollis D, et al.: Association of dietary patterns with cancer recurrence and survival in patients with stage III colon cancer. JAMA 298 (7): 754-64, 2007.
- Meyerhardt JA, Sato K, Niedzwiecki D, et al.: Dietary glycemic load and cancer recurrence and survival in patients with stage III colon cancer: findings from CALGB 89803. J Natl Cancer Inst 104 (22): 1702-11, 2012.
- McCullough ML, Gapstur SM, Shah R, et al.: Association between red and processed meat intake and mortality among colorectal cancer survivors. J Clin Oncol 31 (22): 2773-82, 2013.
- Je Y, Jeon JY, Giovannucci EL, et al.: Association between physical activity and mortality in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int J Cancer 133 (8): 1905-13, 2013.
- Chan AT, Ogino S, Fuchs CS: Aspirin use and survival after diagnosis of colorectal cancer. JAMA 302 (6): 649-58, 2009.
- Liao X, Lochhead P, Nishihara R, et al.: Aspirin use, tumor PIK3CA mutation, and colorectal-cancer survival. N Engl J Med 367 (17): 1596-606, 2012.
Cellular Classification of Colon Cancer
Histological types of colon cancer include:
- Adenocarcinoma (most colon cancers).
- Mucinous (colloid) adenocarcinoma.
- Signet ring adenocarcinoma.
- Scirrhous tumors.
- Neuroendocrine.[
1 ] Tumors with neuroendocrine differentiation typically have a poorer prognosis than pure adenocarcinoma variants.
References:
- Saclarides TJ, Szeluga D, Staren ED: Neuroendocrine cancers of the colon and rectum. Results of a ten-year experience. Dis Colon Rectum 37 (7): 635-42, 1994.
Stage Information for Colon Cancer
Treatment decisions can be made with reference to the TNM (tumor, node, metastasis) classification [
The AJCC and a National Cancer Institute–sponsored panel recommended that at least 12 lymph nodes be examined in patients with colon and rectal cancer to confirm the absence of nodal involvement by tumor.[
AJCC Stage Groupings and TNM Definitions
The AJCC has designated staging by TNM classification to define colon cancer.[
| Stage | TNMb,c | Description | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|
| T = primary tumor; N = regional lymph nodes; M = distant metastasis. | |||
| a Reprinted with permission from AJCC: Colon and rectum. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.:AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp 251–74. | |||
| The explanations for superscripts b and c are at the end of |
|||
| 0 | Tis, N0, M0 | Tis = Carcinomain situ, intramucosal carcinoma (involvement of lamina propria with no extension through muscularis mucosae). | 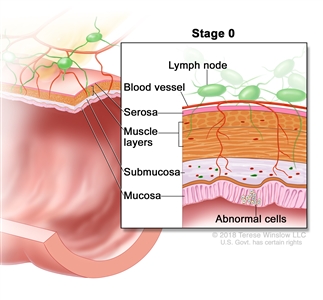 |
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| Stage | TNMb,c | Description | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|
| T = primary tumor; N = regional lymph nodes; M = distant metastasis. | |||
| a Reprinted with permission from AJCC: Colon and rectum. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.:AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp 251–74. | |||
| The explanations for superscripts b and c are at the end of |
|||
| I | T1, T2, N0, M0 | T1 = Tumor invades the submucosa (through the muscularis mucosa but not into the muscularis propria). | 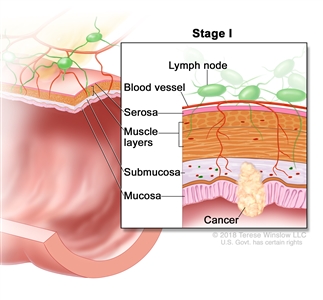 |
| T2 = Tumor invades the muscularis propria. | |||
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| Stage | TNMb,c | Description | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|
| T = primary tumor; N = regional lymph nodes; M = distant metastasis. | |||
| a Reprinted with permission from AJCC: Colon and rectum. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.:AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp 251–74. | |||
| The explanations for superscripts b and c are at the end of |
|||
| IIA | T3, N0, M0 | T3 = Tumor invades through the muscularis propria into pericolorectal tissues. | 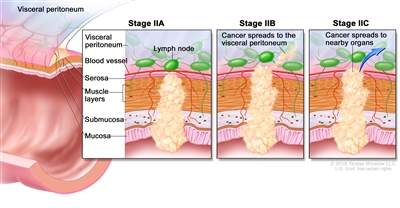 |
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| IIB | T4a, N0, M0 | T4a = Tumor invades through the visceral peritoneum (including gross perforation of the bowel through tumor and continuous invasion of tumor through areas of inflammation to the surface of the visceral peritoneum). | |
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| IIC | T4b, N0, M0 | T4b = Tumor directly invades or adheres to adjacent organs or structures. | |
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| Stage | TNMb,c | Description | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|
| T = primary tumor; N = regional lymph nodes; M = distant metastasis. | |||
| a Reprinted with permission from AJCC: Colon and rectum. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.:AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp 251–74. | |||
| The explanations for superscripts b and c are at the end of |
|||
| IIIA | T1, N2a, M0 | T1 = Tumor invades the submucosa (through the muscularis mucosa but not into the muscularis propria). | 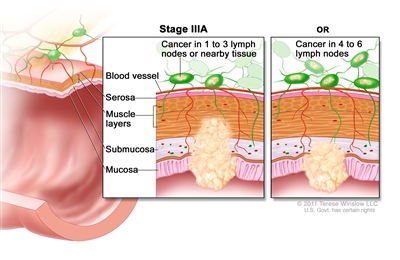 |
| N2a = Four to six regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| T1–2, N1/N1c, M0 | T1 = Tumor invades the submucosa (through the muscularis mucosa but not into the muscularis propria). | ||
| T2 = Tumor invades the muscularis propria. | |||
| N1 = One to three regional lymph nodes are positive (tumor in lymph nodes measuring ≥0.2 mm), or any number of tumor deposits are present and all identifiable lymph nodes are negative. | |||
| –N1c = No regional lymph nodes are positive, but there are tumor deposits in the subserosa, mesentery, or nonperitonealized pericolic, or perirectal/mesorectal tissues. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| IIIB | T1–T2, N2b, M0 | T1 = Tumor invades the submucosa (through the muscularis mucosa but not into the muscularis propria). | 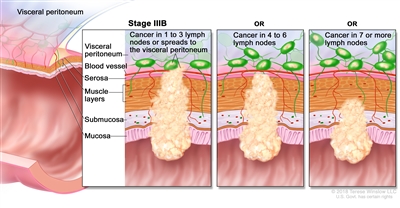 |
| T2 = Tumor invades the muscularis propria. | |||
| N2b = Seven or more regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| T2–T3, N2a, M0 | T2 = Tumor invades the muscularis propria. | ||
| T3 = Tumor invades through the muscularis propria into pericolorectal tissues. | |||
| N2a = Four to six regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| T3–T4a, N1/N1c, M0 | T3 = Tumor invades through the muscularis propria into pericolorectal tissues. | ||
| T4 = Tumor invades the visceral peritoneum or invades or adheres to adjacent organ or structure. | |||
| –T4a = Tumor invades through the visceral peritoneum (including gross perforation of the bowel through tumor and continuous invasion of tumor through areas of inflammation to the surface of the visceral peritoneum). | |||
| N1 = One to three regional lymph nodes are positive (tumor in lymph nodes measuring ≥0.2 mm), or any number of tumor deposits are present and all identifiable lymph nodes are negative. | |||
| –N1c = No regional lymph nodes are positive, but there are tumor deposits in the subserosa, mesentery, or nonperitonealized pericolic, or perirectal/mesorectal tissues. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| IIIC | T3–T4a, N2b, M0 | T3 = Tumor invades through the muscularis propria into pericolorectal tissues. | 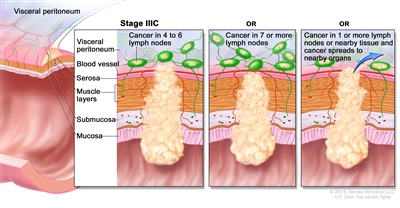 |
| T4 = Tumor invades the visceral peritoneum or invades or adheres to adjacent organ or structure. | |||
| –T4a = Tumor invades through the visceral peritoneum (including gross perforation of the bowel through tumor and continuous invasion of tumor through areas of inflammation to the surface of the visceral peritoneum). | |||
| N2b = Seven or more regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| T4a, N2a, M0 | T4a = Tumor invades through the visceral peritoneum (including gross perforation of the bowel through tumor and continuous invasion of tumor through areas of inflammation to the surface of the visceral peritoneum). | ||
| N2a = Four to six regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| T4b, N1–N2, M0 | T4b = Tumor directly invades or adheres to adjacent organs or structures. | ||
| N1 = One to three regional lymph nodes are positive (tumor in lymph nodes measuring ≥0.2 mm), or any number of tumor deposits are present and all identifiable lymph nodes are negative. | |||
| –N1a = One regional lymph node is positive. | |||
| –N1b = Two or three regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| –N1c = No regional lymph nodes are positive, but there are tumor deposits in the subserosa, mesentery, or nonperitonealized pericolic, or perirectal/mesorectal tissues. | |||
| N2 = Four or more regional nodes are positive. | |||
| –N2a = Four to six regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| –N2b = Seven or more regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| M0 = No distant metastasis by imaging, etc.; no evidence of tumor in distant sites or organs. (This category is not assigned by pathologists.) | |||
| Stage | TNMb,c | Definition | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|
| T = primary tumor; N = regional lymph nodes; M = distant metastasis. | |||
| a Reprinted with permission from AJCC: Colon and rectum. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.:AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp 251–74. | |||
| b Direct invasion in T4 includes invasion of other organs or other segments of the colorectum as a result of direct extension through the serosa, as confirmed on microscopic examination (e.g., invasion of the sigmoid colon by a carcinoma of the cecum) or, for cancers in a retroperitoneal or subperitoneal location, direct invasion of other organs or structures by virtue of extension beyond the muscularis propria (i.e., respectively, a tumor on the posterior wall of the descending colon invading the left kidney or lateral abdominal wall; or a mid or distal rectal cancer with invasion of prostate, seminal vesicles, cervix, or vagina). | |||
| c Tumor that is adherent to other organs or structures, grossly, is classified cT4b. However, if no tumor is present in the adhesion, microscopically, the classification should be pT1-4a depending on the anatomical depth of wall invasion. The V and L classification should be used to identify the presence or absence of vascular or lymphatic invasion whereas the PN prognostic factor should be used for perineural invasion. | |||
| IVA | Any T, Any N, M1a | TX = Primary tumor cannot be assessed. | 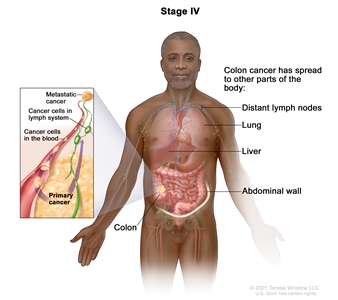 |
| T0 = No evidence of primary tumor. | |||
| Tis = Carcinomain situ, intramucosal carcinoma (involvement of lamina propria with no extension through muscularis mucosae). | |||
| T1 = Tumor invades the submucosa (through the muscularis mucosa but not into the muscularis propria). | |||
| T2 = Tumor invades the muscularis propria. | |||
| T3 = Tumor invades through the muscularis propria into pericolorectal tissues. | |||
| T4 = Tumor invades the visceral peritoneum or invades or adheres to adjacent organ or structure. | |||
| –T4a = Tumor invades through the visceral peritoneum (including gross perforation of the bowel through tumor and continuous invasion of tumor through areas of inflammation to the surface of the visceral peritoneum). | |||
| –T4b = Tumor directly invades or adheres to adjacent organs or structures. | |||
| NX = Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed. | |||
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |||
| N1 = One to three regional lymph nodes are positive (tumor in lymph nodes measuring ≥0.2 mm), or any number of tumor deposits are present and all identifiable lymph nodes are negative. | |||
| –N1a = One regional lymph node is positive. | |||
| –N1b = Two or three regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| –N1c = No regional lymph nodes are positive, but there are tumor deposits in the subserosa, mesentery, or nonperitonealized pericolic, or perirectal/mesorectal tissues. | |||
| N2 = Four or more regional nodes are positive. | |||
| –N2a = Four to six regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| –N2b = Seven or more regional lymph nodes are positive. | |||
| M1a = Metastasis to one site or organ is identified without peritoneal metastasis. | |||
| IVB | Any T, Any N, M1b | Any T = See T descriptions above in Any T, Any N, M1a TNM stage group. | |
| Any N = See N descriptions above in Any T, Any N1, M1a TNM stage group. | |||
| M1b = Metastasis to two or more sites or organs is identified without peritoneal metastasis. | |||
| IVC | Any T, Any N, M1c | Any T = See T descriptions above in Any T, Any N, M1a TNM stage group. | |
| Any N = See N descriptions above in Any T, Any N1, M1a TNM stage group. | |||
| M1c = Metastasis to the peritoneal surface is identified alone or with other site or organ metastases. | |||
References:
- Jessup J, Benson A, Chen V: Colon and Rectum. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. Springer; 2017, pp 251–74.
- Compton CC, Greene FL: The staging of colorectal cancer: 2004 and beyond. CA Cancer J Clin 54 (6): 295-308, 2004 Nov-Dec.
- Nelson H, Petrelli N, Carlin A, et al.: Guidelines 2000 for colon and rectal cancer surgery. J Natl Cancer Inst 93 (8): 583-96, 2001.
- Swanson RS, Compton CC, Stewart AK, et al.: The prognosis of T3N0 colon cancer is dependent on the number of lymph nodes examined. Ann Surg Oncol 10 (1): 65-71, 2003 Jan-Feb.
- Le Voyer TE, Sigurdson ER, Hanlon AL, et al.: Colon cancer survival is associated with increasing number of lymph nodes analyzed: a secondary survey of intergroup trial INT-0089. J Clin Oncol 21 (15): 2912-9, 2003.
- Prandi M, Lionetto R, Bini A, et al.: Prognostic evaluation of stage B colon cancer patients is improved by an adequate lymphadenectomy: results of a secondary analysis of a large scale adjuvant trial. Ann Surg 235 (4): 458-63, 2002.
- Tepper JE, O'Connell MJ, Niedzwiecki D, et al.: Impact of number of nodes retrieved on outcome in patients with rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 19 (1): 157-63, 2001.
Treatment Option Overview for Colon Cancer
| |
Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Stage 0 Colon Cancer | |
| Stage I Colon Cancer | |
| Stage II Colon Cancer | |
| |
|
| Stage III Colon Cancer | |
| |
|
| Liver Metastasis | |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| Stage IV and Recurrent Colon Cancer | |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
Primary Surgical Therapy
Standard treatment for patients with colon cancer has been open surgical resection of the primary and regional lymph nodes for localized disease.
The role of laparoscopic techniques [
Evidence (laparoscopic techniques):
- A multicenter, prospective, randomized, noninferiority trial (NCCTG-934653 [NCT00002575]) compared laparoscopic-assisted colectomy (LAC) with open colectomy in 872 patients.
- At a median follow-up of 4.4 years, 3-year recurrence rates (16% LAC vs. 18% open colectomy; hazard ratio [HR] for recurrence, 0.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.63–1.17; P = .32) and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates (86% LAC vs. 85% open colectomy; HRdeath in LAC, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.68–1.21; P = .51) were similar in both groups for all stages of disease evaluated. Tumor recurrence in surgical incisions was less than 1% for both groups.[
5 ][Level of evidence A1] - Decreased hospital stay (5 days LAC vs. 6 days open colectomy, P < .001) and decreased use of analgesics were reported in the LAC group. A 21% conversion rate from LAC to open procedure was shown.
- This study excluded patients with locally advanced disease, transverse colon and rectal tumor locations, and perforated lesions. Each of the 66 surgeons participating in the trial had performed at least 20 LACs and were accredited for study participation after independent videotape review assured appropriate oncologic and surgical principles were maintained.[
5 ] The quality-of-life component of this trial was published separately and minimal short-term quality-of-life benefits with LAC were reported.[6 ][Level of evidence A3]
- At a median follow-up of 4.4 years, 3-year recurrence rates (16% LAC vs. 18% open colectomy; hazard ratio [HR] for recurrence, 0.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.63–1.17; P = .32) and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates (86% LAC vs. 85% open colectomy; HRdeath in LAC, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.68–1.21; P = .51) were similar in both groups for all stages of disease evaluated. Tumor recurrence in surgical incisions was less than 1% for both groups.[
- One small, single-institution randomized study of 219 patients showed that the LAC procedure was independently associated with reduced tumor recurrence on multivariate analysis.[
7 ][Level of evidence A1]
Surgery is curative in 25% to 40% of highly selected patients who develop resectable metastases in the liver and lung. Improved surgical techniques and advances in preoperative imaging have allowed for better patient selection for resection.
Adjuvant Chemotherapy
The potential value of adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with stage II colon cancer is controversial. Pooled analyses and meta-analyses have suggested a 2% to 4% improvement in OS for patients treated with adjuvant fluorouracil (5-FU)–based therapy compared with observation.[
Before 2000, 5-FU was the only useful cytotoxic chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting for patients with stage III colon cancer. Since 2000, capecitabine has been established as an equivalent alternative to 5-FU and leucovorin (5-FU/LV). The addition of oxaliplatin to 5-FU/LV has been shown to improve OS compared with 5-FU/LV alone. For more information, see the
Chemotherapy regimens
| Regimen Name | Drug Combination | Dose |
|---|---|---|
| 5-FU = fluorouracil; AIO = Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie; bid = twice a day; IV = intravenous; LV = leucovorin. | ||
| AIO or German AIO | Folic acid, 5-FU, and irinotecan | Irinotecan (100 mg/m2) and LV (500 mg/m2) administered as 2-hour infusions on d 1, followed by 5-FU (2,000 mg/m2) IV bolus administered via ambulatory pump weekly over 24 h, 4 times a y (52 wk). |
| CAPOX | Capecitabine and oxaliplatin | Capecitabine (1,000 mg/m2) bid on d 1–14, plus oxaliplatin (70 mg/m2) on d 1 and 8 every 3 wk. |
| Douillard | Folic acid, 5-FU, and irinotecan | Irinotecan (180 mg/m2) administered as a 2-h infusion on d 1, LV (200 mg/m2) administered as a 2-h infusion on d 1 and 2, followed by a loading dose of 5-FU (400 mg/m2) IV bolus, then 5-FU (600 mg/m2) administered via ambulatory pump over 22 h every 2 wk on d 1 and 2. |
| FOLFIRI | LV, 5-FU, and irinotecan | Irinotecan (180 mg/m2) and LV (400 mg/m2) administered as 2-h infusions on d 1, followed by a loading dose of 5-FU (400 mg/m2) IV bolus administered on d 1, then 5-FU (2,400–3,000 mg/m2) administered via ambulatory pump over 46 h every 2 wk. |
| FOLFOX-4 | Oxaliplatin, LV, and 5-FU | Oxaliplatin (85 mg/m2) administered as a 2-h infusion on d 1, LV (200 mg/m2) administered as a 2-h infusion on d 1 and 2, followed by a loading dose of 5-FU (400 mg/m2) IV bolus, then 5-FU (600 mg/m2) administered via ambulatory pump over 22 h every 2 wk on d 1 and 2. |
| FOLFOX-6 | Oxaliplatin, LV, and 5-FU | Oxaliplatin (85–100 mg/m2) and LV (400 mg/m2) administered as 2-h infusions on d 1, followed by a loading dose of 5-FU (400 mg/m2) IV bolus on d 1, then 5-FU (2,400–3,000 mg/m2) administered via ambulatory pump over 46 h every 2 wk. |
| FOLFOXIRI | Irinotecan, oxaliplatin, LV, 5-FU | Irinotecan (165 mg/m2) administered as a 60-min infusion, then concomitant infusion of oxaliplatin (85 mg/m2) and LV (200 mg/m2) over 120 min, followed by 5-FU (3,200 mg/m2) administered as a 48-h continuous infusion. |
| FUFOX | 5-FU, LV, and oxaliplatin | Oxaliplatin (50 mg/m2) plus LV (500 mg/m2) plus 5-FU (2,000 mg/m2) administered as a 22-h continuous infusion on d 1, 8, 22, and 29 every 36 d. |
| FUOX | 5-FU plus oxaliplatin | 5-FU (2,250 mg/m2) administered as a continuous infusion over 48 h on d 1, 8, 15, 22, 29, and 36 plus oxaliplatin (85 mg/m2) on d 1, 15, and 29 every 6 wk. |
| IFL (or Saltz) | Irinotecan, 5-FU, and LV | Irinotecan (125 mg/m2) plus 5-FU (500 mg/m2) IV bolus and LV (20 mg/m2) IV bolus administered weekly for 4 out of 6 wk. |
| XELOX | Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin | Oral capecitabine (1,000 mg/m2) administered bid for 14 d plus oxaliplatin (130 mg/m2) on d 1 every 3 wk. |
Capecitabine and fluorouracil dosing
The DPYD gene encodes an enzyme that catabolizes pyrimidines and fluoropyrimidines, like capecitabine and fluorouracil. An estimated 1% to 2% of the population has germline pathogenic variants in DPYD, which lead to reduced DPD protein function and an accumulation of pyrimidines and fluoropyrimidines in the body.[
Adjuvant Radiation Therapy
While combined modality therapy with chemotherapy and radiation therapy has a significant role in the management of patients with rectal cancer (below the peritoneal reflection), the role of adjuvant radiation therapy for patients with colon cancer (above the peritoneal reflection) is not well defined. Patterns-of-care analyses and single-institution retrospective reviews suggest a role for radiation therapy in certain high-risk subsets of colon cancer patients (e.g., T4, tumor location in immobile sites, local perforation, obstruction, and residual disease postresection).[
Evidence (adjuvant radiation therapy):
- A phase III, randomized, intergroup study evaluated the benefit of adding radiation therapy to surgery and chemotherapy with 5-FU-levamisole in selected patients with high-risk colon cancer (e.g., T4; or T3, N1–N2 ascending and/or descending colon).[
25 ]- This clinical trial closed early secondary to inadequate patient accrual. An analysis of 222 enrolled patients (the original goal was 700 patients) demonstrated no relapse or OS benefit for the group that received radiation therapy, although the sample size and statistical power were inadequate to exclude benefit.
Adjuvant radiation therapy has no current standard role in the management of patients with colon cancer following curative resection, although it may have a role for patients with residual disease.
References:
- Bokey EL, Moore JW, Chapuis PH, et al.: Morbidity and mortality following laparoscopic-assisted right hemicolectomy for cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S24-8, 1996.
- Franklin ME, Rosenthal D, Abrego-Medina D, et al.: Prospective comparison of open vs. laparoscopic colon surgery for carcinoma. Five-year results. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S35-46, 1996.
- Fleshman JW, Nelson H, Peters WR, et al.: Early results of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer. Retrospective analysis of 372 patients treated by Clinical Outcomes of Surgical Therapy (COST) Study Group. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S53-8, 1996.
- Schwenk W, Böhm B, Müller JM: Postoperative pain and fatigue after laparoscopic or conventional colorectal resections. A prospective randomized trial. Surg Endosc 12 (9): 1131-6, 1998.
- Clinical Outcomes of Surgical Therapy Study Group: A comparison of laparoscopically assisted and open colectomy for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 350 (20): 2050-9, 2004.
- Weeks JC, Nelson H, Gelber S, et al.: Short-term quality-of-life outcomes following laparoscopic-assisted colectomy vs open colectomy for colon cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 287 (3): 321-8, 2002.
- Lacy AM, García-Valdecasas JC, Delgado S, et al.: Laparoscopy-assisted colectomy versus open colectomy for treatment of non-metastatic colon cancer: a randomised trial. Lancet 359 (9325): 2224-9, 2002.
- Efficacy of adjuvant fluorouracil and folinic acid in B2 colon cancer. International Multicentre Pooled Analysis of B2 Colon Cancer Trials (IMPACT B2) Investigators. J Clin Oncol 17 (5): 1356-63, 1999.
- Gill S, Loprinzi CL, Sargent DJ, et al.: Pooled analysis of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer: who benefits and by how much? J Clin Oncol 22 (10): 1797-806, 2004.
- Mamounas E, Wieand S, Wolmark N, et al.: Comparative efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with Dukes' B versus Dukes' C colon cancer: results from four National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project adjuvant studies (C-01, C-02, C-03, and C-04) J Clin Oncol 17 (5): 1349-55, 1999.
- Sharma BB, Rai K, Blunt H, et al.: Pathogenic DPYD Variants and Treatment-Related Mortality in Patients Receiving Fluoropyrimidine Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncologist 26 (12): 1008-1016, 2021.
- Lam SW, Guchelaar HJ, Boven E: The role of pharmacogenetics in capecitabine efficacy and toxicity. Cancer Treat Rev 50: 9-22, 2016.
- Shakeel F, Fang F, Kwon JW, et al.: Patients carrying DPYD variant alleles have increased risk of severe toxicity and related treatment modifications during fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy. Pharmacogenomics 22 (3): 145-155, 2021.
- Amstutz U, Henricks LM, Offer SM, et al.: Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase Genotype and Fluoropyrimidine Dosing: 2017 Update. Clin Pharmacol Ther 103 (2): 210-216, 2018.
- Henricks LM, Lunenburg CATC, de Man FM, et al.: DPYD genotype-guided dose individualisation of fluoropyrimidine therapy in patients with cancer: a prospective safety analysis. Lancet Oncol 19 (11): 1459-1467, 2018.
- Lau-Min KS, Varughese LA, Nelson MN, et al.: Preemptive pharmacogenetic testing to guide chemotherapy dosing in patients with gastrointestinal malignancies: a qualitative study of barriers to implementation. BMC Cancer 22 (1): 47, 2022.
- Brooks GA, Tapp S, Daly AT, et al.: Cost-effectiveness of DPYD Genotyping Prior to Fluoropyrimidine-based Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Colon Cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 21 (3): e189-e195, 2022.
- Baker SD, Bates SE, Brooks GA, et al.: DPYD Testing: Time to Put Patient Safety First. J Clin Oncol 41 (15): 2701-2705, 2023.
- Willett C, Tepper JE, Cohen A, et al.: Local failure following curative resection of colonic adenocarcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 10 (5): 645-51, 1984.
- Willett C, Tepper JE, Cohen A, et al.: Obstructive and perforative colonic carcinoma: patterns of failure. J Clin Oncol 3 (3): 379-84, 1985.
- Gunderson LL, Sosin H, Levitt S: Extrapelvic colon--areas of failure in a reoperation series: implications for adjuvant therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 11 (4): 731-41, 1985.
- Willett CG, Fung CY, Kaufman DS, et al.: Postoperative radiation therapy for high-risk colon carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 11 (6): 1112-7, 1993.
- Willett CG, Goldberg S, Shellito PC, et al.: Does postoperative irradiation play a role in the adjuvant therapy of stage T4 colon cancer? Cancer J Sci Am 5 (4): 242-7, 1999 Jul-Aug.
- Schild SE, Gunderson LL, Haddock MG, et al.: The treatment of locally advanced colon cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37 (1): 51-8, 1997.
- Martenson JA, Willett CG, Sargent DJ, et al.: Phase III study of adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy compared with chemotherapy alone in the surgical adjuvant treatment of colon cancer: results of intergroup protocol 0130. J Clin Oncol 22 (16): 3277-83, 2004.
Treatment of Stage 0 Colon Cancer
Stage 0 colon cancer is the most superficial of all the lesions and is limited to the mucosa without invasion of the lamina propria. Because of its superficial nature, the surgical procedure may be limited.
Treatment Options for Stage 0 Colon Cancer
Treatment options for
-
Surgery .
Surgery
Surgical options include local excision or simple polypectomy with clear margins, or colon resection for larger lesions not amenable to local excision.
Current Clinical Trials
Use our
Treatment of Stage I Colon Cancer
Because of its localized nature, stage I colon cancer has a high cure rate.
Treatment Options for Stage I Colon Cancer
Treatment options for
-
Surgery . Wide surgical resection and anastomosis.
Surgery
Evidence (laparoscopic techniques):
- The role of laparoscopic techniques [
1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ] in the treatment of colon cancer was examined in a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial (NCCTG-934653 [NCT00002575]) comparing laparoscopic-assisted colectomy (LAC) with open colectomy.- Three-year recurrence rates and 3-year overall survival rates were similar in the two groups. For more information, see the
Primary Surgical Therapy section. - The quality-of-life component of this trial has been published and minimal short-term quality-of-life benefits with LAC were reported.[
5 ][Level of evidence A3]
- Three-year recurrence rates and 3-year overall survival rates were similar in the two groups. For more information, see the
Current Clinical Trials
Use our
References:
- Bokey EL, Moore JW, Chapuis PH, et al.: Morbidity and mortality following laparoscopic-assisted right hemicolectomy for cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S24-8, 1996.
- Franklin ME, Rosenthal D, Abrego-Medina D, et al.: Prospective comparison of open vs. laparoscopic colon surgery for carcinoma. Five-year results. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S35-46, 1996.
- Fleshman JW, Nelson H, Peters WR, et al.: Early results of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer. Retrospective analysis of 372 patients treated by Clinical Outcomes of Surgical Therapy (COST) Study Group. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S53-8, 1996.
- Schwenk W, Böhm B, Müller JM: Postoperative pain and fatigue after laparoscopic or conventional colorectal resections. A prospective randomized trial. Surg Endosc 12 (9): 1131-6, 1998.
- Weeks JC, Nelson H, Gelber S, et al.: Short-term quality-of-life outcomes following laparoscopic-assisted colectomy vs open colectomy for colon cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 287 (3): 321-8, 2002.
Treatment of Stage II Colon Cancer
Treatment Options for Stage II Colon Cancer
Treatment options for
-
Surgery . Wide surgical resection and anastomosis. -
Adjuvant chemotherapy (under clinical evaluation).
Surgery
Evidence (laparoscopic techniques):
- The role of laparoscopic techniques [
1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ] in the treatment of colon cancer was examined in a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial (NCCTG-934653 [NCT00002575]) comparing laparoscopic-assisted colectomy (LAC) to open colectomy.- Three-year recurrence rates and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were similar in the two groups. For more information, see the
Primary Surgical Therapy section. - The quality-of-life component of this trial reported minimal short-term quality-of-life benefits with LAC.[
4 ][Level of evidence A3]
- Three-year recurrence rates and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were similar in the two groups. For more information, see the
Adjuvant chemotherapy
The potential value of adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with stage II colon cancer remains controversial. Although subgroups of patients with stage II colon cancer may be at higher-than-average risk for recurrence (including those with anatomical features such as tumor adherence to adjacent structures, perforation, and complete obstruction),[
Features in patients with stage II colon cancer that are associated with an increased risk of recurrence include:
- Inadequate lymph node sampling.
- T4 disease.
- Involvement of the visceral peritoneum.
- A poorly differentiated histology.
The decision to use adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with stage II colon cancer is complicated and requires thoughtful consideration by both patients and their physicians. Adjuvant therapy is not indicated for most patients unless they are entered into a clinical trial.
Evidence (adjuvant chemotherapy):
- The GRECCR-03 (NCT00046995) and NCRI-QUASAR1 (NCT00005586) trials evaluated the use of systemic or regional chemotherapy or biological therapy. Following surgery, patients can be considered for entry into a carefully controlled clinical trial.
- Investigators from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project have indicated that the reduction in risk of recurrence by adjuvant therapy in patients with stage II disease is of similar magnitude to the benefit seen in patients with stage III disease treated with adjuvant therapy, though an OS advantage has not been established.[
9 ] - A meta-analysis of 1,000 stage II patients whose experience was amalgamated from a series of trials indicates a 2% advantage in disease-free survival at 5 years when adjuvant therapy–treated patients treated with 5-FU/leucovorin are compared with untreated controls.[
10 ][Level of evidence B1]; [11 ] - The Cancer Care Ontario Practice Guideline Initiative Gastrointestinal Cancer Disease Site Group undertook a meta-analysis of the English language–published literature consisting of randomized trials in which adjuvant chemotherapy was compared with observation for patients with stage II colon cancer.
- The mortality risk ratio was 0.87 (95% confidence interval, 0.75–1.01; P = .07).[
12 ]
- The mortality risk ratio was 0.87 (95% confidence interval, 0.75–1.01; P = .07).[
Based on these data, the American Society of Clinical Oncology issued a guideline stating "direct evidence from randomized controlled trials does not support the routine use of adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with stage II colon cancer."[
Current Clinical Trials
Use our
References:
- Bokey EL, Moore JW, Chapuis PH, et al.: Morbidity and mortality following laparoscopic-assisted right hemicolectomy for cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S24-8, 1996.
- Franklin ME, Rosenthal D, Abrego-Medina D, et al.: Prospective comparison of open vs. laparoscopic colon surgery for carcinoma. Five-year results. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S35-46, 1996.
- Fleshman JW, Nelson H, Peters WR, et al.: Early results of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer. Retrospective analysis of 372 patients treated by Clinical Outcomes of Surgical Therapy (COST) Study Group. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S53-8, 1996.
- Weeks JC, Nelson H, Gelber S, et al.: Short-term quality-of-life outcomes following laparoscopic-assisted colectomy vs open colectomy for colon cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 287 (3): 321-8, 2002.
- Lanza G, Matteuzzi M, Gafá R, et al.: Chromosome 18q allelic loss and prognosis in stage II and III colon cancer. Int J Cancer 79 (4): 390-5, 1998.
- Jen J, Kim H, Piantadosi S, et al.: Allelic loss of chromosome 18q and prognosis in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 331 (4): 213-21, 1994.
- Merkel S, Wein A, Günther K, et al.: High-risk groups of patients with Stage II colon carcinoma. Cancer 92 (6): 1435-43, 2001.
- Moertel CG, Fleming TR, Macdonald JS, et al.: Intergroup study of fluorouracil plus levamisole as adjuvant therapy for stage II/Dukes' B2 colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 13 (12): 2936-43, 1995.
- Mamounas E, Wieand S, Wolmark N, et al.: Comparative efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with Dukes' B versus Dukes' C colon cancer: results from four National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project adjuvant studies (C-01, C-02, C-03, and C-04) J Clin Oncol 17 (5): 1349-55, 1999.
- Efficacy of adjuvant fluorouracil and folinic acid in B2 colon cancer. International Multicentre Pooled Analysis of B2 Colon Cancer Trials (IMPACT B2) Investigators. J Clin Oncol 17 (5): 1356-63, 1999.
- Harrington DP: The tea leaves of small trials. J Clin Oncol 17 (5): 1336-8, 1999.
- Figueredo A, Charette ML, Maroun J, et al.: Adjuvant therapy for stage II colon cancer: a systematic review from the Cancer Care Ontario Program in evidence-based care's gastrointestinal cancer disease site group. J Clin Oncol 22 (16): 3395-407, 2004.
- Benson AB, Schrag D, Somerfield MR, et al.: American Society of Clinical Oncology recommendations on adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 22 (16): 3408-19, 2004.
Treatment of Stage III Colon Cancer
Stage III colon cancer denotes lymph node involvement. Studies have indicated that the number of lymph nodes involved affects prognosis; patients with one to three involved nodes have a significantly better survival than those with four or more involved nodes.
Treatment Options for Stage III Colon Cancer
Treatment options for
-
Surgery . -
Adjuvant chemotherapy . - Clinical trials. Eligible patients can consider enrollment in carefully controlled clinical trials comparing various postoperative chemotherapy regimens.[
1 ]
Surgery
Surgery for stage III colon cancer is wide surgical resection and anastomosis.
Evidence (laparoscopic techniques):
- The role of laparoscopic techniques [
2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ] in the treatment of colon cancer was examined in a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial (NCCTG-934653 [NCT00002575]) comparing laparoscopic-assisted colectomy (LAC) with open colectomy.- Three-year recurrence rates and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were similar in the two groups. For more information, see the
Primary Surgical Therapy section. - The quality-of-life component of this trial has been published and minimal short-term quality-of-life benefits with LAC were reported.[
6 ][Level of evidence A3]
- Three-year recurrence rates and 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were similar in the two groups. For more information, see the
Adjuvant chemotherapy
Chemotherapy regimens before 2000
Before 2000, fluorouracil (5-FU) was the only useful cytotoxic chemotherapy in the adjuvant setting for patients with stage III colon cancer. Many of the early randomized studies of 5-FU in the adjuvant setting failed to show a significant improvement in survival for patients.[
Evidence (5-FU alone and 5-FU/semustine):
- The North Central Cancer Treatment Group conducted a randomized trial comparing surgical resection alone with postoperative levamisole or levamisole/5-FU.[
11 ][Level of evidence A1]- A significant improvement in disease-free survival (DFS) was observed for patients with stage III colon cancer who received levamisole/5-FU, but OS benefits were of borderline statistical significance.
- An absolute survival benefit of approximately 12% (49% vs. 37%) was seen in patients with stage III disease treated with levamisole/5-FU.
- In a large confirmatory intergroup trial, levamisole/5-FU- prolonged DFS and OS in patients with stage III colon cancer compared with patients who received no treatment after surgery.[
12 ][Level of evidence A1] Levamisole alone did not confer these benefits. - Subsequent studies tested the combination of 5-FU/leucovorin (5-FU/LV) in the adjuvant treatment of patients with resected carcinoma of the colon.
- Results of multiple randomized trials that have enrolled more than 4,000 patients comparing adjuvant chemotherapy with 5-FU/LV to surgery or 5-FU/semustine/vincristine demonstrate a relative reduction in mortality of between 22% and 33% (3-year OS of 71%–78% increased to 75%–84%).[
13 ,14 ,15 ]
- Results of multiple randomized trials that have enrolled more than 4,000 patients comparing adjuvant chemotherapy with 5-FU/LV to surgery or 5-FU/semustine/vincristine demonstrate a relative reduction in mortality of between 22% and 33% (3-year OS of 71%–78% increased to 75%–84%).[
- The completed Intergroup trial 0089 (INT-0089 [NCT00201331]) randomly assigned 3,794 patients with high-risk stage II or stage III colon cancer to one of the following four treatment arms:[
16 ]- The Mayo Clinic regimen administered for a total of six cycles.
- The Roswell Park regimen administered for a total of four cycles.
- The Mayo Clinic regimen administered with levamisole for six cycles.
- The levamisole regimen administered for a total of 1 year.
Results:
- Five-year OS ranged from 49% for the Mayo Clinic regimen with levamisole to 60% for the Mayo Clinic regimen, and there were no statistically significant differences among treatment arms.[
16 ][Level of evidence A1] - A preliminary report in November 1997 demonstrated a statistically significant advantage for OS for the Mayo Clinic regimen with levamisole compared with the levamisole regimen. This difference became insignificant with longer follow-up.
- Overall, grade 3 or greater toxicity occurred more frequently for the Mayo Clinic regimen and the Mayo Clinic regimen with levamisole. In addition, the Mayo Clinic regimen was significantly more toxic with levamisole than without levamisole.
- The death rate for all four regimens ranged from 0.5% to 1%.
- Because of its ease of use and its good toxicity profile, the Roswell Park regimen became the preferred adjuvant regimen used in the United States and was often the control arm in subsequent randomized studies.
- In addition to INT-0089, multiple studies have refined the use of 5-FU/LV in the adjuvant setting and can be summarized as follows:
- Levamisole is unnecessary when using leucovorin.[
16 ] - Treatment that includes 6 to 8 months of 5-FU/LV is equivalent to 12 months of therapy.[
17 ,18 ,19 ] - Treatment that includes 24 weeks of adjuvant 5-FU/LV is equivalent to 36 weeks of therapy.[
20 ] - High-dose leucovorin is equivalent to low-dose leucovorin.[
21 ] - A meta-analysis of seven trials revealed no significant difference in efficacy or toxicity among patients aged 70 years or younger compared with patients older than 70 years.[
22 ] - An infusional de Gramont bolus and infusional 5-FU/LV schedule is safer than a bolus modified Mayo Clinic schedule of 5-FU/LV.[
20 ]
- Levamisole is unnecessary when using leucovorin.[
Chemotherapy regimens after 2000
Capecitabine
Capecitabine is an oral fluoropyrimidine that undergoes a three-step enzymatic conversion to 5-FU with the last step occurring in the tumor cell. For patients with metastatic colon cancer, two studies have demonstrated the equivalence of capecitabine to 5-FU/LV.[
For patients with stage III colon cancer, capecitabine provides equivalent outcome to intravenous 5-FU/LV.
Evidence (capecitabine):
- A multicenter European study compared capecitabine (1,250 mg/m2) administered twice daily for days 1 to 14, then given every 21 days for eight cycles against the Mayo Clinic schedule of 5-FU and low-dose LV for patients with stage III colon cancer.[
25 ]- The study demonstrated that DFS at 3 years is equivalent for patients who received capecitabine or 5-FU/LV (hazard ratio [HR], 0.87; P < .001).[
25 ][Level of evidence B1] - Hand-foot syndrome and hyperbilirubinemia were significantly more common for patients receiving capecitabine, but diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, stomatitis, alopecia, and neutropenia were significantly less common.
- Of patients receiving capecitabine, 57% required a dose modification.
- For patients with stage III colon cancer in whom treatment with 5-FU/LV is planned, capecitabine is an equivalent alternative.
- The study demonstrated that DFS at 3 years is equivalent for patients who received capecitabine or 5-FU/LV (hazard ratio [HR], 0.87; P < .001).[
Oxaliplatin
Oxaliplatin has significant activity when combined with 5-FU/LV in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Evidence (oxaliplatin):
- In the 2,246 patients with resected stage II or stage III colon cancer in the completed Multicenter International Study of Oxaliplatin/Fluorouracil/Leucovorin in the Adjuvant Treatment of Colon Cancer study (MOSAIC [NCT00275210]), the toxic effects and efficacy of FOLFOX-4 (oxaliplatin/LV/5-FU) were compared with the same 5-FU/LV regimen without oxaliplatin administered for 6 months.[
26 ] Based on results from the MOSAIC trial, adjuvant FOLFOX-4 demonstrated prolonged OS for patients with stage III colon cancer compared with patients receiving 5-FU/LV without oxaliplatin.[27 ]- The preliminary results of the study with 37 months of follow-up demonstrated a significant improvement in DFS at 3 years (77.8% vs. 72.9%; P = .01) in favor of FOLFOX-4. When initially reported, there was no difference in OS.[
27 ][Level of evidence B1] - Further follow-up at 6 years demonstrated that the OS for all patients (both stage II and stage III) who entered the study was not significantly different (OS, 78.5% vs. 76.0%; HR, 0.84; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.71–1.00). On subset analysis, the 6-year OS in patients with stage III colon cancer was 72.9% in the patients receiving FOLFOX-4 and 68.7% in the patients receiving 5-FU/LV (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.65–0.97; P = .023).[
27 ][Level of evidence A1] - Patients treated with FOLFOX-4 experienced more frequent toxic effects consisting mainly of neutropenia (41% >grade 3) and reversible peripheral sensorial neuropathy (12.4% >grade 3).
- The preliminary results of the study with 37 months of follow-up demonstrated a significant improvement in DFS at 3 years (77.8% vs. 72.9%; P = .01) in favor of FOLFOX-4. When initially reported, there was no difference in OS.[
- In a randomized phase III study (
NSABP C-07 [NCT00004931]), 2,407 patients with stage II or stage III colon cancer were randomly assigned to adjuvant 5-FU/LV or fluorouracil-leucovorin-oxaliplatin (FLOX) (weekly 5-FU/LV with oxaliplatin administered on weeks 1, 3, and 5 of each 6-week cycle). DFS was the primary end point of the study.[28 ]- DFS was significantly longer in the treatment group who received FLOX, but OS was not significantly different. The DFS rate was 69.4% for patients who received FLOX and 64.2% for patients who received 5-FU/LV (HR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.72–0.93; P = .0034).
- The OS rate at 5 years was 80.2% for patients who received FLOX and 78.4% for patients who received 5-FU/LV (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.75–1.02; P = .08).[
28 ][Level of evidence B1] - Grade 3 and grade 4 diarrhea was experienced by 36.9% of patients who received FLOX, and grade 3 and grade 4 dehydration was experienced by 16.1% of patients who received FLOX.
Most physicians have adopted FOLFOX as the standard of care because of toxicity concerns with weekly FLOX. FOLFOX has become the reference standard for the next generation of clinical trials for patients with stage III colon cancer.[
Capecitabine and oxaliplatin
The combination of capecitabine and oxaliplatin (CAPOX) is an accepted standard therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Evidence (CAPOX):
- CAPOX was evaluated in the adjuvant setting for patients with resected stage III colon cancer (capecitabine 1,000 mg/m2 bid on days 1 to 14 every 21 days and oxaliplatin 130 mg/m2 every 21 days for a total of 8 cycles).[
29 ] A randomized phase III trial (NO16968 [NCT00069121]), randomly assigned 1,886 patients with stage III colon cancer to receive CAPOX or bolus 5FU-LV (Roswell Park or Mayo Clinic schedule).- The 7-year DFS rates were 63% for patients who received CAPOX and 56% for patients who received bolus 5-FU/LV (HR, 0.8; 95% CI, 0.69–0.93; P = .004).
- The 7-year OS rates were 73% for patients who received CAPOX and 67% for patients who received a bolus 5-FU/LV (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.70–0.99; P = .04).[
29 ][Level of evidence A1]
Based on this trial, CAPOX has become an acceptable standard regimen for patients with stage III colon cancer.
Oxaliplatin length of therapy
Given the high rate of disabling neuropathy, the duration of oxaliplatin adjuvant therapy became an open question.
Evidence (length of therapy for oxaliplatin):
- The International Duration Evaluation of Adjuvant Therapy (IDEA) collaboration consisted of six separate randomized trials with regimens of 6 months versus 3 months of adjuvant oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. The IDEA study was a prospective, preplanned pooled analysis of these concurrently conducted studies to evaluate the noninferiority of adjuvant therapy of either FOLFOX or CAPOX administered for 3 months versus 6 months. Noninferiority could be claimed if the upper limit of the two-sided 95% CI of the HR did not exceed 1.12.[
30 ]From 2007 through 2015, 13,025 patients with stage III colon cancer were enrolled in six concurrent phase III trials. Of these patients, 12,834 patients met the criteria for intention-to-treat analysis. At a median follow-up of 41.8 months, noninferiority of 3 months versus 6 months was not confirmed in the modified intention-to-treat population (HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.00–1.15, P = .11 for noninferiority of 3 months).
- The 3-year DFS rates were 74.6% in the 3-month group and 75.5% in the 6-month group.
- Neurotoxicity of grade 2 or higher was lower in the 3-month group (16.6% for patients who received FOLFOX and 14.2% for patients who received CAPOX) than in the 6-month group (47.7% for patients who received FOLFOX and 44.9% for patients who received CAPOX). Moreover, all other toxicities were substantially lower with 3 months of treatment than with 6 months.
- A subgroup analyses observed:
- Among patients receiving FOLFOX, 6 months of therapy was superior to 3 months of therapy (HR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.06–1.26; P = .001)
- Among patients receiving CAPOX, 3 months of therapy was like 6 months of therapy (HRDFS, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.85–1.06) and met the prespecified margin for noninferiority.
- Among patients with N1 tumors (<4 positive nodes), the HR was 1.07 (0.97–1.17), and among those patients with N2 tumors (≥4 positive nodes), the HR was 1.07 (0.96–1.19).
- Among patients with T4 tumors, a therapy duration of 3 months was inferior to a duration of 6 months (HR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.03–1.31).
- Among patients with low-risk tumors (T1–3, N1), 3 months of therapy was noninferior to 6 months of therapy (HR, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.90–1.12) with a 3-year DFS rate of 83.1% for patients who received 3 months of therapy and 83.3% for patients who received 6 months of therapy.
- Among patients with high-risk tumors (T4 or N2), 6 months of therapy was superior to 3 months of therapy (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03–1.23; P = .01).
The IDEA study has generated much debate regarding the optimal length of therapy. It is recommended that patients and doctors weigh the pros and cons of potential diminished efficacy of 3 months of therapy versus the definite increased risk of toxicity, particularly neuropathy. CAPOX appears to be slightly more active than FOLFOX in the adjuvant setting.
Current Clinical Trials
Use our
References:
- Rougier P, Nordlinger B: Large scale trial for adjuvant treatment in high risk resected colorectal cancers. Rationale to test the combination of loco-regional and systemic chemotherapy and to compare l-leucovorin + 5-FU to levamisole + 5-FU. Ann Oncol 4 (Suppl 2): 21-8, 1993.
- Bokey EL, Moore JW, Chapuis PH, et al.: Morbidity and mortality following laparoscopic-assisted right hemicolectomy for cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S24-8, 1996.
- Franklin ME, Rosenthal D, Abrego-Medina D, et al.: Prospective comparison of open vs. laparoscopic colon surgery for carcinoma. Five-year results. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S35-46, 1996.
- Fleshman JW, Nelson H, Peters WR, et al.: Early results of laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer. Retrospective analysis of 372 patients treated by Clinical Outcomes of Surgical Therapy (COST) Study Group. Dis Colon Rectum 39 (10 Suppl): S53-8, 1996.
- Schwenk W, Böhm B, Müller JM: Postoperative pain and fatigue after laparoscopic or conventional colorectal resections. A prospective randomized trial. Surg Endosc 12 (9): 1131-6, 1998.
- Weeks JC, Nelson H, Gelber S, et al.: Short-term quality-of-life outcomes following laparoscopic-assisted colectomy vs open colectomy for colon cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 287 (3): 321-8, 2002.
- Panettiere FJ, Goodman PJ, Costanzi JJ, et al.: Adjuvant therapy in large bowel adenocarcinoma: long-term results of a Southwest Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol 6 (6): 947-54, 1988.
- Adjuvant therapy of colon cancer--results of a prospectively randomized trial. Gastrointestinal Tumor Study Group. N Engl J Med 310 (12): 737-43, 1984.
- Higgins GA, Amadeo JH, McElhinney J, et al.: Efficacy of prolonged intermittent therapy with combined 5-fluorouracil and methyl-CCNU following resection for carcinoma of the large bowel. A Veterans Administration Surgical Oncology Group report. Cancer 53 (1): 1-8, 1984.
- Buyse M, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Chalmers TC: Adjuvant therapy of colorectal cancer. Why we still don't know. JAMA 259 (24): 3571-8, 1988.
- Laurie JA, Moertel CG, Fleming TR, et al.: Surgical adjuvant therapy of large-bowel carcinoma: an evaluation of levamisole and the combination of levamisole and fluorouracil. The North Central Cancer Treatment Group and the Mayo Clinic. J Clin Oncol 7 (10): 1447-56, 1989.
- Moertel CG, Fleming TR, Macdonald JS, et al.: Levamisole and fluorouracil for adjuvant therapy of resected colon carcinoma. N Engl J Med 322 (6): 352-8, 1990.
- Wolmark N, Rockette H, Fisher B, et al.: The benefit of leucovorin-modulated fluorouracil as postoperative adjuvant therapy for primary colon cancer: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project protocol C-03. J Clin Oncol 11 (10): 1879-87, 1993.
- Efficacy of adjuvant fluorouracil and folinic acid in colon cancer. International Multicentre Pooled Analysis of Colon Cancer Trials (IMPACT) investigators. Lancet 345 (8955): 939-44, 1995.
- O'Connell M, Mailliard J, Macdonald J, et al.: An intergroup trial of intensive course 5FU and low dose leucovorin as surgical adjuvant therapy for high risk colon cancer. [Abstract] Proceedings of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 12: A-552, 190, 1993.
- Haller DG, Catalano PJ, Macdonald JS, et al.: Phase III study of fluorouracil, leucovorin, and levamisole in high-risk stage II and III colon cancer: final report of Intergroup 0089. J Clin Oncol 23 (34): 8671-8, 2005.
- Wolmark N, Bryant J, Smith R, et al.: Adjuvant 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin with or without interferon alfa-2a in colon carcinoma: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project protocol C-05. J Natl Cancer Inst 90 (23): 1810-6, 1998.
- Wolmark N, Rockette H, Mamounas E, et al.: Clinical trial to assess the relative efficacy of fluorouracil and leucovorin, fluorouracil and levamisole, and fluorouracil, leucovorin, and levamisole in patients with Dukes' B and C carcinoma of the colon: results from National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project C-04. J Clin Oncol 17 (11): 3553-9, 1999.
- Okuno SH, Woodhouse CL, Loprinzi CL, et al.: Phase III placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluation of glutamine for decreasing mucositis in patients receiving 5FU (fluorouracil)-base chemotherapy. [Abstract] Proceedings of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 17: A-256, 1998.
- Andre T, Colin P, Louvet C, et al.: Semimonthly versus monthly regimen of fluorouracil and leucovorin administered for 24 or 36 weeks as adjuvant therapy in stage II and III colon cancer: results of a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 21 (15): 2896-903, 2003.
- Comparison of flourouracil with additional levamisole, higher-dose folinic acid, or both, as adjuvant chemotherapy for colorectal cancer: a randomised trial. QUASAR Collaborative Group. Lancet 355 (9215): 1588-96, 2000.
- Sargent DJ, Goldberg RM, Jacobson SD, et al.: A pooled analysis of adjuvant chemotherapy for resected colon cancer in elderly patients. N Engl J Med 345 (15): 1091-7, 2001.
- Van Cutsem E, Twelves C, Cassidy J, et al.: Oral capecitabine compared with intravenous fluorouracil plus leucovorin in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a large phase III study. J Clin Oncol 19 (21): 4097-106, 2001.
- Hoff PM, Ansari R, Batist G, et al.: Comparison of oral capecitabine versus intravenous fluorouracil plus leucovorin as first-line treatment in 605 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 19 (8): 2282-92, 2001.
- Twelves C, Wong A, Nowacki MP, et al.: Capecitabine as adjuvant treatment for stage III colon cancer. N Engl J Med 352 (26): 2696-704, 2005.
- André T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, et al.: Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 350 (23): 2343-51, 2004.
- André T, Boni C, Navarro M, et al.: Improved overall survival with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment in stage II or III colon cancer in the MOSAIC trial. J Clin Oncol 27 (19): 3109-16, 2009.
- Yothers G, O'Connell MJ, Allegra CJ, et al.: Oxaliplatin as adjuvant therapy for colon cancer: updated results of NSABP C-07 trial, including survival and subset analyses. J Clin Oncol 29 (28): 3768-74, 2011.
- Schmoll HJ, Tabernero J, Maroun J, et al.: Capecitabine Plus Oxaliplatin Compared With Fluorouracil/Folinic Acid As Adjuvant Therapy for Stage III Colon Cancer: Final Results of the NO16968 Randomized Controlled Phase III Trial. J Clin Oncol 33 (32): 3733-40, 2015.
- Grothey A, Sobrero AF, Shields AF, et al.: Duration of Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Stage III Colon Cancer. N Engl J Med 378 (13): 1177-1188, 2018.
Treatment of Stage IV and Recurrent Colon Cancer
Stage IV colon cancer denotes distant metastatic disease. Treatment of recurrent colon cancer depends on the sites of recurrent disease demonstrable by physical examination and/or radiographic studies. In addition to standard radiographic procedures, radioimmunoscintography may add clinical information that may affect management.[
Treatment options for
- Surgical resection of locally recurrent cancer.
- Surgical resection and anastomosis or bypass of obstructing or bleeding primary lesions in selected metastatic cases.
- Resection of liver metastases in selected metastatic patients (5-year cure rate for resection of solitary or combination metastases exceeds 20%) or ablation in selected patients.[
2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,8 ,9 ,10 ,11 ] - Resection of isolated pulmonary or ovarian metastases in selected patients.[
12 ] - Palliative radiation therapy.
- Palliative chemotherapy.
- Targeted therapy.
- Clinical trials comparing various new drugs, chemotherapy regimens, or biological therapies, alone or in combination.
Treatment Options for Liver Metastasis
Approximately 50% of colon cancer patients will be diagnosed with hepatic metastases, either at the time of initial presentation or because of disease recurrence. Although only a small proportion of patients with hepatic metastases are candidates for surgical resection, advances in tumor ablation techniques and in both regional and systemic chemotherapy administration provide for several treatment options. These include:
-
Surgery . -
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy . -
Local ablation . -
Adjuvant chemotherapy . -
Intra-arterial chemotherapy .
Surgery
Hepatic metastasis may be considered to be resectable based on the following factors:[
- Limited number of lesions.
- Intrahepatic locations of lesions.
- Lack of major vascular involvement.
- Absent or limited extrahepatic disease.
- Enough functional hepatic reserve.
For patients with resectable hepatic metastasis, a negative margin resection resulted in 5-year survival rates of 25% to 40% in mostly nonrandomized studies, such as the North Central Cancer Treatment Group trial (NCCTG-934653 [NCT00002575]).[
For patients with unresectable liver metastases, excellent outcomes have been achieved with liver transplant. The optimal patient cohort for this therapy is still being determined, but in general, the goal is to achieve good initial systemic control with chemotherapy, followed by transplant. In one study of 91 patients, 11% underwent live donor liver transplant. At a median follow-up of 1.5 years after transplant, the recurrence-free survival rate was 62% and the overall survival (OS) rate was 100%.[
In the TRANSMET study (NCT02597348), published in abstract form, 94 patients were randomly assigned to receive either chemotherapy and liver transplant (n = 47) or chemotherapy alone (n = 47). In an intent-to-treat analysis, the 5-year OS rate was 57% in the chemotherapy-and-liver transplant arm and 13% in the chemotherapy-alone arm. In a per-protocol analysis, the 5-year OS rate was 73% in the chemotherapy-and-liver transplant arm and 9% in the chemotherapy-alone arm.[
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for unresectable liver metastases
Patients with hepatic metastases that are deemed unresectable will occasionally become candidates for resection if they have a good response to chemotherapy. These patients have 5-year survival rates similar to patients who initially had resectable disease.[
Local ablation
Radiofrequency ablation has emerged as a safe technique (2% major morbidity and <1% mortality rate) that may provide for long-term tumor control.[
Other local ablative techniques that have been used to manage liver metastases include embolization and interstitial radiation therapy.[
Adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy for resectable liver metastases
The role of adjuvant chemotherapy after potentially curative resection of liver metastases is uncertain.
Evidence (adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy for resectable liver metastases):
In the era before the use of FOLFOX (leucovorin calcium [LV], fluorouracil [5-FU], and oxaliplatin) and FOLFIRI (5-FU/LV/irinotecan), two trials attempted to randomly assign patients after resection of liver metastases to 5-FU/LV or observation, but both studies were closed early because of poor accrual.
- The FFCD-9902 trial (NCT00304135) randomly assigned 173 patients (200 patients were planned) to postoperative 5-FU/LV, which is the Mayo Clinic regimen, or observation.[
35 ]- The 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) rate was 33.5% for patients in the chemotherapy group and 26.7% for patients in the control group (Cox multivariate analysis: odds ratio (OR) for recurrence or death, 0.66; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46–0.96; P = .028). The 5-year OS rate was not significantly different between the groups (chemotherapy group, 51.1% vs. the control group, 41.1%; ORdeath, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.48–1.10; P = .13).
- The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer/National Cancer Institute of Canada/Gruppo Interdisciplinare Valutazione Interventi in Oncologia (EORTC/NCIC/GIVIO) International trial attempted a similar random assignment of patients after surgical resection of liver metastases. The study closed because of poor accrual, and a combined analysis of the study and the FFCD-9902 study was done instead. In the combined analysis, 278 patients (138 of whom received chemotherapy; 14 of whom received surgery alone) were included.[
36 ]- The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 27.9 months in the chemotherapy arm and 18.8 months in the surgery alone arm (hazard ratio [HR], 1.32; 95% CI, 1.00–1.76; P = .058).
- The median OS was 62.2 months in the chemotherapy arm compared with 47.3 months in the surgery-alone arm (HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 0.95–1.82; P = .095).
In the era of multiagent chemotherapy, two subsequent studies evaluated its role in the adjuvant setting following resection of liver metastases from colorectal cancer.
- A phase III study randomly assigned 306 patients to 5-FU/LV or FOLFIRI after a resection of liver metastases.[
37 ]- There was no difference in DFS (21.6 months for 5-FU/LV vs. 24.7 months for FOLFIRI; HR, 0.89; log-rank P = .44) or OS (HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.72–1.64).
- The EORTC-40983 trial (NCT00006479) randomly assigned 364 patients with up to four resectable liver metastases to perioperative FOLFOX (six cycles presurgery and six cycles postsurgery) or surgery alone.[
38 ]- The PFS rate was 28.1% (95.66% CI, 21.3%–35.5%) for the surgery-alone group and 35.4% (28.1%–42.7%; HR, 0.79; 0.62–1.02; P = .058) for the perioperative chemotherapy group. There was no difference in OS. Subsequent post hoc analysis demonstrated that the difference in PFS in truly eligible patients rose 8.1% (from 28.1% [21.2%–36.6%] to 36.2% [28.7%–43.8%]; HR, 0.77 [0.60–1.00]; P = .041). In patients who underwent resection of liver metastases, the difference in PFS rose 9.2% (from 33.2% [25.3%–41.2%] to 42.4% [34.0%–50.5%]; HR, 0.73 [0.55–0.97]; P = .025).
- Reversible postoperative complications occurred more often after chemotherapy than after surgery (40 [25%] of the 159 complications vs. 27 [16%] of the 170 complications; P = .04). After surgery, there were two deaths in the surgery-alone group and one in the perioperative chemotherapy group.
There is no high-level evidence to demonstrate that perioperative or postoperative chemotherapy improves OS for patients undergoing resection of liver metastases. Nevertheless, on the basis of post hoc subset analyses of the EORTC study, some physicians feel perioperative or postoperative therapy is reasonable in this setting.
Intra-arterial chemotherapy after liver resection
Hepatic intra-arterial chemotherapy with floxuridine for liver metastases has produced higher overall response rates but no consistent improvement in survival when compared with systemic chemotherapy.[
Evidence (intra-arterial chemotherapy after liver resection):
Two trials evaluated hepatic arterial floxuridine in the adjuvant setting after liver resection.
- A trial of hepatic arterial floxuridine and dexamethasone plus systemic 5-FU/LV compared with systemic 5-FU/LV alone showed improved 2-year PFS rates (57% vs. 42%, P = .07) and OS rates (86% vs. 72%, P = .03) for patients in the combined therapy arm but did not show a significant statistical difference in median survival compared with systemic 5-FU therapy alone.[
45 ][Level of evidence A1]- The median survival in the combined therapy arm was 72.2 months versus 59.3 months in the monotherapy arm (P = .21).
- A second trial preoperatively randomly assigned 109 patients who had one to three potentially resectable colorectal hepatic metastases to either no further therapy or postoperative hepatic arterial floxuridine plus systemic 5-FU.[
46 ] Of those randomly assigned patients, 27% were deemed ineligible at the time of surgery, which left only 75 patients evaluable for recurrence and survival.- While liver cancer recurrence was decreased, median or 4-year survival was not significantly different between the patient groups.
Further studies are required to evaluate this treatment approach and to determine whether more effective systemic combination chemotherapy alone may provide similar results compared with hepatic intra-arterial therapy plus systemic treatment.
Several studies show increased local toxic effects with hepatic infusional therapy, including liver function abnormalities and fatal biliary sclerosis.
Treatment Options for Stage IV and Recurrent Colon Cancer
Treatment of patients with recurrent or advanced colon cancer depends on the location of the disease.
-
Surgery . -
Systemic therapy . -
Immunotherapy .
Surgery
For patients with locally recurrent and/or liver-only and/or lung-only metastatic disease, surgical resection, if feasible, is the only potentially curative treatment.
Systemic therapy
The following drugs are used alone and in combination with other drugs for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer:
-
5-FU . -
Capecitabine . -
Irinotecan . -
Oxaliplatin . -
Bevacizumab . -
FOLFOXIRI (irinotecan, oxaliplatin, LV, and 5-FU). -
Cetuximab . -
Ziv-aflibercept . -
Ramucirumab . -
Panitumumab . -
Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibody versus anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibody with first-line chemotherapy . -
Trifluridine-tipiracil . -
Regorafenib . -
Fruquintinib . -
Encorafenib with cetuximab for patients with BRAF V600E variants . -
Sotorasib with panitumumab for patients with KRAS G12C variants .
5-FU
When 5-FU was the only active chemotherapy drug, trials in patients with locally advanced, unresectable, or metastatic disease demonstrated partial responses and prolongation of the time-to-progression (TTP) of disease,[
Capecitabine
Before the advent of multiagent chemotherapy, two randomized studies demonstrated that capecitabine was associated with equivalent efficacy when compared with the Mayo Clinic regimen of 5-FU/LV.[
Irinotecan
Three randomized studies demonstrated improved response rates, PFS, and OS when irinotecan or oxaliplatin was combined with 5-FU/LV.[
Evidence (irinotecan):
- An intergroup study (NCCTG-N9741 [NCT00003594]) compared irinotecan/5-FU/LV (IFL) with oxaliplatin/LV/5-FU (FOLFOX-4) in first-line treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
- Patients assigned to FOLFOX-4 experienced an improved PFS (median, 6.9 months vs. 8.7 months; P = .014; HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.61–0.89) and OS (15.0 months vs. 19.5 months, P = .001; HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.54–0.82) compared with patients randomly assigned to IFL.
- Subsequently, two studies compared FOLFOX with FOLFIRI, and patients were allowed to cross over upon progression on first-line therapy, respectively.[
58 ,59 ][Level of evidence B1]- PFS and OS were identical between the treatment arms in both studies.
- The Bolus, Infusional, or Capecitabine with Camptosar-Celecoxib (BICC-C [NCT00094965]) trial evaluated several different irinotecan-based regimens in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer, including FOLFIRI, irinotecan plus bolus 5-FU/LV (mIFL), and capecitabine/irinotecan (CAPIRI).[
60 ][Level of evidence A1]- The study randomly assigned 430 patients and was closed early because of poor accrual.
- The patients who received FOLFIRI had a better PFS than the patients who received either mIFL (7.6 months vs. 5.9 months, P = .004) or CAPIRI (7.6 months vs. 5.8 months, P = .015).
- Patients who received CAPIRI had the highest grade 3 or higher rates of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, and hand-foot syndrome.
Since the publication of these studies, the use of either FOLFOX or FOLFIRI is considered acceptable for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
When using an irinotecan-based regimen as first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer, FOLFIRI is preferred.[
Oxaliplatin
Randomized phase III trials have addressed the equivalence of substituting capecitabine for infusional 5-FU. Two phase III studies have evaluated 5-FU/oxaliplatin (FUOX) versus capecitabine/oxaliplatin (CAPOX).[
Evidence (oxaliplatin):
- The AIO Colorectal Study Group randomly assigned 474 patients to either 5-FU/LV/oxaliplatin (FUFOX) or CAPOX.
- The median PFS was 7.1 months for the CAPOX arm and 8.0 months for the FUFOX arm (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.96–1.43; P = .117), and the HR was in the prespecified equivalence range.
- The Spanish Grupo de Tratamiento de los Tumores Digestivos randomly assigned 348 patients to CAPOX or FUOX.[
61 ][Level of evidence B1]- The TTP was 8.9 months versus 9.5 months (P = .153) and met the prespecified range for noninferiority.
When using an oxaliplatin-based regimen as first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer, a CAPOX regimen is not inferior to a FUOX regimen.
Before the availability of cetuximab, panitumumab, bevacizumab, and ziv-aflibercept as second-line therapy, second-line chemotherapy with irinotecan in patients treated with 5-FU/LV as first-line therapy demonstrated improved OS when compared with either infusional 5-FU or supportive care.[
Similarly, a phase III trial randomly assigned patients who progressed on irinotecan and 5-FU/LV to bolus and infusional 5-FU/LV (LV5FU2), single-agent oxaliplatin, or FOLFOX-4. The median TTP for FOLFOX-4 versus LV5FU2 was 4.6 months versus 2.7 months (stratified log-rank test, 2-sided P < .001).[
Bevacizumab
Bevacizumab is a partially humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to VEGF. Bevacizumab can reasonably be added to either FOLFIRI or FOLFOX for patients undergoing first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer.
Evidence (bevacizumab):
- After bevacizumab was approved, the BICC-C trial was amended, and an additional 117 patients were randomly assigned to receive FOLFIRI/bevacizumab or mIFL/bevacizumab.
- Although the primary end point of PFS was not significantly different, patients who received FOLFIRI/bevacizumab had a significantly better OS (not yet reached with a median follow-up of 22.6 months vs. 19.2 months, P = .007).
- Patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer were randomly assigned to either IFL or IFL/bevacizumab.[
68 ][Level of evidence A1]- The patients randomly assigned to IFL/bevacizumab experienced a significantly better PFS (10.6 months in the IFL/bevacizumab arm compared with 6.2 months in the IFL/placebo arm; HRdisease progression, 0.54; P < .001) and OS (20.3 months in the IFL/ bevacizumab arm compared with 15.6 months in the IFL/placebo arm; HRdeath , 0.66; P < .001).[
68 ]
- The patients randomly assigned to IFL/bevacizumab experienced a significantly better PFS (10.6 months in the IFL/bevacizumab arm compared with 6.2 months in the IFL/placebo arm; HRdisease progression, 0.54; P < .001) and OS (20.3 months in the IFL/ bevacizumab arm compared with 15.6 months in the IFL/placebo arm; HRdeath , 0.66; P < .001).[
- Despite the lack of direct data, in standard practice, bevacizumab was added to FOLFOX as a standard first-line regimen based on the results of the NCCTG-N9741 trial.[
69 ] Subsequently, in a randomized phase III study, patients with untreated, stage IV, colorectal cancer were randomly assigned in a 2 × 2 factorial design to CAPOX versus FOLFOX-4, then to bevacizumab versus placebo. PFS was the primary end point.- In this trial, 1,401 patients were randomly assigned, and the median PFS was 9.4 months for patients who received bevacizumab and 8.0 months for the patients who received placebo (HR, 0.83; 97.5% CI, 0.72–0.95; P = .0023).[
70 ][Level of evidence B1] - The median OS was 21.3 months for patients who received bevacizumab and 19.9 months for patients who received placebo (HR, 0.89; 97.5% CI, 0.76–1.03; P = .077).
- The median PFS (intention-to-treat analysis) was 8.0 months in the pooled CAPOX-containing arms versus 8.5 months in the FOLFOX-4-containing arms (HR, 1.04; 97.5% CI, 0.93–1.16), with the upper limit of the 97.5% CI being below the predefined noninferiority margin of 1.23.[
70 ,71 ] - The effect of bevacizumab on OS is likely to be less than what was seen in the original Hurwitz study.[
68 ]
- In this trial, 1,401 patients were randomly assigned, and the median PFS was 9.4 months for patients who received bevacizumab and 8.0 months for the patients who received placebo (HR, 0.83; 97.5% CI, 0.72–0.95; P = .0023).[
- Investigators from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group randomly assigned patients who had progressed on 5-FU/leucovorin and irinotecan to either FOLFOX or FOLFOX /bevacizumab.
- Patients randomly assigned to FOLFOX/bevacizumab experienced a statistically significant improvement in PFS (7.43 months vs. 4.7 months, HR, 0.61; P < .0001) and OS (12.9 months vs. 10.8 months, HR, 0.75; P = .0011).[
72 ][Level of evidence A1]
- Patients randomly assigned to FOLFOX/bevacizumab experienced a statistically significant improvement in PFS (7.43 months vs. 4.7 months, HR, 0.61; P < .0001) and OS (12.9 months vs. 10.8 months, HR, 0.75; P = .0011).[
Based on these studies, bevacizumab can reasonably be added to either FOLFIRI or FOLFOX for patients undergoing first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. A major question was whether the use of bevacizumab after first-line therapy was warranted when bevacizumab was used as a component of first-line therapy. At the 2012 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, data were presented from a randomized, controlled trial.[
FOLFOXIRI
Evidence (FOLFOXIRI):
- The combination of FOLFOXIRI with bevacizumab was compared with FOLFIRI with bevacizumab in a randomized, phase III study of 508 patients with untreated metastatic colorectal cancer.[
74 ][Level of evidence B1]- The median PFS was 12.1 months in the FOLFOXIRI group, compared with 9.7 months in the FOLFIRI group (HRprogression, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.62–0.90; P = .003). OS was not significantly different between the groups (31.0 vs. 25.8 months; HRdeath, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.63–1.00; P = .054).
- Patients who received FOLFOXIRI had significantly more grade 3 and 4 toxicities, including neutropenia, stomatitis, and peripheral neuropathy.
Cetuximab
Cetuximab is a partially humanized monoclonal antibody against EGFR. Because cetuximab affects tyrosine kinase signaling at the surface of the cell membrane, tumors with activating variants of the pathway downstream of the EGFR, such as KRAS variants, are not sensitive to its effects. The addition of cetuximab to multiagent chemotherapy improves survival in patients with colon cancers that lack a KRAS variant (i.e., KRAS wild type). Importantly, patients with KRAS-altered tumors may experience worse outcome when cetuximab is added to multiagent chemotherapy regimens containing bevacizumab.
Evidence (cetuximab):
- For patients who had disease progression while receiving irinotecan-containing regimens, a randomized phase II study was performed using either cetuximab or irinotecan and cetuximab.[
75 ][Level of evidence C3]- The median TTP for patients who received cetuximab was 1.5 months, compared with the median TTP of 4.2 months for patients who received irinotecan/cetuximab.[
75 ][Level of evidence B1] - Based on this study, cetuximab was approved for use in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to 5-FU and irinotecan.
- The median TTP for patients who received cetuximab was 1.5 months, compared with the median TTP of 4.2 months for patients who received irinotecan/cetuximab.[
- The Crystal Study (EMR 62202-013 [NCT00154102]) randomly assigned 1,198 patients with stage IV colorectal cancer to FOLFIRI with or without cetuximab.[
76 ][Level of evidence B1]- The addition of cetuximab was associated with an improved PFS (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.72–0.99; stratified log-rank P = .048) but not OS.
- Retrospective studies of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer have suggested that responses to anti-EGFR antibody therapy are confined to patients with tumors that harbor wild types of KRAS (i.e., lack activating variants at codon 12 or 13 of the KRAS gene).
- A subset analysis evaluating efficacy in relation to KRAS status was done in patients enrolled in the Crystal Study. There was a significant interaction for KRAS variant status and treatment for tumor response (P = .03) but not for PFS (P = .07). Among patients with KRAS wild-type tumors, the HR favored the FOLFIRI/cetuximab group (HR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.50–0.94).
- In a randomized trial, patients with metastatic colorectal cancer received capecitabine/oxaliplatin/bevacizumab with or without cetuximab.[
77 ][Level of evidence B1]- The median PFS was 9.4 months in the group who received cetuximab and 10.7 months in the group who did not receive cetuximab (P = .01).
- In a subset analysis, patients with tumors with KRAS variants who received cetuximab had significantly decreased PFS compared with patients with wild-type KRAS tumors who received cetuximab (8.1 months vs. 10.5 months; P = .04).
- Among patients with KRAS-altered tumors, PFS was significantly shorter in those who received cetuximab than those did not receive cetuximab (8.1 months vs. 12.5 months; P = .003). OS was also significantly shorter (17.2 months vs. 24.9 months, respectively; P = .03).
- The Medical Research Council (MRC) COIN trial (NCT00182715) sought to determine if adding cetuximab to combination chemotherapy with a fluoropyrimidine and oxaliplatin in first-line treatment for patients with KRAS wild-type tumors was beneficial.[
78 ,79 ] In addition, the MRC sought to evaluate the effect of intermittent chemotherapy versus continuous chemotherapy. The 1,630 patients were randomly assigned to three treatment groups:- Arm A: fluoropyrimidine/oxaliplatin.
- Arm B: fluoropyrimidine/oxaliplatin/cetuximab.
- Arm C: intermittent fluoropyrimidine/oxaliplatin.
The comparisons between arms A and B and arms A and C were analyzed and published separately.[
78 ,79 ]- In patients with KRAS wild-type tumors (arm A, n = 367; arm B, n = 362), OS did not differ between treatment groups (median survival, 17.9 months [interquartile range (IQR) 10.3–29.2] in the control group vs. 17.0 months [IQR, 9.4–30.1] in the cetuximab group; HR, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.87–1.23; P = .67). Similarly, there was no effect on PFS (8.6 months [IQR, 5.0–12.5] in the control group versus 8.6 months [IQR, 5.1–13.8] in the cetuximab group; HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.82–1.12; P = .60).[
78 ,79 ][Level of evidence A1] - The reasons for lack of benefit in adding cetuximab are unclear. Subset analyses suggest that the use of capecitabine was associated with an inferior outcome, and the use of second-line therapy was less frequent in patients treated with cetuximab.
- There was no difference between the continuously treated patients (arm A) and the intermittently treated patients (arm C). Median survival in the intent-to-treat population (n = 815 in both groups) was 15.8 months (IQR, 9.4–26.1) in arm A and 14.4 months (IQR, 8.0–24.7) in arm C (HR, 1.084; 80% CI, 1.008–1.165). In the per-protocol population, which included only those patients who were free from progression at 12 weeks and randomly assigned to continue treatment or go on a chemotherapy holiday (arm A, n = 467; arm C, n = 511), median survival was 19.6 months (IQR, 13.0–28.1) in arm A and 18.0 months (IQR, 12.1–29.3) in arm C (HR, 1.087; 95% CI, 0.986–1.198).
- The upper limits of CIs for HRs in both analyses were greater than the predefined noninferiority boundary. While intermittent chemotherapy was not deemed noninferior, there appeared to be clinically insignificant differences in patient outcomes.
- The OPUS study sought to evaluate the effect of adding cetuximab to first-line treatment with a FOLFOX regimen in an open-label, randomized, multicenter, phase II study of patients with EGFR-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer.[
80 ]- In the trial, 344 patients were randomly assigned to receive FOLFOX-4 alone or FOLFOX-4/cetuximab. There was no statistically significant difference in response rate or PFS.
- On subset analysis, patients with KRAS wild-type tumors were analyzed separately. In the KRAS wild-type tumor population, there was a statistically significant improvement in response rate (61% vs. 37%, P = .011) and PFS (7.7 months vs. 7.2 months, P = .0163).
- On subset analysis among patients with KRAS-altered tumors, those who received FOLFOX-4/cetuximab had a statistically significant worse PFS than patients who received FOLFOX-4 alone (5.5 months vs. 8.6 months; P = .0192).[
80 ][Level of evidence B1]
Ziv-aflibercept
Ziv-aflibercept is an anti-VEGF molecule and has been evaluated as a component of second-line therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Evidence (ziv-aflibercept):
- In one trial, 1,226 patients were randomly assigned to receive ziv-aflibercept (4 mg/kg intravenously [IV]) or placebo every 2 weeks in combination with FOLFIRI.[
81 ][Level of evidence A2]- Patients who received ziv-aflibercept/FOLFIRI had significantly improved OS rates, with median survival times of 13.50 months compared with patients who received placebo/FOLFIRI, with median survival times of 12.06 months (HR, 0.817; 95.34% CI, 0.713–0.937; P = .0032).
- Patients who received ziv-aflibercept/FOLFIRI also had significantly improved PFS rates, with median PFS rates of 6.90 months compared with patients who received placebo/FOLFIRI, with median PFS rates of 4.67 months (HR, 0.758; 95% CI, 0.661–0.869; P < .0001).
- Based on these results, the use of ziv-aflibercept/FOLFIRI is an acceptable second-line regimen for patients previously treated with FOLFOX-based chemotherapy. Whether to continue bevacizumab or initiate ziv-aflibercept in second-line therapy has not been addressed yet in any clinical trial, and there are no data available.
Ramucirumab
Ramucirumab is a fully humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2.
Evidence (ramucirumab):
- In the randomized, unblinded, phase III RAISE study (NCT01183780), 1,072 patients with stage IV colorectal cancer who had progressed on first-line chemotherapy were randomly assigned to FOLFIRI with or without ramucirumab (8 mg/kg).[
82 ][Level of evidence A1]- Patients assigned to FOLFIRI/ramucirumab had a significant improvement in median OS (13.3 months vs. 11.7 months; HR, 0.84; P = .0219) and PFS (5.7 months vs. 4.5 months; HR, 0.793; P = .0005).
- Grade 3 adverse events were more common in the ramucirumab group, including grade 3 neutropenia.
- Based on these data, FOLFIRI/ramucirumab is an acceptable second-line regimen for patients previously treated with FOLFOX/bevacizumab. Whether to continue bevacizumab in second-line chemotherapy or use ramucirumab in second-line chemotherapy has not yet been addressed in a clinical trial.
Panitumumab
Panitumumab is a fully humanized antibody against the EGFR. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved
Evidence (panitumumab):
- In a phase III trial, patients with chemotherapy-refractory colorectal cancer were randomly assigned to panitumumab or best supportive care.[
83 ][Level of evidence B1]- Patients who received panitumumab experienced an improved PFS (8 weeks vs. 7.3 weeks; HR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.44–0.66; P < .0001).
- There was no difference in OS, which was thought to be the result of 76% of patients on best supportive care crossing over to panitumumab.
- In the Panitumumab Randomized Trial in Combination With Chemotherapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer to Determine Efficacy (PRIME) study [NCT00364013], 1,183 patients were randomly assigned to FOLFOX-4 with or without panitumumab as first-line therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. The study was amended to enlarge the sample size to address patients with the KRAS wild-type tumors and patients with KRAS-altered tumors separately.[
84 ][Level of evidence B1]- For patients with KRAS wild-type tumors, a statistically significant improvement in PFS was observed in those who received panitumumab/FOLFOX-4 compared with those who received only FOLFOX-4 (HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.66–0.97; stratified log-rank P = .02).
- The median PFS was 9.6 months (95% CI, 9.2–11.1) for patients who received panitumumab/FOLFOX-4 and 8.0 months (95% CI, 7.5–9.3) for patients who received FOLFOX-4. OS was not significantly different between the groups (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, 0.67–1.02; P = .072).
- For patients with KRAS-altered tumors, there was worse PFS with the addition of panitumumab (HR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.04–1.62; stratified log-rank P = .02).
- The median PFS was 7.3 months (95% CI, 6.3–8.0) for panitumumab/FOLFOX-4 and 8.8 months (95% CI, 7.7–9.4) for FOLFOX-4 alone.
- Subsequently, a retrospective analysis evaluated patients with wild-type KRAS exon 2 status for other KRAS and BRAF variants.[
85 ][Level of evidence C1]- Of the 620 patients who were initially identified as not having a variant in exon 2 of KRAS, 108 patients (17%) were found to have additional RAS variants and 53 patients (8%) were found to have BRAF variants. In a retrospective analysis, patients without any RAS or BRAF variants had a longer PFS (10.8 months vs. 9.2 months, P = .002) and OS (28.3 months vs. 20.9 months, P = .02) when assigned to the FOLFOX-4/panitumumab arm than the patients assigned to the FOLFOX-4 arm.
- Similarly, the addition of panitumumab to a regimen of FOLFOX/bevacizumab resulted in a worse PFS and worse toxicity compared with a regimen of FOLFOX/bevacizumab alone in patients not selected for KRAS variant in metastatic colon cancer (11.4 months vs. 10.0 months, HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.06–1.52).[
86 ][Level of evidence B1] - In another study (NCT00339183), patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who had already received a fluoropyrimidine regimen were randomly assigned to either FOLFIRI or FOLFIRI/panitumumab.[
87 ][Level of evidence B1]- In a post hoc analysis, patients with KRAS wild-type tumors experienced a statistically significant PFS advantage (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.59–0.90; stratified log-rank P = .004).
- The median PFS was 5.9 months (95% CI, 5.5–6.7) for panitumumab/FOLFIRI and 3.9 months (95% CI, 3.7–5.3) for FOLFIRI alone.
- OS was not significantly different. Patients with KRAS-altered tumors experienced no benefit from the addition of panitumumab.
- In a post hoc analysis, patients with KRAS wild-type tumors experienced a statistically significant PFS advantage (HR, 0.73; 95% CI, 0.59–0.90; stratified log-rank P = .004).
Anti-EGFR antibody versus anti-VEGF antibody with first-line chemotherapy
In the management of patients with stage IV colorectal cancer, it is unknown whether patients with KRAS wild-type cancer should receive an anti-EGFR antibody with chemotherapy or an anti-VEGF antibody with chemotherapy. Two studies attempted to answer this question.[
Evidence (anti-EGFR antibody vs. anti-VEGF antibody with first-line chemotherapy)
- The FIRE-3 study (NCT00433927) randomly assigned 592 patients with KRAS exon 2 wild-type tumors who were previously untreated to FOLFIRI/cetuximab (297 patients) or FOLFIRI/bevacizumab (295 patients). The primary end point of the study was objective response rate.[
88 ][Level of evidence A1]- The objective response rate was not significantly different between the groups (objective response rate, 62.0%; 95% CI, 56.2%–67.5% vs. objective response rate, 58.0%; 95% CI, 52.1%–63.7%; OR, 1.18; 95% CI, 0.85–1.64; P = .18).
- The median PFS was 10.0 months (95% CI, 8.8–10.8) in the cetuximab group and 10.3 months (95% CI, 9.8–11.3) in the bevacizumab group (HR, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.88–1.26; P = .55).
- The median OS was 28.7 months (95% CI, 24.0–36.6) in the cetuximab group compared with 25.0 months (22.7–27.6) in the bevacizumab group (HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62–0.96; P = .017).
- In a post hoc analysis of patients with expanded RAS wild-type tumors (sequencing for mutational hot spots within KRAS and NRAS genes, including exon 2 codons 12 and 13; exon 3 codons 59 and 61; and exon 4 codons 117 and 146), the median OS was 33.1 months (95% CI, 24.5–39.4) in the cetuximab group compared with 25.0 months (95% CI, 23.0–28.1) in the bevacizumab group (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.54–0.90; P = .0059).[
90 ] - Of note, only 52% of patients assigned to the bevacizumab arm subsequently received cetuximab or panitumumab.[
91 ]
- The Cancer and Leukemia Group B Intergroup study 80405 (NCT00265850) was presented at the ASCO meeting in 2014. This study randomly assigned 2,334 previously untreated patients with KRAS wild-type cancer to chemotherapy (FOLFOX or FOLFIRI) plus bevacizumab or chemotherapy/cetuximab. OS was the primary end point.[
89 ][Level of evidence B1]- There was no statistically significant difference in OS among the patients assigned to bevacizumab or cetuximab (for OS differences, chemotherapy/bevacizumab = 29.04 [25.66–31.21] months vs. chemotherapy/cetuximab = 29.93 [27.56–31.21] months; HR, 0.92 [0.78–1.09]; P = .34).
Based on these two studies, no apparent significant difference is evident about starting treatment with chemotherapy/bevacizumab or chemotherapy/cetuximab in patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. However, in patients with KRAS wild-type cancer, administration of an anti-EGFR antibody during management improves OS.
Trifluridine-tipiracil
Trifluridine-tipiracil (
Evidence (trifluridine-tipiracil):
- A phase III, double-blind study (RECOURSE [NCT01607957]) randomly assigned 800 stage IV colorectal cancer patients whose cancer had been refractory to two previous therapies. Patients were required to have received 5-FU, oxaliplatin, irinotecan, bevacizumab and, if the patients had KRAS wild-type cancer, cetuximab or panitumumab. Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive best supportive care plus trifluridine-tipiracil (n = 534) or placebo (n = 266). The median age of patients was 63 years, and most patients (60%–63%) received four or more previous lines of therapy. All patients had formerly received fluoropyrimidine, irinotecan, oxaliplatin, and bevacizumab, and 52% of them had received an EGFR inhibitor. Approximately 20% of the patients had received previous treatment with regorafenib.[
92 ][Level of evidence A1]- Trifluridine-tipiracil was administered at 35 mg/m2 twice daily with meals for 5 days, with 2 days of rest for 2 weeks, followed by a 14-day rest period.
- The primary end point of the study was OS. The median OS for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who received trifluridine-tipiracil was 7.1 months compared with 5.3 months for those who received a placebo (HR, 0.68; P < .0001).
- The median PFS time in the trifluridine-tipiracil arm was 2 months versus 1.7 months with a placebo (HR, 0.48; P < .0001).
- Secondary end points focused on PFS, overall response rate, and disease control rate.
- The overall response rate was 1.6% with trifluridine-tipiracil, which consisted of a complete response in one patient and partial responses in other patients. The overall response rate with a placebo was 0.4% (P = .29).
The FDA approved trifluridine-tipiracil for the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer, based on the results of the RECOURSE trial.
Evidence (combination of trifluridine-tipiracil and bevacizumab):
- A phase III, international, multi-institutional trial (SUNLIGHT [NCT04737187]) included 492 patients with stage IV colorectal cancer whose cancer was refractory to up to two prior chemotherapy regimens. Patients were required to have received 5-FU, oxaliplatin, irinotecan, an anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody, or an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody (for patients with RAS wild-type disease). Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either trifluridine-tipiracil monotherapy (n = 246) or trifluridine-tipiracil combined with bevacizumab (n = 246). The median patient age was 62 years for the combination arm, and 64 years for the monotherapy arm and most patients (93% and 91%) had received two prior lines of therapy. Over 98% of patients in both arms had received 5-FU, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin, and over 93% of patients with RAS wild-type variants in both arms had received anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody therapy. The median follow-up was 14.2 months. Trifluridine-tipiracil was given at 35 mg/m2 twice daily on days 1 to 5 and 8 to 12 of a 28-day cycle. Bevacizumab was given on days 1 and 15 of each cycle at 5 mg/kg. The primary end point of the study was OS.[
93 ]- The median OS was 10.8 months for patients who received trifluridine-tipiracil and bevacizumab and 7.5 months for patients who received trifluridine-tipiracil monotherapy (HR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.49–0.77; P < .001).[
93 ][Level of evidence A1] - OS was significant across subgroups, including patients with RAS variants and wild-type variants, patients with microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) and microsatellite stability (MSS) cancers, and both for patients previously treated with bevacizumab and bevacizumab-naïve patients.
- The median PFS was 5.6 months in the combination arm and 2.4 months in the trifluridine-tipiracil monotherapy arm (HR, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.36–0.54; P < .001).
- Secondary end points focused on PFS, overall response rate, and safety.
- The overall response rate was 6.1% for the combination arm and 1.2% for the monotherapy arm.
- Adverse events leading to therapy discontinuation were observed in 12.6% of patients in both arms. Dose reductions occurred in 16.3% of patients in the combination group and 12.2% of patients in the trifluridine-tipiracil monotherapy group. The most common adverse event was neutropenia, with grade 3 or 4 neutropenia observed in 43% of patients in the combination arm and 32% of patients in the monotherapy arm.
- The median OS was 10.8 months for patients who received trifluridine-tipiracil and bevacizumab and 7.5 months for patients who received trifluridine-tipiracil monotherapy (HR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.49–0.77; P < .001).[
The FDA approved the combination of trifluridine-tipiracil and bevacizumab for the treatment of patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer based on the results of the SUNLIGHT trial.
Regorafenib
Regorafenib is an inhibitor of multiple tyrosine kinase pathways, including VEGF. In 2012, the FDA approved regorafenib for patients who had progressed on previous therapy.
Evidence (regorafenib):
- The safety and effectiveness of regorafenib were evaluated in a single, clinical study of 760 patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer. Patients were randomly assigned 2:1 to receive regorafenib or a placebo in addition to the best supportive care.[
94 ,95 ]- Patients treated with regorafenib had a statistically significant improvement in OS (6.4 months in the regorafenib group vs. 5.0 months in the placebo group; HR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.64–0.94; one-sided P = .0052).
With the improved OS from the combination of trifluridine-tipiracil and bevacizumab discussed above, regorafenib is now often considered a fourth-line or later option for treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Fruquintinib
Fruquintinib is an inhibitor of VEGF receptors 1, 2 and 3. In 2023, the FDA approved fruquintinib for adults with metastatic colorectal cancer who had previously received fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and irinotecan-based chemotherapy and an anti-VEGF therapy. If patients had RAS wild-type disease and were medically appropriate, an anti-EGFR therapy was also required.
Evidence (fruquintinib):
- The phase III, international, double-blind, placebo-controlled FRESCO-2 trial (NCT04322539) included 691 patients with metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma who had received all standard approved cytotoxic and targeted therapies. Patients had disease progression during, or were intolerant of, trifluridine-tipiracil, regorafenib, or both. Patients had received a median of four lines of prior systemic therapy. Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 fashion to receive one of the following regimens:
- Fruquintinib (5 mg orally once daily on days 1–21 of a 28-day cycle).
- Placebo (orally once daily on days 1–21 of a 28-day cycle).
All patients received best supportive care. A total of 461 patients received fruquintinib, and 230 received placebo. The primary end point was OS.[
96 ] The results were as follows:- The median OS was significantly longer in the fruquintinib group (7.4 months; 95% CI, 6.7–8.2) than in the placebo group (4.8 months; 95% CI, 4.0–5.8) (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.55–0.80; P < .0001).[
96 ][Level of evidence A1] - The median PFS was 3.7 months (95% CI, 3.5–3.8) in the fruquintinib group and 1.8 months (95% CI, 1.8–1.9) in the placebo group (HR, 0.26; 95% CI, 0.21–0.34; P < .001).
- Subgroup analyses demonstrated the benefit of fruquintinib as opposed to placebo in most subgroups. Notably, this benefit was seen in patients with both RAS variants and RAS wild-type disease, patients with liver metastases, and patients pretreated with trifluridine-tipiracil with or without regorafenib.
- The disease control rate was significantly longer in the fruquintinib group (56%) than in the placebo group (16%), with an adjusted difference of 39% (95% CI, 32.8%–46.0%; P < .0001).
- Grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred in 65% of patients in the fruquintinib group. The most common adverse events were hypertension (14%), asthenia (8%), abnormal hepatic function (8%), dermatologic toxicity (7%), and hand-foot syndrome (6%). Grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred in 50% of patients in the placebo group. The most common were abnormal hepatic function (9%), infection (6%), and asthenia (4%).
Encorafenib with cetuximab in patients withBRAFV600E variants
BRAF V600E variants occur in about 10% of metastatic colorectal cancers and are an indicator of poor prognosis. Unlike in melanoma, BRAF inhibitor monotherapy has not shown a benefit in colorectal cancer, and multiple studies have evaluated concurrent targeting of the EGFR-MAPK pathway.
Evidence (encorafenib with cetuximab in patients with BRAF V600E variants):
- Encorafenib (BRAF inhibitor), binimetinib (MEK inhibitor), and cetuximab (EGFR inhibitor): In the international, open-label, randomized, phase III BEACON trial, patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and BRAF V600E variants who previously received one or two treatment regimens were enrolled.[
97 ] The trial randomly assigned 665 patients in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive one of the following:- Triplet therapy: encorafenib (300 mg PO daily), binimetinib (45 mg PO twice daily), and cetuximab (400 mg/m2 IV loading dose followed by 250 mg/m2 IV weekly) (n = 224).
- Doublet therapy: encorafenib and cetuximab (as per triplet therapy dosing) (n = 220).
- Control group: FOLFIRI or irinotecan (every 2 weeks) with cetuximab (400 mg/m2 IV loading dose followed by 250 mg/m2 IV weekly) (n = 221).
- The OS was 9.0 months in the triplet-therapy arm and 5.4 months in the control group (HR, 0.52; 95% CI, 0.39–0.70, P < .0001).[
97 ][Level of evidence A1] - Grade 3 or higher side effects occurred in 58% of patients in the triplet-therapy arm, with 10% of patients experiencing diarrhea and 11% of patients experiencing anemia. Grade 3 or higher side effects occurred in 50% of patients in the doublet-therapy arm and 61% of patients in the control arm. Fourteen percent of patients who received the doublet regimen developed melanocytic nevi.
98 ]- The median OS was 9.3 months in both the triplet-therapy and doublet-therapy arms and 5.9 months in the control arm (HR, 0.60 for triplet therapy vs. control; 95% CI, 0.47–0.75; HR, 0.61 for doublet therapy vs. control; 95% CI, 0.48–0.77).
- The objective response rate was 26.8% for patients who received triplet therapy (95% CI, 21.1%–33.1%) and 19.5% for patients who received doublet therapy (95% CI, 14.5%–25.4%).
Based on these data, the FDA approved the combination of encorafenib with cetuximab for patients with previously treated metastatic colon cancer and BRAF V600E variants.
Sotorasib with panitumumab for patients withKRASG12C variants
KRAS G12C variants are found in approximately 4% of patients with colorectal cancer and are associated with poor prognosis.[
- The phase III, multicenter, open-label CodeBreaK 300 trial (NCT05198934) included patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and KRAS G12C variants who previously received treatment with a fluoropyrimidine, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan.[
103 ] The trial randomly assigned 160 patients 1:1:1 to receive one of the following:- Doublet therapy with sotorasib 960 mg once daily plus panitumumab (6 mg/kg IV every 2 weeks) (n = 53).
- Doublet therapy with sotorasib 240 mg once daily plus panitumumab (6 mg/kg IV every 2 weeks) (n = 53).
- Investigator's choice standard-of-care therapy with trifluridine-tipiracil (35 mg/m2) or regorafenib (160 mg once daily) (control group).
The primary end point was PFS assessed by blinded independent central review according to RECIST 1.1. Secondary end points included OS and objective response rate.
- The median PFS was 5.6 months (95% CI, 4.2–6.3) in the 960 mg-sotorasib/panitumumab group, 3.9 months (95% CI, 3.7–5.8) in the 240 mg-sotorasib/panitumumab group, and 2.2 months (95% CI, 1.9–3.9) in the standard-of-care group.[
103 ][Level of evidence B1] - The HR for progression of disease or death was 0.49 (95% CI, 0.3–0.8; P = .006) for the 960 mg-sotorasib/panitumumab group and 0.58 (95% CI, 0.36–0.98; P = .03) for the 240 mg-sotorasib/panitumumab group.
- The objective response rate was 26.4% (95% CI, 15.3%–40.3%) in the 960 mg-sotorasib/panitumumab group, 5.7% (95% CI, 1.2%–15.7%) in the 240 mg-sotorasib/panitumumab group, and 0% (95% CI, 0.0%–6.6%) in the standard-of-care group. OS data are still not mature. However, at data cutoff the HRs were 0.77 (95% CI, 0.4–1.45) for the 960 mg-sotorasib/panitumumab group and 0.91 (95% CI, 0.48–1.71) for the 240 mg-sotorasib/panitumumab group when compared with standard-of-care therapy.
- Grade 3 or higher side effects occurred in 35.8% of patients who received 960 mg sotorasib/panitumumab, 30.2% of patients who received 240 mg sotorasib/panitumumab, and 43.1% of patients who received the standard of care. The most common adverse effects with combined sotorasib and panitumumab therapy were skin-related toxicities and hypomagnesemia.
Immunotherapy
Approximately 4% of patients with stage IV colorectal cancer have tumors that are mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) or microsatellite unstable/MSI-H. The MSI-H phenotype is associated with germline defects in the MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 genes and is the primary phenotype observed in tumors from patients with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) or Lynch syndrome. Patients can also have the MSI-H phenotype because one of these genes was silenced via DNA methylation. Testing for microsatellite instability can be done with molecular genetic tests, which look for microsatellite instability in the tumor tissue, or with immunohistochemistry, which looks for the loss of mismatch repair proteins. MSI-H status has historically been prognostic of increased survival for patients with earlier-stage disease and since 2015, has also been found to predict tumor response to checkpoint inhibition.
The FDA approved pembrolizumab for patients with treatment-naïve, metastatic, dMMR/MSI-H colorectal cancer in 2020. Studies regarding first-line treatment with dual checkpoint inhibitors are ongoing. The FDA approved the anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) antibodies pembrolizumab and nivolumab in 2017 for patients with microsatellite-unstable tumors who had previously received 5-FU, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan-based therapy. In 2018, the FDA granted accelerated approval for the combination of nivolumab with ipilimumab (a CTLA-4 inhibitor) to treat MSI-H colorectal cancers that progressed on prior 5-FU, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan-based therapies.
First-line immunotherapy
Pembrolizumab monotherapy
Evidence (pembrolizumab monotherapy):
- In the phase III, open-label, international, randomized KEYNOTE-177 trial (NCT02563002), 307 patients with treatment-naïve MSI-H or dMMR metastatic colorectal cancer were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive either pembrolizumab (200 mg every 3 weeks) or chemotherapy (FOLFIRI or modified FOLFOX-6 with or without bevacizumab or cetuximab).[
105 ]- The median PFS was 16.5 months for patients who received pembrolizumab and 8.2 months for patients who received chemotherapy (HR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.45–0.80; P = .0002).[
105 ][Level of evidence A3] - The PFS in prespecified subgroups showed HRs that favored the pembrolizumab arm, except in patients with KRAS/NRAS variants.
- The objective response rate was 43.8% in the pembrolizumab arm and 33.3% in the chemotherapy arm. The median duration of response was not reached in the pembrolizumab arm (range, 2.3–41.4 months) and was 10.6 months in the chemotherapy arm (range, 2.8–37.5 months).
- Grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred in 56% of patients who received pembrolizumab (with 9% experiencing grade 3 or higher infusion-related adverse events), compared with 78% of patients who received chemotherapy.
- A final review of OS, presented in abstract form, showed that median OS was not reached in the pembrolizumab arm and was 36.7 months in the chemotherapy arm (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.53–1.03; P = .0359).[
106 ]
- The median PFS was 16.5 months for patients who received pembrolizumab and 8.2 months for patients who received chemotherapy (HR, 0.60; 95% CI, 0.45–0.80; P = .0002).[
Nivolumab and ipilimumab
Evidence (nivolumab and ipilimumab):
- In a single-arm cohort of the phase II, multicenter CheckMate-142 study (NCT02060188) presented in abstract form, 45 treatment-naïve patients with MSI-H/dMMR metastatic colorectal cancer received nivolumab (3 mg/kg every 2 weeks) with ipilimumab (1 mg/kg every 6 weeks). The primary end point was objective response rate.[
107 ]- The objective response rate was 69% among all enrolled patients and 80% for patients with KRAS variants (n = 10).[
107 ][Level of evidence C2] - At a 2-year clinical follow-up, the median PFS and OS had not been reached.
- The objective response rate was 69% among all enrolled patients and 80% for patients with KRAS variants (n = 10).[
- In the CheckMate 8HW trial (NCT04008030), published in abstract form, 303 patients who had received various lines of treatment were randomly assigned to receive either nivolumab and ipilimumab (n = 202) or chemotherapy alone (n = 101). Some patients were also randomly assigned to receive nivolumab, but results from these patients were not presented in the abstract. Treatments were continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (all arms), or for up to 2 years (nivolumab-ipilimumab arm). A total of 171 patients who received nivolumab and ipilimumab and 84 patients who received chemotherapy alone were centrally confirmed to have dMMR/MSI-H metastatic colorectal cancer.[
108 ]- At a median follow-up of 31.5 months, the PFS was superior for patients who received nivolumab and ipilimumab compared with those who received chemotherapy alone (HR, 0.21; 97.91% CI, 0.13–0.35; P < .0001). Of note, in the chemotherapy arm, 67% of patients received subsequent immunotherapy.
- Two grade 5 deaths occurred in the nivolumab-ipilimumab arm. Grade 3 to 4 events occurred in 23% of patients in the nivolumab-ipilimumab arm and 48% of patients in the chemotherapy-alone arm.
Second-line immunotherapy
Pembrolizumab monotherapy
Evidence (pembrolizumab monotherapy):
- The FDA approval of pembrolizumab monotherapy was based on data from 149 patients with MSI-H or dMMR cancers enrolled across five uncontrolled, multicohort, multicenter, single-arm clinical trials. Ninety patients had colorectal cancer, and 59 patients were diagnosed with 1 of 14 other cancer types. Patients received either 200 mg of pembrolizumab every 3 weeks or 10 mg/kg of pembrolizumab every 2 weeks. Treatment continued until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression occurred. The major efficacy outcome measures were objective response rate (assessed by blinded independent central radiologists' review in accordance with Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors [RECIST] 1.1) and response duration.
- The objective response rate was 39.6% (95% CI, 31.7%–47.9%).
- Responses lasted 6 months or longer for 78% of patients who responded to pembrolizumab. There were 11 complete responses and 48 partial responses.
- The objective response rate was similar whether patients were diagnosed with colorectal cancer (36%) or a different cancer (46% across the 14 other cancer types).
Nivolumab monotherapy
Evidence (nivolumab monotherapy):
- In the CheckMate-142 trial (NCT02060188), 74 patients with previously treated dMMR/MSI-H colorectal cancer were enrolled in an open-label, single-arm, phase II study to receive nivolumab (3 mg/kg every 2 weeks). The primary end point was objective response as per RECIST 1.1.[
109 ]- The objective response rate was 31.1% (95% CI, 20.8%–42.9%).
- Grade 3 to 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 21% of patients.
Nivolumab and ipilimumab
Evidence (nivolumab and ipilimumab):
- CheckMate-142 (NCT02060188) was a multicenter, open-label, phase II trial with a cohort for patients with recurrent or metastatic dMMR and/or MSI-H colorectal cancer who had progressed on, were intolerant of, or declined at least one line of chemotherapy (including 5-FU and oxaliplatin and/or irinotecan). The trial enrolled 119 patients who received four doses of nivolumab (3 mg/kg) and ipilimumab (1 mg/kg) every 3 weeks (induction), then nivolumab (3 mg/kg IV) every 2 weeks (maintenance). The primary end point was objective response rate.[
109 ]- The objective response rate was 55% (95% CI, 45.2%–63.8%).
- Among patients experiencing a response, 83% had responses lasting more than 6 months.
- Grade 3 to 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 32% of patients.
Current Clinical Trials
Use our
References:
- Serafini AN, Klein JL, Wolff BG, et al.: Radioimmunoscintigraphy of recurrent, metastatic, or occult colorectal cancer with technetium 99m-labeled totally human monoclonal antibody 88BV59: results of pivotal, phase III multicenter studies. J Clin Oncol 16 (5): 1777-87, 1998.
- Wagman LD, Kemeny MM, Leong L, et al.: A prospective, randomized evaluation of the treatment of colorectal cancer metastatic to the liver. J Clin Oncol 8 (11): 1885-93, 1990.
- Scheele J, Stangl R, Altendorf-Hofmann A: Hepatic metastases from colorectal carcinoma: impact of surgical resection on the natural history. Br J Surg 77 (11): 1241-6, 1990.
- Scheele J, Stangl R, Altendorf-Hofmann A, et al.: Indicators of prognosis after hepatic resection for colorectal secondaries. Surgery 110 (1): 13-29, 1991.
- Adson MA, van Heerden JA, Adson MH, et al.: Resection of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Arch Surg 119 (6): 647-51, 1984.
- Coppa GF, Eng K, Ranson JH, et al.: Hepatic resection for metastatic colon and rectal cancer. An evaluation of preoperative and postoperative factors. Ann Surg 202 (2): 203-8, 1985.
- Gayowski TJ, Iwatsuki S, Madariaga JR, et al.: Experience in hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: analysis of clinical and pathologic risk factors. Surgery 116 (4): 703-10; discussion 710-1, 1994.
- Fernández-Trigo V, Shamsa F, Sugarbaker PH: Repeat liver resections from colorectal metastasis. Repeat Hepatic Metastases Registry. Surgery 117 (3): 296-304, 1995.
- Jaeck D, Bachellier P, Guiguet M, et al.: Long-term survival following resection of colorectal hepatic metastases. Association Française de Chirurgie. Br J Surg 84 (7): 977-80, 1997.
- Taylor M, Forster J, Langer B, et al.: A study of prognostic factors for hepatic resection for colorectal metastases. Am J Surg 173 (6): 467-71, 1997.
- Elias D, Cavalcanti A, Sabourin JC, et al.: Resection of liver metastases from colorectal cancer: the real impact of the surgical margin. Eur J Surg Oncol 24 (3): 174-9, 1998.
- Girard P, Ducreux M, Baldeyrou P, et al.: Surgery for lung metastases from colorectal cancer: analysis of prognostic factors. J Clin Oncol 14 (7): 2047-53, 1996.
- Hughes KS, Simon R, Songhorabodi S, et al.: Resection of the liver for colorectal carcinoma metastases: a multi-institutional study of patterns of recurrence. Surgery 100 (2): 278-84, 1986.
- Schlag P, Hohenberger P, Herfarth C: Resection of liver metastases in colorectal cancer--competitive analysis of treatment results in synchronous versus metachronous metastases. Eur J Surg Oncol 16 (4): 360-5, 1990.
- Rosen CB, Nagorney DM, Taswell HF, et al.: Perioperative blood transfusion and determinants of survival after liver resection for metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Ann Surg 216 (4): 493-504; discussion 504-5, 1992.
- Fong Y, Fortner J, Sun RL, et al.: Clinical score for predicting recurrence after hepatic resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: analysis of 1001 consecutive cases. Ann Surg 230 (3): 309-18; discussion 318-21, 1999.
- Leonard GD, Brenner B, Kemeny NE: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy before liver resection for patients with unresectable liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 23 (9): 2038-48, 2005.
- Hernandez-Alejandro R, Ruffolo LI, Sasaki K, et al.: Recipient and Donor Outcomes After Living-Donor Liver Transplant for Unresectable Colorectal Liver Metastases. JAMA Surg 157 (6): 524-530, 2022.
- Adam R, Piedvache C, Chiche L, et al.: Chemotherapy and liver transplantation versus chemotherapy alone in patients with definitively unresectable colorectal liver metastases: A prospective multicentric randomized trial (TRANSMET). [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 46 (Suppl 16): A-3500, 2024.
- Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F, et al.: Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170 (4): 1015-22, 1998.
- Solbiati L, Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, et al.: Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: long-term results in 117 patients. Radiology 221 (1): 159-66, 2001.
- Lencioni R, Goletti O, Armillotta N, et al.: Radio-frequency thermal ablation of liver metastases with a cooled-tip electrode needle: results of a pilot clinical trial. Eur Radiol 8 (7): 1205-11, 1998.
- Curley SA, Izzo F, Delrio P, et al.: Radiofrequency ablation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: results in 123 patients. Ann Surg 230 (1): 1-8, 1999.
- Oshowo A, Gillams A, Harrison E, et al.: Comparison of resection and radiofrequency ablation for treatment of solitary colorectal liver metastases. Br J Surg 90 (10): 1240-3, 2003.
- Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni F, et al.: Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases in potential candidates for resection: the "test-of-time approach". Cancer 97 (12): 3027-35, 2003.
- Pawlik TM, Izzo F, Cohen DS, et al.: Combined resection and radiofrequency ablation for advanced hepatic malignancies: results in 172 patients. Ann Surg Oncol 10 (9): 1059-69, 2003.
- Jarnagin WR, Fong Y, Ky A, et al.: Liver resection for metastatic colorectal cancer: assessing the risk of occult irresectable disease. J Am Coll Surg 188 (1): 33-42, 1999.
- Ravikumar TS, Kaleya R, Kishinevsky A: Surgical ablative therapy of liver tumors. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology Updates 14 (3): 1-12, 2000.
- Seifert JK, Morris DL: Prognostic factors after cryotherapy for hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Surg 228 (2): 201-8, 1998.
- Bageacu S, Kaczmarek D, Lacroix M, et al.: Cryosurgery for resectable and unresectable hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 33 (5): 590-6, 2007.
- Thomas DS, Nauta RJ, Rodgers JE, et al.: Intraoperative high-dose rate interstitial irradiation of hepatic metastases from colorectal carcinoma. Results of a phase I-II trial. Cancer 71 (6): 1977-81, 1993.
- Ravikumar TS: Interstitial therapies for liver tumors. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 5 (2): 365-77, 1996.
- McAfee MK, Allen MS, Trastek VF, et al.: Colorectal lung metastases: results of surgical excision. Ann Thorac Surg 53 (5): 780-5; discussion 785-6, 1992.
- Headrick JR, Miller DL, Nagorney DM, et al.: Surgical treatment of hepatic and pulmonary metastases from colon cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 71 (3): 975-9; discussion 979-80, 2001.
- Portier G, Elias D, Bouche O, et al.: Multicenter randomized trial of adjuvant fluorouracil and folinic acid compared with surgery alone after resection of colorectal liver metastases: FFCD ACHBTH AURC 9002 trial. J Clin Oncol 24 (31): 4976-82, 2006.
- Mitry E, Fields AL, Bleiberg H, et al.: Adjuvant chemotherapy after potentially curative resection of metastases from colorectal cancer: a pooled analysis of two randomized trials. J Clin Oncol 26 (30): 4906-11, 2008.
- Ychou M, Hohenberger W, Thezenas S, et al.: A randomized phase III study comparing adjuvant 5-fluorouracil/folinic acid with FOLFIRI in patients following complete resection of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 20 (12): 1964-70, 2009.
- Nordlinger B, Sorbye H, Glimelius B, et al.: Perioperative chemotherapy with FOLFOX4 and surgery versus surgery alone for resectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer (EORTC Intergroup trial 40983): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 371 (9617): 1007-16, 2008.
- Kemeny N, Daly J, Reichman B, et al.: Intrahepatic or systemic infusion of fluorodeoxyuridine in patients with liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. A randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 107 (4): 459-65, 1987.
- Chang AE, Schneider PD, Sugarbaker PH, et al.: A prospective randomized trial of regional versus systemic continuous 5-fluorodeoxyuridine chemotherapy in the treatment of colorectal liver metastases. Ann Surg 206 (6): 685-93, 1987.
- Rougier P, Laplanche A, Huguier M, et al.: Hepatic arterial infusion of floxuridine in patients with liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma: long-term results of a prospective randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 10 (7): 1112-8, 1992.
- Kemeny N, Cohen A, Seiter K, et al.: Randomized trial of hepatic arterial floxuridine, mitomycin, and carmustine versus floxuridine alone in previously treated patients with liver metastases from colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 11 (2): 330-5, 1993.
- Reappraisal of hepatic arterial infusion in the treatment of nonresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Meta-Analysis Group in Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 88 (5): 252-8, 1996.
- Mocellin S, Pilati P, Lise M, et al.: Meta-analysis of hepatic arterial infusion for unresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer: the end of an era? J Clin Oncol 25 (35): 5649-54, 2007.
- Kemeny N, Huang Y, Cohen AM, et al.: Hepatic arterial infusion of chemotherapy after resection of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 341 (27): 2039-48, 1999.
- Kemeny MM, Adak S, Gray B, et al.: Combined-modality treatment for resectable metastatic colorectal carcinoma to the liver: surgical resection of hepatic metastases in combination with continuous infusion of chemotherapy--an intergroup study. J Clin Oncol 20 (6): 1499-505, 2002.
- Petrelli N, Herrera L, Rustum Y, et al.: A prospective randomized trial of 5-fluorouracil versus 5-fluorouracil and high-dose leucovorin versus 5-fluorouracil and methotrexate in previously untreated patients with advanced colorectal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 5 (10): 1559-65, 1987.
- Petrelli N, Douglass HO, Herrera L, et al.: The modulation of fluorouracil with leucovorin in metastatic colorectal carcinoma: a prospective randomized phase III trial. Gastrointestinal Tumor Study Group. J Clin Oncol 7 (10): 1419-26, 1989.
- Scheithauer W, Rosen H, Kornek GV, et al.: Randomised comparison of combination chemotherapy plus supportive care with supportive care alone in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. BMJ 306 (6880): 752-5, 1993.
- Expectancy or primary chemotherapy in patients with advanced asymptomatic colorectal cancer: a randomized trial. Nordic Gastrointestinal Tumor Adjuvant Therapy Group. J Clin Oncol 10 (6): 904-11, 1992.
- Buyse M, Thirion P, Carlson RW, et al.: Relation between tumour response to first-line chemotherapy and survival in advanced colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Meta-Analysis Group in Cancer. Lancet 356 (9227): 373-8, 2000.
- Leichman CG, Fleming TR, Muggia FM, et al.: Phase II study of fluorouracil and its modulation in advanced colorectal cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 13 (6): 1303-11, 1995.
- Van Cutsem E, Twelves C, Cassidy J, et al.: Oral capecitabine compared with intravenous fluorouracil plus leucovorin in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a large phase III study. J Clin Oncol 19 (21): 4097-106, 2001.
- Hoff PM, Ansari R, Batist G, et al.: Comparison of oral capecitabine versus intravenous fluorouracil plus leucovorin as first-line treatment in 605 patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: results of a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 19 (8): 2282-92, 2001.
- Saltz LB, Cox JV, Blanke C, et al.: Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. Irinotecan Study Group. N Engl J Med 343 (13): 905-14, 2000.
- de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, et al.: Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 18 (16): 2938-47, 2000.
- Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD, et al.: Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with fluorouracil alone as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 355 (9209): 1041-7, 2000.
- Tournigand C, André T, Achille E, et al.: FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol 22 (2): 229-37, 2004.
- Colucci G, Gebbia V, Paoletti G, et al.: Phase III randomized trial of FOLFIRI versus FOLFOX4 in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: a multicenter study of the Gruppo Oncologico Dell'Italia Meridionale. J Clin Oncol 23 (22): 4866-75, 2005.
- Fuchs CS, Marshall J, Mitchell E, et al.: Randomized, controlled trial of irinotecan plus infusional, bolus, or oral fluoropyrimidines in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the BICC-C Study. J Clin Oncol 25 (30): 4779-86, 2007.
- Díaz-Rubio E, Tabernero J, Gómez-España A, et al.: Phase III study of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with continuous-infusion fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: final report of the Spanish Cooperative Group for the Treatment of Digestive Tumors Trial. J Clin Oncol 25 (27): 4224-30, 2007.
- Porschen R, Arkenau HT, Kubicka S, et al.: Phase III study of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil and leucovorin plus oxaliplatin in metastatic colorectal cancer: a final report of the AIO Colorectal Study Group. J Clin Oncol 25 (27): 4217-23, 2007.
- Rothenberg ML, Eckardt JR, Kuhn JG, et al.: Phase II trial of irinotecan in patients with progressive or rapidly recurrent colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 14 (4): 1128-35, 1996.
- Conti JA, Kemeny NE, Saltz LB, et al.: Irinotecan is an active agent in untreated patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 14 (3): 709-15, 1996.
- Rougier P, Van Cutsem E, Bajetta E, et al.: Randomised trial of irinotecan versus fluorouracil by continuous infusion after fluorouracil failure in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet 352 (9138): 1407-12, 1998.
- Cunningham D, Pyrhönen S, James RD, et al.: Randomised trial of irinotecan plus supportive care versus supportive care alone after fluorouracil failure for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet 352 (9138): 1413-8, 1998.
- Rothenberg ML, Oza AM, Bigelow RH, et al.: Superiority of oxaliplatin and fluorouracil-leucovorin compared with either therapy alone in patients with progressive colorectal cancer after irinotecan and fluorouracil-leucovorin: interim results of a phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 21 (11): 2059-69, 2003.
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et al.: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350 (23): 2335-42, 2004.
- Sanoff HK, Sargent DJ, Campbell ME, et al.: Five-year data and prognostic factor analysis of oxaliplatin and irinotecan combinations for advanced colorectal cancer: N9741. J Clin Oncol 26 (35): 5721-7, 2008.
- Saltz LB, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E, et al.: Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 26 (12): 2013-9, 2008.
- Cassidy J, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E, et al.: Randomized phase III study of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil/folinic acid plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26 (12): 2006-12, 2008.
- Giantonio BJ, Catalano PJ, Meropol NJ, et al.: High-dose bevacizumab improves survival when combined with FOLFOX4 in previously treated advanced colorectal cancer: results from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) study E3200. [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 23 (Suppl 16): A-2, 1s, 2005.
- Arnold D, Andre T, Bennouna J, et al.: Bevacizumab (BEV) plus chemotherapy (CT) continued beyond first progression in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) previously treated with BEV plus CT: results of a randomized phase III intergroup study (TML study). [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 30 (Suppl 15): A-CRA3503, 2012.
- Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Masi G, et al.: Initial therapy with FOLFOXIRI and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 371 (17): 1609-18, 2014.
- Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, et al.: Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351 (4): 337-45, 2004.
- Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Hitre E, et al.: Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 360 (14): 1408-17, 2009.
- Tol J, Koopman M, Cats A, et al.: Chemotherapy, bevacizumab, and cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 360 (6): 563-72, 2009.
- Maughan TS, Adams RA, Smith CG, et al.: Addition of cetuximab to oxaliplatin-based first-line combination chemotherapy for treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: results of the randomised phase 3 MRC COIN trial. Lancet 377 (9783): 2103-14, 2011.
- Adams RA, Meade AM, Seymour MT, et al.: Intermittent versus continuous oxaliplatin and fluoropyrimidine combination chemotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: results of the randomised phase 3 MRC COIN trial. Lancet Oncol 12 (7): 642-53, 2011.
- Bokemeyer C, Cutsem EV, Rougier P, et al.: Addition of cetuximab to chemotherapy as first-line treatment for KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: pooled analysis of the CRYSTAL and OPUS randomised clinical trials. Eur J Cancer 48 (10): 1466-75, 2012.
- Van Cutsem E, Tabernero J, Lakomy R, et al.: Addition of aflibercept to fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan improves survival in a phase III randomized trial in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer previously treated with an oxaliplatin-based regimen. J Clin Oncol 30 (28): 3499-506, 2012.
- Tabernero J, Yoshino T, Cohn AL, et al.: Ramucirumab versus placebo in combination with second-line FOLFIRI in patients with metastatic colorectal carcinoma that progressed during or after first-line therapy with bevacizumab, oxaliplatin, and a fluoropyrimidine (RAISE): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 16 (5): 499-508, 2015.
- Van Cutsem E, Peeters M, Siena S, et al.: Open-label phase III trial of panitumumab plus best supportive care compared with best supportive care alone in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 25 (13): 1658-64, 2007.
- Douillard JY, Siena S, Cassidy J, et al.: Randomized, phase III trial of panitumumab with infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4) versus FOLFOX4 alone as first-line treatment in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: the PRIME study. J Clin Oncol 28 (31): 4697-705, 2010.
- Douillard JY, Oliner KS, Siena S, et al.: Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 369 (11): 1023-34, 2013.
- Hecht JR, Mitchell E, Chidiac T, et al.: A randomized phase IIIB trial of chemotherapy, bevacizumab, and panitumumab compared with chemotherapy and bevacizumab alone for metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27 (5): 672-80, 2009.
- Peeters M, Price TJ, Cervantes A, et al.: Randomized phase III study of panitumumab with fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) compared with FOLFIRI alone as second-line treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 28 (31): 4706-13, 2010.
- Heinemann V, von Weikersthal LF, Decker T, et al.: FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (FIRE-3): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 15 (10): 1065-75, 2014.
- Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz HJ, et al.: CALGB/SWOG 80405: Phase III trial of irinotecan/5-FU/leucovorin (FOLFIRI) or oxaliplatin/5-FU/leucovorin (mFOLFOX6) with bevacizumab (BV) or cetuximab (CET) for patients (pts) with KRAS wild-type (wt) untreated metastatic adenocarcinoma of the colon or rectum (MCRC). [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 32 (Suppl 5): A-LBA3, 2014.
- Stintzing S, Modest DP, Rossius L, et al.: FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer (FIRE-3): a post-hoc analysis of tumour dynamics in the final RAS wild-type subgroup of this randomised open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 17 (10): 1426-1434, 2016.
- Modest DP, Stintzing S, von Weikersthal LF, et al.: Impact of Subsequent Therapies on Outcome of the FIRE-3/AIO KRK0306 Trial: First-Line Therapy With FOLFIRI Plus Cetuximab or Bevacizumab in Patients With KRAS Wild-Type Tumors in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J Clin Oncol 33 (32): 3718-26, 2015.
- Mayer RJ, Van Cutsem E, Falcone A, et al.: Randomized trial of TAS-102 for refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 372 (20): 1909-19, 2015.
- Prager GW, Taieb J, Fakih M, et al.: Trifluridine-Tipiracil and Bevacizumab in Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. N Engl J Med 388 (18): 1657-1667, 2023.
- Grothey A, Sobrero AF, Siena S, et al.: Results of a phase III randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial (CORRECT) of regorafenib plus best supportive care (BSC) versus placebo plus BSC in patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) who have progressed after standard therapies. [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 30 (Suppl 4): A-LBA385, 2012.
- Grothey A, Van Cutsem E, Sobrero A, et al.: Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): an international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 381 (9863): 303-12, 2013.
- Dasari A, Lonardi S, Garcia-Carbonero R, et al.: Fruquintinib versus placebo in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (FRESCO-2): an international, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet 402 (10395): 41-53, 2023.
- Kopetz S, Grothey A, Yaeger R, et al.: Encorafenib, Binimetinib, and Cetuximab in BRAF V600E-Mutated Colorectal Cancer. N Engl J Med 381 (17): 1632-1643, 2019.
- Kopetz S, Grothey A, Van Cutsem E, et al.: Encorafenib plus cetuximab with or without binimetinib for BRAF V600E metastatic colorectal cancer: updated survival results from a randomized, three-arm, phase III study versus choice of either irinotecan or FOLFIRI plus cetuximab (BEACON CRC). [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 38 (15) (suppl): A-4001, 2020.
Available online . Last accessed January 30, 2025. - Fakih M, Tu H, Hsu H, et al.: Real-World Study of Characteristics and Treatment Outcomes Among Patients with KRAS p.G12C-Mutated or Other KRAS Mutated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Oncologist 27 (8): 663-674, 2022.
- Lee JK, Sivakumar S, Schrock AB, et al.: Comprehensive pan-cancer genomic landscape of KRAS altered cancers and real-world outcomes in solid tumors. NPJ Precis Oncol 6 (1): 91, 2022.
- Neumann J, Zeindl-Eberhart E, Kirchner T, et al.: Frequency and type of KRAS mutations in routine diagnostic analysis of metastatic colorectal cancer. Pathol Res Pract 205 (12): 858-62, 2009.
- Henry JT, Coker O, Chowdhury S, et al.: Comprehensive Clinical and Molecular Characterization of KRAS G12C-Mutant Colorectal Cancer. JCO Precis Oncol 5: , 2021.
- Fakih MG, Salvatore L, Esaki T, et al.: Sotorasib plus Panitumumab in Refractory Colorectal Cancer with Mutated KRAS G12C. N Engl J Med 389 (23): 2125-2139, 2023.
- Yaeger R, Weiss J, Pelster MS, et al.: Adagrasib with or without Cetuximab in Colorectal Cancer with Mutated KRAS G12C. N Engl J Med 388 (1): 44-54, 2023.
- André T, Shiu KK, Kim TW, et al.: Pembrolizumab in Microsatellite-Instability-High Advanced Colorectal Cancer. N Engl J Med 383 (23): 2207-2218, 2020.
- Andre T, Shiu K, Kim TW, et al.: Final overall survival for the phase III KN177 study: pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair deficient (MSI-H/dMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 39 (15) (suppl): A-3500, 2021.
Available online . Last accessed January 30, 2025. - Lenz H, Lonardi S, Zagonel V, et al.: Subgroup analyses of patients (pts) with microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient (MSI-H/dMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) treated with nivolumab (NIVO) plus low-dose ipilimumab (IPI) as first-line (1L) therapy: two-year clinical update. [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 39 (3) (suppl): A-58, 2021.
Available online . Last accessed January 30, 2025. - Lenz HJ, Lonardi S, Elez E, et al.: Nivolumab (NIVO) plus ipilimumab (IPI) vs chemotherapy (chemo) as first-line (1L) treatment for microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient (MSI-H/dMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): Expanded efficacy analysis from CheckMate 8HW. [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 42 (Suppl 16): A-3503, 2024.
- Overman MJ, McDermott R, Leach JL, et al.: Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 18 (9): 1182-1191, 2017.
Latest Updates to This Summary (02 / 12 / 2025)
The PDQ cancer information summaries are reviewed regularly and updated as new information becomes available. This section describes the latest changes made to this summary as of the date above.
Added
Updated
Added
This summary is written and maintained by the
About This PDQ Summary
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary for health professionals provides comprehensive, peer-reviewed, evidence-based information about the treatment of colon cancer. It is intended as a resource to inform and assist clinicians in the care of their patients. It does not provide formal guidelines or recommendations for making health care decisions.
Reviewers and Updates
This summary is reviewed regularly and updated as necessary by the
Board members review recently published articles each month to determine whether an article should:
- be discussed at a meeting,
- be cited with text, or
- replace or update an existing article that is already cited.
Changes to the summaries are made through a consensus process in which Board members evaluate the strength of the evidence in the published articles and determine how the article should be included in the summary.
The lead reviewers for Colon Cancer Treatment are:
- Amit Chowdhry, MD, PhD (University of Rochester Medical Center)
- Leon Pappas, MD, PhD (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute)
Any comments or questions about the summary content should be submitted to Cancer.gov through the NCI website's
Levels of Evidence
Some of the reference citations in this summary are accompanied by a level-of-evidence designation. These designations are intended to help readers assess the strength of the evidence supporting the use of specific interventions or approaches. The PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board uses a
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. Although the content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text, it cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless it is presented in its entirety and is regularly updated. However, an author would be permitted to write a sentence such as "NCI's PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks succinctly: [include excerpt from the summary]."
The preferred citation for this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Colon Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at:
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use within the PDQ summaries only. Permission to use images outside the context of PDQ information must be obtained from the owner(s) and cannot be granted by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the illustrations in this summary, along with many other cancer-related images, is available in
Disclaimer
Based on the strength of the available evidence, treatment options may be described as either "standard" or "under clinical evaluation." These classifications should not be used as a basis for insurance reimbursement determinations. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our
Last Revised: 2025-02-12
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the
Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Ignite Healthwise, LLC.
Page Footer
I want to...
Audiences
Secure Member Sites
The Cigna Group Information
Disclaimer
Individual and family medical and dental insurance plans are insured by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (CHLIC), Cigna HealthCare of Arizona, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Illinois, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Georgia, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of North Carolina, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of South Carolina, Inc., and Cigna HealthCare of Texas, Inc. Group health insurance and health benefit plans are insured or administered by CHLIC, Connecticut General Life Insurance Company (CGLIC), or their affiliates (see
All insurance policies and group benefit plans contain exclusions and limitations. For availability, costs and complete details of coverage, contact a licensed agent or Cigna sales representative. This website is not intended for residents of New Mexico.