Condition Basics
What is esophagitis?
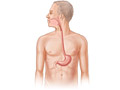
Esophagitis is irritation or inflammation of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that carries food from your throat to your stomach. Esophagitis can be painful and can make it hard to swallow.
What causes it?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, is the most common cause of esophagitis. When you have GERD, stomach acid and juices flow backward into your esophagus. This can irritate the esophagus.
Other causes include:
- A hiatal hernia.
- Medicines that irritate the esophagus, such as:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen.
- Medicines for osteoporosis (bisphosphonates), such as alendronate, ibandronate, or risedronate.
- Antibiotics, such as clindamycin or tetracycline.
- Vitamin and mineral supplements, such as vitamin C, iron, and potassium pills.
- Infection. People who have a weak immune system are more likely to get esophagitis. This includes people with HIV, diabetes, or kidney problems, as well as older adults and people who take steroid medicine.
- Radiation therapy.
- Certain diseases that make it hard to swallow, such as scleroderma.
- Allergies, often food allergies, especially to seafood, milk, nuts, soy, or eggs.
What are the symptoms?
Common symptoms of esophagitis include:
- Heartburn.
- Pain when you swallow.
- Trouble swallowing food or liquids.
- Chest pain (may be similar to the pain of a heart attack).
- A cough.
Sometimes it also causes:
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Fever.
- Belly pain.
How is it diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and past health. The doctor may do tests such as:
- An endoscopy. During this test, the doctor puts a thin, flexible tube down your throat to look at your esophagus. This test also lets the doctor get a sample of the cells to test for infection. Sometimes a small piece of tissue is removed for a biopsy. A biopsy is a test that checks for inflammation or cancer cells.
- A barium swallow. This is an X-ray of the throat and esophagus. Before the X-ray, you will drink a chalky liquid called barium. Barium coats the inside of your esophagus so that it shows up better on an X-ray.
How is esophagitis treated?
The treatment you need depends on what is causing the esophagitis. If you have esophagitis caused by acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), your doctor will likely recommend that you change your diet, lose weight if needed, and make other lifestyle changes. Here are some things to try:
- Change your eating habits.
- It's best to eat several small meals instead of two or three large meals.
- After you eat, wait 2 to 3 hours before you lie down. Late-night snacks aren't a good idea.
- Avoid foods that make your symptoms worse. These may include chocolate, mint, alcohol, pepper, spicy foods, high-fat foods, or drinks with caffeine in them, such as tea, coffee, colas, or energy drinks. If your symptoms are worse after you eat a certain food, you may want to stop eating it to see if your symptoms get better.
- Do not smoke or use smokeless tobacco.
- If you have GERD symptoms at night, raise the head of your bed 6 in. (15 cm) to 8 in. (20 cm) by putting the frame on blocks or placing a foam wedge under the head of your mattress. Adding extra pillows does not work.
- Do not wear tight clothing around your middle.
- Lose weight if you are overweight or obese. Losing just 5 to 10 pounds can help.
If lifestyle changes alone aren't enough to help your esophagitis, your doctor may suggest you try medicines that reduce stomach acid. Reducing the reflux gives the esophagus a chance to heal. Over-the-counter medicines include:
- Antacids, such as Maalox, Mylanta, or Tums. Be careful when you take over-the-counter antacid medicines. Many of these medicines have aspirin in them. Read the label to make sure that you are not taking more than the recommended dose. Too much aspirin can be harmful.
- Stronger acid reducers, such as famotidine (for example, Pepcid) and omeprazole (for example, Prilosec). Your doctor may also prescribe acid reducers for you.
If esophagitis is caused by an infection, you may need to take antibiotics or other medicines to treat the infection.
If you or your child has esophagitis caused by a food allergy, your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids.
You might need surgery if you have a tear in your esophagus or if something is blocking your esophagus, such as a tumor.