Stages of Ovarian Borderline Tumors
After ovarian borderline tumor has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if abnormal cells have spread within the ovary or to other parts of the body.
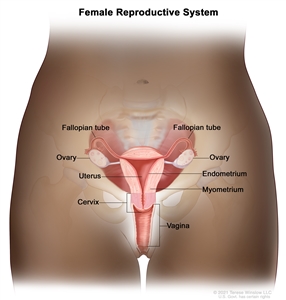
Cancer stage describes the extent of cancer in the body, such as the size of the tumor, whether it has spread, and how far it has spread from where it first formed. It is important to know the stage of the ovarian borderline tumors to plan the best treatment. Most people are diagnosed with stage I disease.
Borderline ovarian tumor staging usually uses the FIGO staging system. The tumor may be described by this staging system in your pathology report. Based on the FIGO results, a stage (I, II, III, or IV, also written as 1, 2, 3, or 4) is assigned to your tumor. When talking to you about your diagnosis, your doctor may describe the tumor as one of these stages.
The following stages are used for ovarian borderline tumor:
Stage I (also called stage 1) ovarian borderline tumor
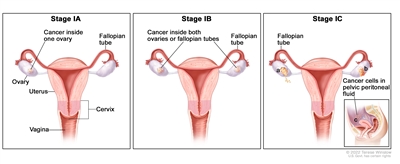
In stage IA, cancer is found inside a single ovary or fallopian tube. In stage IB, cancer is found inside both ovaries or fallopian tubes. In stage IC, cancer is found inside one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and one of the following is true: (a) either the tumor or the capsule (outer covering) of the ovary has ruptured (broken open), or (b) cancer is also found on the surface of the ovary or fallopian tube, or (c) cancer cells are found in the pelvic peritoneal fluid.
In stage I, the tumor is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes. Stage I is divided into stage IA, stage IB, and stage IC.
- Stage IA: The tumor is found inside a single ovary or fallopian tube.
- Stage IB: The tumor is found inside both ovaries or fallopian tubes.
- Stage IC: The tumor is found inside one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and one of the following is true:
- tumor cells are found on the outside surface of one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes; or
- the capsule (outer covering) of the ovary ruptured (broke open) before or during surgery; or
- tumor cells are found in the fluid of the peritoneal cavity (the body cavity that contains most of the organs in the abdomen) or in washings of the peritoneum (tissue lining the peritoneal cavity).
Stage II (also called stage 2) ovarian borderline tumor
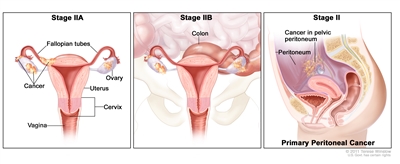
In stage IIA, cancer is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread to the uterus and/or the fallopian tubes and/or the ovaries. In stage IIB, cancer is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread to organs in the peritoneal cavity, such as the colon. In primary peritoneal cancer, cancer is found in the pelvic peritoneum and has not spread there from another part of the body.
In stage II, the tumor is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread into other areas of the pelvis, or primary peritoneal cancer is found within the pelvis. Stage II is divided into stage IIA and stage IIB.
- Stage IIA: The tumor has spread from where it first formed to the uterus and/or the fallopian tubes and/or the ovaries.
- Stage IIB: The tumor has spread from the ovary or fallopian tube to organs in the peritoneal cavity (the space that contains the abdominal organs).
Stage III (also called stage 3) ovarian borderline tumor
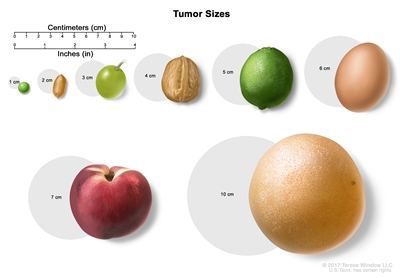
Tumor sizes are often measured in centimeters (cm) or inches. Common food items that can be used to show tumor size in cm include: a pea (1 cm), a peanut (2 cm), a grape (3 cm), a walnut (4 cm), a lime (5 cm or 2 inches), an egg (6 cm), a peach (7 cm), and a grapefruit (10 cm or 4 inches).
In stage III, the tumor is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes, or is primary peritoneal cancer, and has spread outside the pelvis to other parts of the abdomen and/or to nearby lymph nodes. Stage III is divided into stage IIIA, stage IIIB, and stage IIIC.
- In stage IIIA, one of the following is true:
- The tumor has spread to lymph nodes in the area outside or behind the peritoneum only; or
- Tumor cells that can be seen only with a microscope have spread to the surface of the peritoneum outside the pelvis, such as the omentum (a fold of the peritoneum that surrounds the stomach and other organs in the abdomen). The tumor may have spread to nearby lymph nodes.
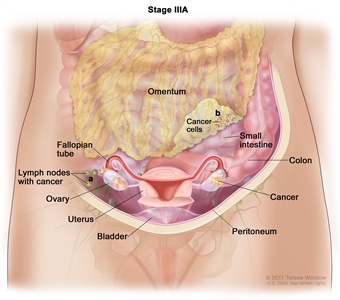
In stage IIIA, cancer is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and (a) cancer has spread to lymph nodes behind the peritoneum only, or (b) cancer cells that can be seen only with a microscope have spread to the surface of the peritoneum outside the pelvis, such as the omentum. Cancer may have also spread to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage IIIB: The tumor has spread to the peritoneum outside the pelvis, such as the omentum, and the tumor in the peritoneum is 2 centimeters or smaller. The tumor may have spread to lymph nodes behind the peritoneum.
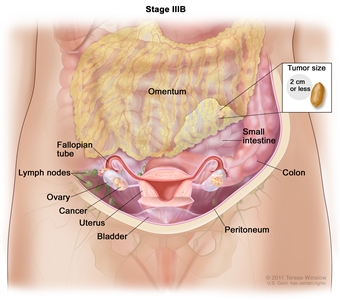
In stage IIIB, cancer is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread to the peritoneum outside the pelvis, such as the omentum. The cancer in the omentum is 2 centimeters or smaller. Cancer may have also spread to lymph nodes behind the peritoneum.
- Stage IIIC: The tumor has spread to the peritoneum outside the pelvis, such as the omentum, and the tumor in the peritoneum is larger than 2 centimeters. The tumor may have spread to lymph nodes behind the peritoneum or to the surface of the liver or spleen.
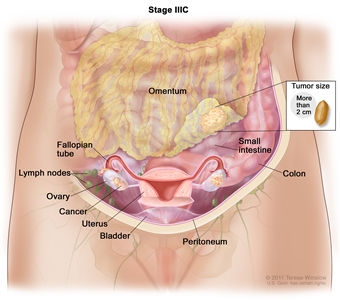
In stage IIIC, cancer is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread to the peritoneum outside the pelvis, such as the omentum. The cancer in the omentum is larger than 2 centimeters. Cancer may have also spread to lymph nodes behind the peritoneum or to the surface of the liver or spleen (not shown).
Stage IV (also called stage 4) ovarian borderline tumor
In stage IV, tumor cells have spread beyond the abdomen to other parts of the body. Stage IV is divided into stage IVA and stage IVB. 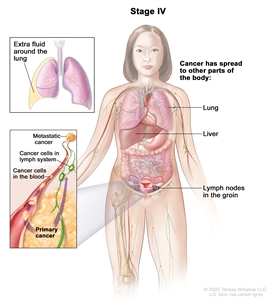
In stage IV, cancer has spread beyond the abdomen to other parts of the body. In stage IVA, cancer cells are found in extra fluid that builds up around the lungs. In stage IVB, cancer has spread to organs and tissues outside the abdomen, including the lung, liver, and lymph nodes in the groin.
- Stage IVA: Tumor cells are found in extra fluid that builds up around the lungs.
- Stage IVB: The tumor has spread to organs and tissues outside the abdomen, including lymph nodes in the groin.
Ovarian borderline tumors can recur (come back) after they have been treated.
Recurrent ovarian borderline tumors are tumors that have come back after they have been treated. The tumors may come back in the other ovary or in other parts of the body. Tests will be done to help determine where the tumor has returned. The type of treatment for a recurrent ovarian borderline tumor will depend on where it has come back.