Skip to main navigation
Skip to main content
Skip to footer
For
Medicare
For
Providers
For
Brokers
For
Employers
Español
For Individuals & Families:
For Individuals & Families
Medical
Dental
Other Supplemental
Explore coverage through work
How to Buy Health Insurance
Types of Dental Insurance
Open Enrollment vs. Special Enrollment
See all topics
Shop for international insurance plans
Member Guide
Find a Doctor
Log in to myCigna
Home
Knowledge Center
Wellness Library
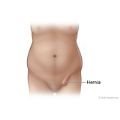
Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic hernia repair is similar to other laparoscopic procedures. General anesthesia is given, and a small cut (incision) is made in or just below the navel. The belly is inflated with air so that the surgeon can see the organs in the belly.
A thin, lighted scope called a laparoscope is inserted through the incision. The tools to repair the hernia are inserted through other small incisions in the lower belly. The edges of healthy tissue may be sewn together. Or a special patch may be used to support the weak spot.
What To Expect
What To Expect
Most people who have laparoscopic hernia repair surgery are able to go home the same day. Recovery time is about 1 to 2 weeks.
You most likely can return to light activity after 1 to 2 weeks. Strenuous exercise should wait until after 4 weeks of recovery or until your doctor says it's okay.
People generally have less pain after laparoscopic hernia repair than after open hernia surgery.
Why It Is Done
Why It Is Done
Surgical repair is recommended for inguinal hernias that are causing pain or other symptoms. Surgery is always recommended for inguinal hernias in children.
Laparoscopic surgery repair may not be an option for people who:
- Have an incarcerated or strangulated hernia.
- Cannot have general anesthesia.
- Have bleeding disorders such as hemophilia or immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP).
- Are taking a blood thinner that prevents blood clots.
- Have had many belly surgeries. Scar tissue may make the surgery harder to do through the laparoscope.
- Have severe lung diseases such as emphysema. The carbon dioxide used to inflate the belly may interfere with their breathing.
- Are pregnant.
- Have severe obesity.
Laparoscopic hernia repair in children allows the doctor to check the opposite groin area for a hernia and repair both hernias during the same surgery.
How Well It Works
How Well It Works
Laparoscopic surgery for inguinal hernia repair is safe. The chance of a hernia coming back is low. The chance that a hernia needs more than one repair also depends on your age and overall health.
Laparoscopic surgery has the following advantages over open hernia repair:
- Laparoscopic hernia repair causes less pain.
- People are able to return to work sooner than they would after open surgery.
- Repair of a recurrent hernia often is easier using laparoscopy than using open surgery.
- It is possible to check for and repair a second hernia on the opposite side at the time of the surgery.
Risks
Risks
Risks of laparoscopic hernia repair include:
- Infection.
- Bleeding.
- Blood clots.
- Bruising and swelling.
- Urinary problems.
- The hernia coming back.
- The low risk of injury to belly organs, testicles, blood vessels, or nerves.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.
<cipublic-spinner variant="large"><span>Loading…</span></cipublic-spinner>