Shop for Plans
Shop for your own coverage
Plans through your employer
Learn about the medical, dental, pharmacy, behavioral, and voluntary benefits your employer may offer.
Learn
Living or working abroad?
Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Treatment (PDQ®): Treatment - Health Professional Information [NCI]
General Information About Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer
This PDQ summary addresses the staging and treatment of ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer (FTC), and primary peritoneal cancer (PPC).
Regardless of the site of origin, the hallmark of these cancers is their early peritoneal spread of metastases. The inclusion of FTC and PPC within the ovarian epithelial cancer designation is generally accepted because of much evidence that points to a common Müllerian epithelium derivation and similar management of these three neoplasms. The hypothesis that many high-grade serous ovarian cancers (the most common histological subtype) may arise from precursor lesions that originate in the fimbriae of the fallopian tubes has been supported by findings from risk-reducing surgeries in healthy women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants.[
Clear cell and endometrioid ovarian cancers that are linked to endometriosis have different gene-expression signatures, as do mucinous subtypes.[
Stromal and germ cell tumors are relatively uncommon and comprise fewer than 10% of cases. For more information, see
Incidence and Mortality
Epithelial carcinoma of the ovary is one of the most common gynecologic malignancies, with almost 50% of all cases occurring in women older than 65 years. It is the sixth most frequent cause of cancer death in women.[
Estimated new cases and deaths from ovarian cancer in the United States in 2025:[
- New cases: 20,890.
- Deaths: 12,730.
Anatomy
The fimbriated ends of the fallopian tubes are in close apposition to the ovaries and in the peritoneal space, as opposed to the corpus uteri (body of the uterus) that is located under a layer of peritoneum.
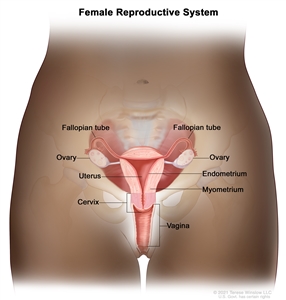
Normal female reproductive system anatomy.
Risk Factors
Increasing age is the most important risk factor for most cancers. Other risk factors for ovarian (epithelial) cancer include:
- Family history of ovarian cancer.[
6 ,7 ,8 ]- A first-degree relative (e.g., mother, daughter, or sister) with the disease.
- Inherited risk.[
9 ]- BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants.[
6 ,10 ]
- BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants.[
- Other hereditary conditions such as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC; also called Lynch syndrome).[
6 ,9 ] - Endometriosis.[
11 ,12 ,13 ] - Hormone therapy.[
14 ,15 ]- Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy.
- Obesity.[
16 ,17 ,18 ]- High body mass index.
- Tall height.[
16 ,17 ,18 ]
Family history and genetic alterations
The most important risk factor for ovarian cancer is a history of ovarian cancer in a first-degree relative (mother, daughter, or sister). Approximately 20% of ovarian cancers are familial, and although most of these are linked to pathogenic variants in either the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene, several other genes have been implicated.[
In most families affected with breast and ovarian cancer syndrome or site-specific ovarian cancer, genetic linkage to the BRCA1 locus on chromosome 17q21 has been identified.[
The lifetime risk of developing ovarian cancer in patients with germline pathogenic variants in BRCA1 is substantially increased over that of the general population.[
For women at increased risk, prophylactic oophorectomy may be considered after age 35 years if childbearing is complete. A family-based study included 551 women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants. Of the 259 women who had undergone bilateral prophylactic oophorectomy, 2 (0.8%) developed subsequent papillary serous peritoneal carcinoma, and 6 (2.8%) had stage I ovarian cancer at the time of surgery. Of the 292 matched controls, 20% who did not have prophylactic surgery developed ovarian cancer. Prophylactic surgery was associated with a reduction in the risk of ovarian cancer that exceeded 90% (relative risk, 0.04; 95% confidence interval, 0.01–0.16), with an average follow-up of 9 years.[
For more information, see
Clinical Presentation
Ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, or PPC may not cause early signs or symptoms. When signs or symptoms do appear, cancer is often advanced. Signs and symptoms include:
- Pain, swelling, or a feeling of pressure in the abdomen or pelvis.
- Urinary urgency or frequency.
- Difficulty eating or feeling full.
- A lump in the pelvic area.
- Gastrointestinal problems such as gas, bloating, or constipation.
These symptoms often go unrecognized, leading to delays in diagnosis. Efforts have been made to enhance physician and patient awareness of the occurrence of these nonspecific symptoms.[
Screening procedures such as gynecologic assessment, vaginal ultrasonography, and cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) assay have had low predictive value in detecting ovarian cancer in women without special risk factors.[
Most patients with ovarian cancer have widespread disease at presentation. Early peritoneal spread of the most common subtype of high-grade serous cancers may relate to serous cancers starting in the fimbriae of the fallopian tubes or in the peritoneum, readily explaining why such cancers are detected at an advanced stage. Conversely, high-grade serous cancers are underrepresented among stage I cancers of the ovary. Other types of ovarian cancers are, in fact, overrepresented in cancers detected in stages I and II. This type of ovarian cancer usually spreads via local shedding into the peritoneal cavity followed by implantation on the peritoneum and via local invasion of bowel and bladder. The incidence of positive nodes at primary surgery has been reported to be as high as 24% in patients with stage I disease, 50% in patients with stage II disease, 74% in patients with stage III disease, and 73% in patients with stage IV disease. The pelvic nodes were involved as often as the para-aortic nodes.[
Diagnostic and Staging Evaluation
The following tests and procedures may be used in the diagnosis and staging of ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, or PPC:
- Physical examination and history.
- Pelvic examination.
- CA-125 assay.
- Ultrasonography (pelvic or transvaginal).
- Computed tomography (CT) scan.
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- Chest x-ray.
- Biopsy.
CA-125 levels can be elevated in other malignancies and benign gynecologic problems such as endometriosis. CA-125 levels and histology are used to diagnose epithelial ovarian cancer.[
Prognostic Factors
Prognosis for patients with ovarian cancer is influenced by multiple factors. Multivariate analyses suggest that the most important favorable prognostic factors include:[
- Younger age.
- Good performance status.
- Cell type other than mucinous or clear cell.
- Well-differentiated tumor.
- Early-stage disease.
- Absence of ascites.
- Lower disease volume before surgical debulking.
- Smaller residual tumor after primary cytoreductive surgery.
- BRCA1 or BRCA2 variant.
For patients with stage I disease, the most important prognostic factor associated with relapse is grade, followed by dense adherence and large-volume ascites.[
If the tumor is grade 3, densely adherent, or stage IC, the chance of relapse and death from ovarian cancer is as much as 30%.[
The use of DNA flow cytometric analysis of tumors from patients with stage I and stage IIA disease may identify those at high risk.[
Case-control studies suggest that women with BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants have improved responses to chemotherapy when compared with patients with sporadic epithelial ovarian cancer. This may be the result of a deficient homologous DNA repair mechanism in these tumors, which leads to increased sensitivity to chemotherapy agents.[
Follow-Up After Treatment
Because of the low specificity and sensitivity of the CA-125 assay, serial CA-125 monitoring of patients undergoing treatment for recurrence may be useful. However, whether that confers a net benefit has not yet been determined. There is little guidance about patient follow-up after initial induction therapy. Neither early detection by imaging nor by CA-125 elevation has been shown to alter outcomes.[
References:
- Levanon K, Crum C, Drapkin R: New insights into the pathogenesis of serous ovarian cancer and its clinical impact. J Clin Oncol 26 (32): 5284-93, 2008.
- Birrer MJ: The origin of ovarian cancer—is it getting clearer? N Engl J Med 363 (16): 1574-5, 2010.
- Dubeau L, Drapkin R: Coming into focus: the nonovarian origins of ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol 24 (Suppl 8): viii28-viii35, 2013.
- National Cancer Institute: SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Ovarian Cancer. Bethesda, Md: National Institutes of Health.
Available online . Last accessed February 10, 2025. - American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts and Figures 2025. American Cancer Society, 2025.
Available online . Last accessed January 16, 2025. - Bolton KL, Ganda C, Berchuck A, et al.: Role of common genetic variants in ovarian cancer susceptibility and outcome: progress to date from the Ovarian Cancer Association Consortium (OCAC). J Intern Med 271 (4): 366-78, 2012.
- Weissman SM, Weiss SM, Newlin AC: Genetic testing by cancer site: ovary. Cancer J 18 (4): 320-7, 2012 Jul-Aug.
- Hunn J, Rodriguez GC: Ovarian cancer: etiology, risk factors, and epidemiology. Clin Obstet Gynecol 55 (1): 3-23, 2012.
- Pal T, Akbari MR, Sun P, et al.: Frequency of mutations in mismatch repair genes in a population-based study of women with ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 107 (10): 1783-90, 2012.
- Gayther SA, Pharoah PD: The inherited genetics of ovarian and endometrial cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 20 (3): 231-8, 2010.
- Poole EM, Lin WT, Kvaskoff M, et al.: Endometriosis and risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers in a large prospective cohort of U.S. nurses. Cancer Causes Control 28 (5): 437-445, 2017.
- Pearce CL, Templeman C, Rossing MA, et al.: Association between endometriosis and risk of histological subtypes of ovarian cancer: a pooled analysis of case-control studies. Lancet Oncol 13 (4): 385-94, 2012.
- Mogensen JB, Kjær SK, Mellemkjær L, et al.: Endometriosis and risks for ovarian, endometrial and breast cancers: A nationwide cohort study. Gynecol Oncol 143 (1): 87-92, 2016.
- Lacey JV, Brinton LA, Leitzmann MF, et al.: Menopausal hormone therapy and ovarian cancer risk in the National Institutes of Health-AARP Diet and Health Study Cohort. J Natl Cancer Inst 98 (19): 1397-405, 2006.
- Trabert B, Wentzensen N, Yang HP, et al.: Ovarian cancer and menopausal hormone therapy in the NIH-AARP diet and health study. Br J Cancer 107 (7): 1181-7, 2012.
- Engeland A, Tretli S, Bjørge T: Height, body mass index, and ovarian cancer: a follow-up of 1.1 million Norwegian women. J Natl Cancer Inst 95 (16): 1244-8, 2003.
- Lahmann PH, Cust AE, Friedenreich CM, et al.: Anthropometric measures and epithelial ovarian cancer risk in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Int J Cancer 126 (10): 2404-15, 2010.
- Collaborative Group on Epidemiological Studies of Ovarian Cancer: Ovarian cancer and body size: individual participant meta-analysis including 25,157 women with ovarian cancer from 47 epidemiological studies. PLoS Med 9 (4): e1001200, 2012.
- Lynch HT, Watson P, Lynch JF, et al.: Hereditary ovarian cancer. Heterogeneity in age at onset. Cancer 71 (2 Suppl): 573-81, 1993.
- Pennington KP, Swisher EM: Hereditary ovarian cancer: beyond the usual suspects. Gynecol Oncol 124 (2): 347-53, 2012.
- Piver MS, Goldberg JM, Tsukada Y, et al.: Characteristics of familial ovarian cancer: a report of the first 1,000 families in the Gilda Radner Familial Ovarian Cancer Registry. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol 17 (3): 169-76, 1996.
- Miki Y, Swensen J, Shattuck-Eidens D, et al.: A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science 266 (5182): 66-71, 1994.
- Easton DF, Bishop DT, Ford D, et al.: Genetic linkage analysis in familial breast and ovarian cancer: results from 214 families. The Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am J Hum Genet 52 (4): 678-701, 1993.
- Steichen-Gersdorf E, Gallion HH, Ford D, et al.: Familial site-specific ovarian cancer is linked to BRCA1 on 17q12-21. Am J Hum Genet 55 (5): 870-5, 1994.
- Wooster R, Neuhausen SL, Mangion J, et al.: Localization of a breast cancer susceptibility gene, BRCA2, to chromosome 13q12-13. Science 265 (5181): 2088-90, 1994.
- Easton DF, Ford D, Bishop DT: Breast and ovarian cancer incidence in BRCA1-mutation carriers. Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am J Hum Genet 56 (1): 265-71, 1995.
- Struewing JP, Hartge P, Wacholder S, et al.: The risk of cancer associated with specific mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 among Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med 336 (20): 1401-8, 1997.
- Rubin SC, Benjamin I, Behbakht K, et al.: Clinical and pathological features of ovarian cancer in women with germ-line mutations of BRCA1. N Engl J Med 335 (19): 1413-6, 1996.
- Aida H, Takakuwa K, Nagata H, et al.: Clinical features of ovarian cancer in Japanese women with germ-line mutations of BRCA1. Clin Cancer Res 4 (1): 235-40, 1998.
- Rebbeck TR, Lynch HT, Neuhausen SL, et al.: Prophylactic oophorectomy in carriers of BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations. N Engl J Med 346 (21): 1616-22, 2002.
- Klaren HM, van't Veer LJ, van Leeuwen FE, et al.: Potential for bias in studies on efficacy of prophylactic surgery for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation. J Natl Cancer Inst 95 (13): 941-7, 2003.
- Piver MS, Jishi MF, Tsukada Y, et al.: Primary peritoneal carcinoma after prophylactic oophorectomy in women with a family history of ovarian cancer. A report of the Gilda Radner Familial Ovarian Cancer Registry. Cancer 71 (9): 2751-5, 1993.
- Steenbeek MP, van Bommel MHD, Bulten J, et al.: Risk of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis After Risk-Reducing Salpingo-Oophorectomy: A Systematic Review and Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis. J Clin Oncol 40 (17): 1879-1891, 2022.
- Goff BA, Mandel L, Muntz HG, et al.: Ovarian carcinoma diagnosis. Cancer 89 (10): 2068-75, 2000.
- Friedman GD, Skilling JS, Udaltsova NV, et al.: Early symptoms of ovarian cancer: a case-control study without recall bias. Fam Pract 22 (5): 548-53, 2005.
- Smith LH, Morris CR, Yasmeen S, et al.: Ovarian cancer: can we make the clinical diagnosis earlier? Cancer 104 (7): 1398-407, 2005.
- Goff BA, Mandel LS, Melancon CH, et al.: Frequency of symptoms of ovarian cancer in women presenting to primary care clinics. JAMA 291 (22): 2705-12, 2004.
- Goff BA, Mandel LS, Drescher CW, et al.: Development of an ovarian cancer symptom index: possibilities for earlier detection. Cancer 109 (2): 221-7, 2007.
- Partridge E, Kreimer AR, Greenlee RT, et al.: Results from four rounds of ovarian cancer screening in a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol 113 (4): 775-82, 2009.
- van Nagell JR, Miller RW, DeSimone CP, et al.: Long-term survival of women with epithelial ovarian cancer detected by ultrasonographic screening. Obstet Gynecol 118 (6): 1212-21, 2011.
- Burghardt E, Girardi F, Lahousen M, et al.: Patterns of pelvic and paraaortic lymph node involvement in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 40 (2): 103-6, 1991.
- Berek JS, Knapp RC, Malkasian GD, et al.: CA 125 serum levels correlated with second-look operations among ovarian cancer patients. Obstet Gynecol 67 (5): 685-9, 1986.
- Atack DB, Nisker JA, Allen HH, et al.: CA 125 surveillance and second-look laparotomy in ovarian carcinoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol 154 (2): 287-9, 1986.
- Omura GA, Brady MF, Homesley HD, et al.: Long-term follow-up and prognostic factor analysis in advanced ovarian carcinoma: the Gynecologic Oncology Group experience. J Clin Oncol 9 (7): 1138-50, 1991.
- van Houwelingen JC, ten Bokkel Huinink WW, van der Burg ME, et al.: Predictability of the survival of patients with advanced ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 7 (6): 769-73, 1989.
- Neijt JP, ten Bokkel Huinink WW, van der Burg ME, et al.: Long-term survival in ovarian cancer. Mature data from The Netherlands Joint Study Group for Ovarian Cancer. Eur J Cancer 27 (11): 1367-72, 1991.
- Hoskins WJ, Bundy BN, Thigpen JT, et al.: The influence of cytoreductive surgery on recurrence-free interval and survival in small-volume stage III epithelial ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol 47 (2): 159-66, 1992.
- Thigpen T, Brady MF, Omura GA, et al.: Age as a prognostic factor in ovarian carcinoma. The Gynecologic Oncology Group experience. Cancer 71 (2 Suppl): 606-14, 1993.
- Dembo AJ, Davy M, Stenwig AE, et al.: Prognostic factors in patients with stage I epithelial ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol 75 (2): 263-73, 1990.
- Ahmed FY, Wiltshaw E, A'Hern RP, et al.: Natural history and prognosis of untreated stage I epithelial ovarian carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 14 (11): 2968-75, 1996.
- Monga M, Carmichael JA, Shelley WE, et al.: Surgery without adjuvant chemotherapy for early epithelial ovarian carcinoma after comprehensive surgical staging. Gynecol Oncol 43 (3): 195-7, 1991.
- Kolomainen DF, A'Hern R, Coxon FY, et al.: Can patients with relapsed, previously untreated, stage I epithelial ovarian cancer be successfully treated with salvage therapy? J Clin Oncol 21 (16): 3113-8, 2003.
- Schueler JA, Cornelisse CJ, Hermans J, et al.: Prognostic factors in well-differentiated early-stage epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer 71 (3): 787-95, 1993.
- Young RC, Walton LA, Ellenberg SS, et al.: Adjuvant therapy in stage I and stage II epithelial ovarian cancer. Results of two prospective randomized trials. N Engl J Med 322 (15): 1021-7, 1990.
- Gershenson DM, Silva EG, Mitchell MF, et al.: Transitional cell carcinoma of the ovary: a matched control study of advanced-stage patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 168 (4): 1178-85; discussion 1185-7, 1993.
- Vencken PM, Kriege M, Hoogwerf D, et al.: Chemosensitivity and outcome of BRCA1- and BRCA2-associated ovarian cancer patients after first-line chemotherapy compared with sporadic ovarian cancer patients. Ann Oncol 22 (6): 1346-52, 2011.
- Safra T, Borgato L, Nicoletto MO, et al.: BRCA mutation status and determinant of outcome in women with recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer treated with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther 10 (10): 2000-7, 2011.
- Rustin GJ, van der Burg ME, Griffin CL, et al.: Early versus delayed treatment of relapsed ovarian cancer (MRC OV05/EORTC 55955): a randomised trial. Lancet 376 (9747): 1155-63, 2010.
Cellular Classification of Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer
| Histological Classification | Histological Subtypes |
|---|---|
| FTC = fallopian tube cancer; PPC = primary peritoneal cancer. | |
| Serous cystomas | Serous benign cystadenomas. |
| Serous cystadenomas with proliferating activity of the epithelial cells and nuclear abnormalities but with no infiltrative destructive growth. | |
| Serous cystadenocarcinomas. | |
| Mucinous cystomas | Mucinous benign cystadenomas. |
| Mucinous cystadenomas with proliferating activity of the epithelial cells and nuclear abnormalities but with no infiltrative destructive growth (low malignant potential or borderline malignancy). | |
| Mucinous cystadenocarcinomas. | |
| Endometrioid tumors (similar to adenocarcinomas in the endometrium) | Endometrioid benign cysts. |
| Endometrioid tumors with proliferating activity of the epithelial cells and nuclear abnormalities but with no infiltrative destructive growth (low malignant potential or borderline malignancy). | |
| Endometrioid adenocarcinomas. | |
| Clear cell (mesonephroid) tumors | Benign clear cell tumors. |
| Clear cell tumors with proliferating activity of the epithelial cells and nuclear abnormalities but with no infiltrative destructive growth (low malignant potential or borderline malignancy). | |
| Clear cell cystadenocarcinomas. | |
| Unclassified tumors that cannot be allotted to one of the above groups | |
| No histology (cytology-only diagnosis) | |
| Other malignant tumors (malignant tumors other than those of the common epithelial types are not to be included with the categories listed above) | |
Stage Information for Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer
In the absence of extra-abdominal metastatic disease, definitive staging of ovarian cancer requires surgery. The role of surgery in patients with stage IV ovarian cancer and extra-abdominal disease is yet to be established. If disease appears to be limited to the ovaries or pelvis, it is essential at laparotomy to obtain peritoneal washings and to examine and biopsy or obtain cytological brushings of the following sites:
- Diaphragm.
- Both paracolic gutters.
- Pelvic peritoneum.
- Para-aortic and pelvic nodes.
- Infracolic omentum.[
1 ]
The Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique (FIGO) Staging
The FIGO and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) have designated staging to define ovarian epithelial cancer. The FIGO-approved staging system for ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer (FTC), and primary peritoneal cancer (PPC) is the one most commonly used.[
| Stage | Definition | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| FIGO = Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique. | ||
| a Adapted from FIGO Committee for Gynecologic Oncology.[ |
||
| I | Tumor confined to ovaries or fallopian tube(s). | 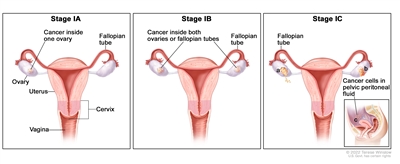 |
| IA | Tumor limited to one ovary (capsule intact) or fallopian tube; no tumor on ovarian or fallopian tube surface; no malignant cells in the ascites or peritoneal washings. | |
| IB | Tumor limited to both ovaries (capsules intact) or fallopian tubes; no tumor on ovarian or fallopian tube surface; no malignant cells in the ascites or peritoneal washings. | |
| IC | Tumor limited to one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes, with any of the following: | |
| IC1: Surgical spill. | ||
| IC2: Capsule ruptured before surgery or tumor on ovarian or fallopian tube surface. | ||
| IC3: Malignant cells in the ascites or peritoneal washings. | ||
| Stage | Definition | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| FIGO = Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique. | ||
| a Adapted from FIGO Committee for Gynecologic Oncology.[ |
||
| II | Tumor involves one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes with pelvic extension (below pelvic brim) or primary peritoneal cancer. | 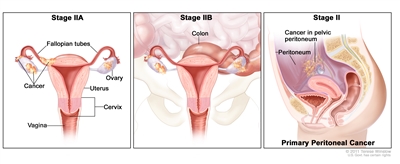 |
| IIA | Extension and/or implants on the uterus and/or fallopian tubes and/or ovaries. | |
| IIB | Extension to other pelvic intraperitoneal tissues. | |
| Stage | Definition | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| FIGO = Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique. | ||
| a Adapted from FIGO Committee for Gynecologic Oncology.[ |
||
| III | Tumor involves one or both ovaries, or fallopian tubes, or primary peritoneal cancer, with cytologically or histologically confirmed spread to the peritoneum outside the pelvis and/or metastasis to the retroperitoneal lymph nodes. | |
| IIIA1 | Positive retroperitoneal lymph nodes only (cytologically or histologically proven): | 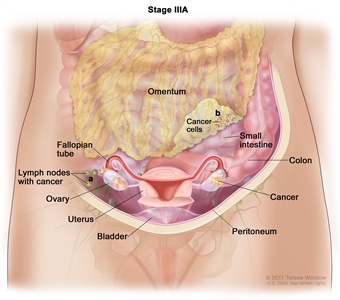 |
| IIIA1(I): Metastasis ≤10 mm in greatest dimension. | ||
| IIIA1(ii): Metastasis >10 mm in greatest dimension. | ||
| IIIA2 | Microscopic extrapelvic (above the pelvic brim) peritoneal involvement with or without positive retroperitoneal lymph nodes. | |
| IIIB | Macroscopic peritoneal metastases beyond the pelvis ≤2 cm in greatest dimension, with or without metastasis to the retroperitoneal lymph nodes. | 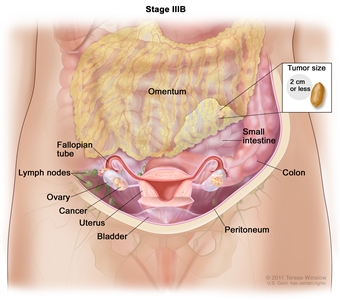 |
| IIIC | Macroscopic peritoneal metastasis beyond the pelvis >2 cm in greatest dimension, with or without metastasis to the retroperitoneal nodes (includes extension of tumor to capsule of liver and spleen without parenchymal involvement of either organ). | 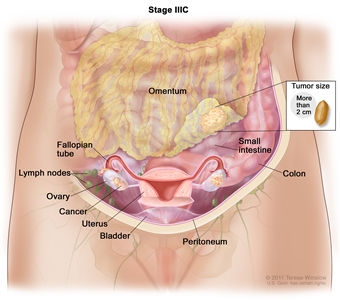 |
| Stage | Definition | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| FIGO = Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique. | ||
| a Adapted from FIGO Committee for Gynecologic Oncology.[ |
||
| IV | Distant metastasis excluding peritoneal metastases. | 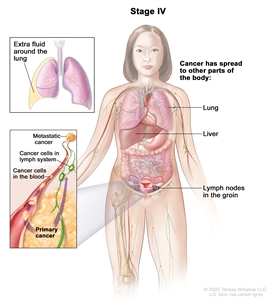 |
| IVA | Pleural effusion with positive cytology. | |
| IVB | Parenchymal metastases and metastases to extra-abdominal organs (including inguinal lymph nodes and lymph nodes outside of the abdominal cavity). | |
References:
- Hoskins WJ: Surgical staging and cytoreductive surgery of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer 71 (4 Suppl): 1534-40, 1993.
- Berek JS, Renz M, Kehoe S, et al.: Cancer of the ovary, fallopian tube, and peritoneum: 2021 update. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 155 (Suppl 1): 61-85, 2021.
- Ovary, fallopian tube, and primary peritoneal carcinoma. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. Springer; 2017, pp 681-90.
Treatment Option Overview for Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer
Treatment options for patients with all stages of ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer (FTC), and primary peritoneal cancer (PPC) have consisted of surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy.
Early stage refers to stages I and II. However, because of high recurrence rates for stage II patients in early-stage disease trials, patients with stage II cancers have been included with patients who have more advanced-stage cancer in Gynecologic Oncology Group clinical trials since 2009. Going forward, stage I will remain a separate category for treatment considerations, but high-grade serous stage II cancers are likely to be included with more advanced stages.
Numerous clinical trials are in progress to refine existing therapies and test the value of different approaches to postoperative drug and radiation therapy. Patients with any stage of ovarian cancer are appropriate candidates for clinical trials.[
The treatment options for ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, and PPC are presented in
| Stage | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| FTC = fallopian tube cancer; HIPEC = hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy; OS = overall survival; PARP = poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; PPC = primary peritoneal cancer. | |
| Low-grade serous carcinoma | |
| |
|
| |
|
| Hormone therapy alone or combined with chemotherapy (under clinical evaluation) | |
| Early-stage ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, and PPC | |
| Advanced-stage ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, and PPC | |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| Chemotherapy for patients who cannot have surgery (although the impact on OS has not been proven) | |
| Recurrent ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, and PPC | |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
Capecitabine and Fluorouracil Dosing
The DPYD gene encodes an enzyme that catabolizes pyrimidines and fluoropyrimidines, like capecitabine and fluorouracil. An estimated 1% to 2% of the population has germline pathogenic variants in DPYD, which lead to reduced DPD protein function and an accumulation of pyrimidines and fluoropyrimidines in the body.[
References:
- Ozols RF, Young RC: Ovarian cancer. Curr Probl Cancer 11 (2): 57-122, 1987 Mar-Apr.
- Cannistra SA: Cancer of the ovary. N Engl J Med 329 (21): 1550-9, 1993.
- Sharma BB, Rai K, Blunt H, et al.: Pathogenic DPYD Variants and Treatment-Related Mortality in Patients Receiving Fluoropyrimidine Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncologist 26 (12): 1008-1016, 2021.
- Lam SW, Guchelaar HJ, Boven E: The role of pharmacogenetics in capecitabine efficacy and toxicity. Cancer Treat Rev 50: 9-22, 2016.
- Shakeel F, Fang F, Kwon JW, et al.: Patients carrying DPYD variant alleles have increased risk of severe toxicity and related treatment modifications during fluoropyrimidine chemotherapy. Pharmacogenomics 22 (3): 145-155, 2021.
- Amstutz U, Henricks LM, Offer SM, et al.: Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase Genotype and Fluoropyrimidine Dosing: 2017 Update. Clin Pharmacol Ther 103 (2): 210-216, 2018.
- Henricks LM, Lunenburg CATC, de Man FM, et al.: DPYD genotype-guided dose individualisation of fluoropyrimidine therapy in patients with cancer: a prospective safety analysis. Lancet Oncol 19 (11): 1459-1467, 2018.
- Lau-Min KS, Varughese LA, Nelson MN, et al.: Preemptive pharmacogenetic testing to guide chemotherapy dosing in patients with gastrointestinal malignancies: a qualitative study of barriers to implementation. BMC Cancer 22 (1): 47, 2022.
- Brooks GA, Tapp S, Daly AT, et al.: Cost-effectiveness of DPYD Genotyping Prior to Fluoropyrimidine-based Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Colon Cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 21 (3): e189-e195, 2022.
- Baker SD, Bates SE, Brooks GA, et al.: DPYD Testing: Time to Put Patient Safety First. J Clin Oncol 41 (15): 2701-2705, 2023.
Treatment of Low-Grade Serous Carcinoma
Treatment Options for Low-Grade Serous Carcinoma
Low-grade serous carcinoma (LGSC), also known as invasive micropapillary serous carcinoma, arises either from serous borderline tumors or de novo. These tumors are uncommon, making up 5% of ovarian carcinomas, and occur in younger women. These tumors are associated with a better clinical prognosis than high-grade serous carcinomas. Molecular characterization of LGSC detected a lower frequency of TP53 variants, greater expression of estrogen and progesterone receptors, and a higher prevalence of BRAF and NRAS variants.[
Treatment approaches for patients with recurrent disease can include cytoreductive surgery, cytotoxic chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, or targeted agents.
Treatment options for LGSC include:
-
Surgery with or without chemotherapy . -
Secondary cytoreductive surgery . -
Targeted therapies . - Hormone therapy alone or combined with chemotherapy (under clinical evaluation [NCT04095364]).
Surgery with or without chemotherapy
While complete cytoreductive surgery is a major component of the treatment approach to LGSC, these tumors tend to be chemoresistant.[
Secondary cytoreductive surgery
Evidence (secondary cytoreductive surgery):
- A single-institution retrospective review evaluated secondary cytoreductive surgery performed between 1995 and 2002 in 41 patients with recurrent LGSC. The study concluded that secondary cytoreduction is beneficial.[
6 ][Level of evidence C3] The median time from primary tumor debulking until secondary cytoreduction was 33.2 months.- Thirty-two patients (78%) had gross residual disease at completion of secondary cytoreduction.
- Patients with no gross residual disease after secondary cytoreduction had a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 60.3 months, compared with 10.7 months for those with gross residual disease (P = .008).
- After secondary cytoreduction surgery, the overall survival (OS) was 93.6 months for those with no gross residual disease and 45.8 months for those with gross residual disease (P = .04).
Targeted therapies
As LGSC is relatively chemoresistant, attention has focused on targeted therapies.
Evidence (targeted therapies):
- Anastrozole: Estrogen receptor (ER) expression is noted in most LGSCs and is a potential target. The PARAGON phase II basket trial evaluated the activity of anastrozole in patients with ER-positive tumors, including 36 patients with recurrent LGSC.[
7 ][Level of evidence C3]- The trial demonstrated clinical benefit in 61% of patients at 6 months and 34% of patients at 12 months. Notably, the study included patients with LGSC and other ER-positive tumors.
- The median duration of clinical benefit was 9.5 months.
- Trametinib: Trametinib is a selective, reversible, allosteric inhibitor of MEK1/MEK2. A recent international, randomized, multicenter, phase II/III trial evaluated trametinib in patients with LGSC. An unlimited number of prior therapies, including chemotherapy or hormone therapy, was allowed. Patients must have received at least one prior platinum-based regimen, but not all five standard-of-care drugs. Patients received either oral trametinib (2 mg once daily) or the standard of care with the physician's choice of chemotherapy (paclitaxel, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, topotecan, oral letrozole, or oral tamoxifen).[
8 ][Level of evidence B1]- The median PFS was 13.0 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 9.9–15.0) in the trametinib group and 7.5 months (95% CI, 5.6–9.9) in the standard-of-care group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.48; 95% CI, 0.36–0.64; one-sided P < .0001).
- A post hoc analysis was performed on a subgroup of 87 patients who were preplanned to receive letrozole if randomly assigned to the standard-of-care group. The PFS was 15.0 months (95% CI, 7.7–23.1) in the trametinib group and 10.6 months (95% CI, 6.5–12.8) in the letrozole group (HR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.36–0.95; one-sided P = .0085).
- The overall response rate was 26% (34 of 130 patients) in the trametinib group. An additional 59% of patients (77 of 130) had stable disease for at least 8 weeks.
- The median OS was 37.6 months (95% CI, 32.0–not evaluable) in the trametinib group and 29.2 months (95% CI, 23.5–51.6) in the standard-of-care group (HRdeath, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.51–1.12; one-sided P = .056).
- There was no evidence that BRAF, KRAS, or NRAS variant status predicted PFS.
- Binimetinib: MILO/ENGOT-ov11 (NCT01849874) was a phase III trial of binimetinib, a small molecule inhibitor of MEK1/MEK2. The trial included 303 patients with recurrent LGSC who had received one to three prior lines of chemotherapy. Patients were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive either binimetinib (45 mg orally twice daily) or physician's choice of chemotherapy (pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, paclitaxel, or topotecan).[
9 ]- The median PFS was 9.1 months (95% CI, 7.3–11.3) for patients who received binimetinib and 10.6 months (95% CI, 9.2–14.5) for patients who received chemotherapy. The study closed early according to the prespecified futility boundary.
- The overall response rate was 16% for patients who received binimetinib (including 32 patients with complete/partial responses), and 13% for patients who received chemotherapy (including 13 patients with complete/partial responses).
- The median duration of response was 8.1 months (range, 0.03 to ≥12.0) for patients who received binimetinib and 6.7 months (range, 0.03 to ≥9.7) for patients who received chemotherapy.
- The OS was 25.3 months for patients who received binimetinib and 20.8 months for patients who received chemotherapy.
- OS was similar and viewed as no better or worse than chemotherapy.
- A post hoc analysis was conducted on tumor molecular testing samples from 215 patients. KRAS variants were seen in 32% to 34% of patients. The analysis showed that KRAS variants were associated with a response to treatment with binimetinib (odds ratio, 3.4; 95% CI, 1.53–7.66; unadjusted P = .003) and with prolonged PFS in patients treated with binimetinib (median PFS: KRAS variant, 17.7 months [95% CI, 12–not reached]; KRAS wild-type, 10.8 months [95% CI, 5.5–16.7]; P = .006).
- Bevacizumab: Bevacizumab is an anti-VEGFA monoclonal antibody. A single institution enrolled 13 patients with LGSC and 4 patients with borderline tumors. Two patients received bevacizumab as a single agent while the other patients received bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy (i.e., paclitaxel, topotecan, oral cyclophosphamide, gemcitabine, or gemcitabine and carboplatin).[
10 ][Level of evidence C3]- After a median duration of 23 weeks (range, 6–79.4), there were no patients with a complete response and six patients with partial responses (five of whom had received concurrent paclitaxel, and one who received concurrent gemcitabine). The overall response rate was 40% among all evaluable patients, and 55% among the subgroup of LGSC patients.
- Ribociclib and letrozole: GOG-3026 (NCT03673124) was a phase II trial evaluating the combination of ribociclib and letrozole in patients with recurrent LGSC. Patients received ribociclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, at 600 mg daily on a 3-weeks-on/1-week-off schedule, plus 2.5 mg of oral letrozole once daily for a 28-day cycle.[
11 ]- The overall response rate was 23% (90% CI, 13.4%–35.1%), and the clinical benefit rate was 97% (90% CI, 67.2%–88.2%).
- The median duration of response was 19.1 months. The median PFS was 19.1 months, and the median OS was not reached.
- Selumetinib: Selumetinib is a selective small molecule inhibitor of MEK1/MEK2. A phase II study included 52 patients with recurrent LGSC who received 50 mg of selumetinib twice daily until progression.[
12 ][Level of evidence C3]- There were 8 patients (15%) with complete responses, 7 patients (13%) with partial responses, and 34 patients (65%) with stable disease.
- The median time to response was 4.8 months, and the median duration of response was 10.5 months.
- The median PFS was 11 months, and 63% of patients had a PFS of more than 6 months.
- Responses were irrespective of BRAF or KRAS variant status.
- Imatinib: LGSC has a high expression of PDGFRB and BCR::ABL1. A phase II study evaluated imatinib mesylate in patients with platinum-resistant recurrent LGSC. The trial enrolled 13 patients who had received at least four prior lines of platinum- and/or taxane-containing chemotherapy and had been screened for a targeted biomarker (i.e., c-kit, PDGFRB, or BCR::ABL1). Patients received 600 mg of imatinib mesylate daily for 6 weeks.[
13 ]- There was no evidence of efficacy in patients who received imatinib mesylate despite high expression of PDGFRB.
Current Clinical Trials
Use our
References:
- Gershenson DM: Low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary or peritoneum. Ann Oncol 27 (Suppl 1): i45-i49, 2016.
- Fader AN, Java J, Krivak TC, et al.: The prognostic significance of pre- and post-treatment CA-125 in grade 1 serous ovarian carcinoma: a gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol 132 (3): 560-5, 2014.
- Norquist BM, Brady MF, Harrell MI, et al.: Mutations in Homologous Recombination Genes and Outcomes in Ovarian Carcinoma Patients in GOG 218: An NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. Clin Cancer Res 24 (4): 777-783, 2018.
- Gershenson DM, Sun CC, Lu KH, et al.: Clinical behavior of stage II-IV low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary. Obstet Gynecol 108 (2): 361-8, 2006.
- Scott SA, Llaurado Fernandez M, Kim H, et al.: Low-grade serous carcinoma (LGSC): A Canadian multicenter review of practice patterns and patient outcomes. Gynecol Oncol 157 (1): 36-45, 2020.
- Crane EK, Sun CC, Ramirez PT, et al.: The role of secondary cytoreduction in low-grade serous ovarian cancer or peritoneal cancer. Gynecol Oncol 136 (1): 25-9, 2015.
- Tang M, O'Connell RL, Amant F, et al.: PARAGON: A Phase II study of anastrozole in patients with estrogen receptor-positive recurrent/metastatic low-grade ovarian cancers and serous borderline ovarian tumors. Gynecol Oncol 154 (3): 531-538, 2019.
- Gershenson DM, Miller A, Brady WE, et al.: Trametinib versus standard of care in patients with recurrent low-grade serous ovarian cancer (GOG 281/LOGS): an international, randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet 399 (10324): 541-553, 2022.
- Monk BJ, Grisham RN, Banerjee S, et al.: MILO/ENGOT-ov11: Binimetinib Versus Physician's Choice Chemotherapy in Recurrent or Persistent Low-Grade Serous Carcinomas of the Ovary, Fallopian Tube, or Primary Peritoneum. J Clin Oncol 38 (32): 3753-3762, 2020.
- Grisham RN, Iyer G, Sala E, et al.: Bevacizumab shows activity in patients with low-grade serous ovarian and primary peritoneal cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 24 (6): 1010-4, 2014.
- Slomovitz B, Deng W, Killion J, et al.: GOG 3026 A phase II trial of letrozole + ribociclib in women with recurrent low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary, fallopian tube or peritoneum: A GOG foundation study. [Abstract] Gynecol Oncol 176 (Suppl 1): A-001, S2, 2023.
- Farley J, Brady WE, Vathipadiekal V, et al.: Selumetinib in women with recurrent low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary or peritoneum: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 14 (2): 134-40, 2013.
- Noguera IR, Sun CC, Broaddus RR, et al.: Phase II trial of imatinib mesylate in patients with recurrent platinum- and taxane-resistant low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary, peritoneum, or fallopian tube. Gynecol Oncol 125 (3): 640-5, 2012.
Treatment of Early-Stage Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer
Early stage refers to stage I and stage II. However, because of high recurrence rates for stage II patients in early-stage disease trials, patients with stage II cancers have been included with patients who have more advanced-stage cancer in Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) clinical trials since 2009. Going forward, stage I will remain a separate category for treatment considerations, but high-grade serous stage II cancers are likely to be included with more advanced stages.
Treatment Options for Early-Stage Ovarian Epithelial Cancer, FTC, and PPC
Treatment options for early-stage ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer (FTC), and primary peritoneal cancer (PPC) include:
-
Surgery with or without chemotherapy.
Surgery with or without chemotherapy
If the tumor is well differentiated or moderately well differentiated, surgery alone may be adequate treatment for patients with stage IA or IB disease. Surgery includes hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and omentectomy. The undersurface of the diaphragm is visualized and biopsied. Biopsies of the pelvic and abdominal peritoneum and the pelvic and para-aortic lymph nodes are also performed. Peritoneal washings are routinely obtained.[
In the United States, except for the most favorable subset of patients (those with stage IA well-differentiated disease), evidence based on double-blinded, randomized, controlled trials with total mortality end points supports adjuvant treatment with cisplatin, carboplatin, and paclitaxel.
Evidence (surgery with or without chemotherapy):
- In two large European trials, the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Adjuvant ChemoTherapy in Ovarian Neoplasm trial (EORTC-ACTION) and International Collaborative Ovarian Neoplasm trial (MRC-ICON1 [NCT00002477]), patients with stage IA (grade 2) and stage IB (grade 3), all stage IC and stage II ovarian epithelial, and all stage I and stage IIA clear cell carcinoma were randomly assigned to receive adjuvant chemotherapy or observation.[
4 ,5 ,6 ]- The EORTC-ACTION trial required at least four cycles of carboplatin or cisplatin-based chemotherapy as treatment. Although surgical staging criteria were monitored, inadequate staging was not an exclusion criterion.[
4 ]- Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was improved for patients in the adjuvant chemotherapy arm (hazard ratio [HR], 0.63; P = .02), but overall survival (OS) was not affected (HR, 0.69; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.44–1.08; P = .10).
- OS was improved by chemotherapy in the subset of patients with inadequate surgical staging.
- The MRC-ICON1 trial randomly assigned patients to receive six cycles of single-agent carboplatin or cisplatin or platinum-based chemotherapy (usually cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and cisplatin) versus observation and had entry criteria similar to the EORTC-ACTION trial; however, the MRC-ICON1 trial did not monitor whether adequate surgical staging was performed.[
5 ] When the results of the trials were combined, the difference in OS achieved statistical significance.- Both RFS and OS were significantly improved; the 5-year survival rates were 79% for patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy versus 70% for those who did not receive adjuvant chemotherapy.
- An analysis of pooled data from both studies demonstrated the following results:[
6 ][Level of evidence A1]- Patients who received chemotherapy showed significant improvement in RFS (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.50–0.82; P = .001) and OS (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.50–0.90; P = .008). The 5-year OS rate was 82% for patients who received chemotherapy and 74% for patients who underwent observation (difference, 8%; 95% CI, 2%–12%).[
6 ][Level of evidence A1] - An accompanying editorial emphasized that the focus of subsequent trials must be to identify patients who do not require additional therapy among the early ovarian cancer subset.[
7 ] Optimal staging is one way to better identify these patients.
- Patients who received chemotherapy showed significant improvement in RFS (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.50–0.82; P = .001) and OS (HR, 0.67; 95% CI, 0.50–0.90; P = .008). The 5-year OS rate was 82% for patients who received chemotherapy and 74% for patients who underwent observation (difference, 8%; 95% CI, 2%–12%).[
- The EORTC-ACTION trial required at least four cycles of carboplatin or cisplatin-based chemotherapy as treatment. Although surgical staging criteria were monitored, inadequate staging was not an exclusion criterion.[
- The GOG-0157 trial evaluated whether six cycles of chemotherapy were superior to three cycles for patients with early-stage, high-risk epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery. Eligible patients were those with stage IA grade 3 or clear cell histology, stage IB grade 3 or clear cell histology, all stage IC, and all stage II. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either three or six cycles of the combination of paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 administered over 3 hours) and carboplatin dosed (area under the curve, 7.5) over 30 minutes and given every 21 days. The primary end point was RFS, and the study was powered to detect a 50% decrease in the recurrence rate at 5 years. A total of 427 patients were eligible.[
8 ]- No significant difference in cumulative incidence of recurrence was found when three cycles (25.4%) were compared with six cycles (20.1%) (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.5–1.13) or OS for three cycles (81%) versus six cycles (83%) (HR, 1.02; P = .94).[
8 ][Level of evidence B1] - As expected, the use of six cycles was associated with increased grade 3 or 4 neurological toxic effects and increased grade 4 hematologic toxic effects.
- Although surgical staging was required for study entry, an audit revealed that 29% of the patients had either incomplete documentation of their surgery or insufficient surgical effort.
- In a post hoc analysis of the patients who underwent complete surgical staging, three additional cycles of chemotherapy decreased the risk of recurrence by only 3%. The cumulative incidence of recurrence within 5 years was 18% for women with stage I disease and 33% for women with stage II disease.
Given the increased risk of recurrence in patients with stage II disease and in those classified as having high-grade serous cancer, the GOG after 2007 opted to include patients with stage II disease in advanced ovarian cancer trials (for more information, see the
Treatment of Advanced-Stage Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer section). Although the routine use of six cycles of chemotherapy is promulgated by guidelines, on subset analyses it is a source of controversy. Platinum-based chemotherapy including paclitaxel for three or six cycles has been evaluated by the GOG in additional trials that included prolonged maintenance paclitaxel, before phasing out early-stage clinical trials. - No significant difference in cumulative incidence of recurrence was found when three cycles (25.4%) were compared with six cycles (20.1%) (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.5–1.13) or OS for three cycles (81%) versus six cycles (83%) (HR, 1.02; P = .94).[
- Patients with stage II ovarian cancer were enrolled in a Japanese Gynecology Oncology Group study (JGOG-3016 [NCT00226915]) that tested a weekly dosing schedule versus the conventional every-3-week dosing schedule in first-line ovarian cancer.[
9 ,10 ,11 ]
The following treatments have been largely displaced by the adoption of carboplatin plus paclitaxel for early stages of high-grade ovarian cancers:
- Intraperitoneal phosphorus P 32 or radiation therapy.[
1 ,12 ,13 ] - Platinum-based systemic chemotherapy alone or in combination with alkylating agents.[
1 ,12 ,14 ,15 ,16 ]
Current Clinical Trials
Use our
References:
- Young RC, Decker DG, Wharton JT, et al.: Staging laparotomy in early ovarian cancer. JAMA 250 (22): 3072-6, 1983.
- Fader AN, Java J, Ueda S, et al.: Survival in women with grade 1 serous ovarian carcinoma. Obstet Gynecol 122 (2 Pt 1): 225-32, 2013.
- Zanetta G, Chiari S, Rota S, et al.: Conservative surgery for stage I ovarian carcinoma in women of childbearing age. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 104 (9): 1030-5, 1997.
- Trimbos JB, Vergote I, Bolis G, et al.: Impact of adjuvant chemotherapy and surgical staging in early-stage ovarian carcinoma: European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Adjuvant ChemoTherapy in Ovarian Neoplasm trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 95 (2): 113-25, 2003.
- Colombo N, Guthrie D, Chiari S, et al.: International Collaborative Ovarian Neoplasm trial 1: a randomized trial of adjuvant chemotherapy in women with early-stage ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95 (2): 125-32, 2003.
- Trimbos JB, Parmar M, Vergote I, et al.: International Collaborative Ovarian Neoplasm trial 1 and Adjuvant ChemoTherapy In Ovarian Neoplasm trial: two parallel randomized phase III trials of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with early-stage ovarian carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 95 (2): 105-12, 2003.
- Young RC: Early-stage ovarian cancer: to treat or not to treat. J Natl Cancer Inst 95 (2): 94-5, 2003.
- Bell J, Brady MF, Young RC, et al.: Randomized phase III trial of three versus six cycles of adjuvant carboplatin and paclitaxel in early stage epithelial ovarian carcinoma: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol 102 (3): 432-9, 2006.
- Katsumata N, Yasuda M, Takahashi F, et al.: Dose-dense paclitaxel once a week in combination with carboplatin every 3 weeks for advanced ovarian cancer: a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 374 (9698): 1331-8, 2009.
- Katsumata N, Yasuda M, Isonishi S, et al.: Long-term results of dose-dense paclitaxel and carboplatin versus conventional paclitaxel and carboplatin for treatment of advanced epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer (JGOG 3016): a randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Oncol 14 (10): 1020-6, 2013.
- Scambia G, Salutari V, Amadio G: Controversy in treatment of advanced ovarian cancer. Lancet Oncol 14 (10): 920-1, 2013.
- Vergote IB, Vergote-De Vos LN, Abeler VM, et al.: Randomized trial comparing cisplatin with radioactive phosphorus or whole-abdomen irradiation as adjuvant treatment of ovarian cancer. Cancer 69 (3): 741-9, 1992.
- Piver MS, Lele SB, Bakshi S, et al.: Five and ten year estimated survival and disease-free rates after intraperitoneal chromic phosphate; stage I ovarian adenocarcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol 11 (5): 515-9, 1988.
- Bolis G, Colombo N, Pecorelli S, et al.: Adjuvant treatment for early epithelial ovarian cancer: results of two randomised clinical trials comparing cisplatin to no further treatment or chromic phosphate (32P). G.I.C.O.G.: Gruppo Interregionale Collaborativo in Ginecologia Oncologica. Ann Oncol 6 (9): 887-93, 1995.
- Piver MS, Malfetano J, Baker TR, et al.: Five-year survival for stage IC or stage I grade 3 epithelial ovarian cancer treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Gynecol Oncol 46 (3): 357-60, 1992.
- McGuire WP: Early ovarian cancer: treat now, later or never? Ann Oncol 6 (9): 865-6, 1995.
Treatment of Advanced-Stage Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer
Treatment options for patients with all stages of ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer (FTC), and primary peritoneal cancer (PPC) have consisted of surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy. Because of high recurrence rates for stage II patients in early-stage disease trials, patients with stage II cancers have been included with patients who have more advanced-stage cancer in Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) clinical trials since 2009. Going forward, stage I will remain a separate category for treatment considerations, but high-grade serous stage II cancers are likely to be included with more advanced stages.
The most common approach to advanced ovarian cancer is surgery followed by adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy. Published trials, most with primary end points of progression-free survival (PFS), are listed in
Treatment Options for Advanced-Stage Ovarian Epithelial Cancer, FTC, and PPC
Treatment options for advanced-stage ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, and PPC include:
-
Surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy. -
Surgery before or after platinum-based chemotherapy and/or additional consolidation therapy . -
Surgery before or after platinum-based chemotherapy and the addition of bevacizumab to induction therapy and/or consolidation therapy . -
Surgery after platinum-based chemotherapy and the addition of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) . -
Surgery before or after platinum-based chemotherapy and the addition of PARP inhibitors to induction therapy and/or consolidation therapy . - Chemotherapy for patients who cannot have surgery (although the impact on OS has not been proven).
Platinum-based chemotherapy is the initial treatment for all patients diagnosed with advanced disease who undergo surgical resection and are staged with cancer that has spread to the pelvic peritoneum (stage II) and beyond (stages III and IV). The role of surgery for patients with stage IV disease is unclear, but in most instances, the bulk of the disease is intra-abdominal, and surgical procedures similar to those used in the management of patients with stage II and III disease are applied.
Surgery has historically been done by open laparotomy performed by gynecologic oncology surgeons, and has included hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, omentectomy, and debulking of peritoneal implants (often including resection of the bowel or adjacent organs as needed) to reduce tumor to microscopic, if it can safely be performed.
The volume of disease left at the completion of the primary surgical procedure in GOG studies has been related to patient survival.[
However, in an analysis of 2,655 of the 4,312 patients enrolled in the largest GOG study (GOG-0182 [NCT00011986]), only cytoreduction to nonvisible disease that is R0 (i.e., complete surgical resection) had an independent effect on survival. For more information, see the
Suboptimally debulked stage III and stage IV patients have inferior 5-year survival rates, but the gap has narrowed in trials that included taxanes and other drugs added to platinums.[
Surgery followed by platinum-based chemotherapy
Platinum agents, such as cisplatin or its less-toxic second-generation analog, carboplatin, given either alone or in combination with other drugs, are the foundation of chemotherapy regimens used. Trials by various cooperative groups (conducted from 1999 to 2010) addressed issues of optimal dose intensity [
With the introduction of the taxane paclitaxel, two trials confirmed the superiority of cisplatin combined with paclitaxel when compared with the previous standard treatment of cisplatin plus cyclophosphamide.[
Based on the evidence, the initial standard treatment for patients with ovarian cancer is the combination of cisplatin or carboplatin with paclitaxel (defined as induction chemotherapy).
Evidence (combination of cisplatin or carboplatin with paclitaxel):
- GOG-132 was widely regarded as showing that sequential treatment with cisplatin and paclitaxel was equivalent to the combination of cisplatin-plus-paclitaxel; however, many patients crossed over before disease progression. Moreover, the cisplatin-only arm was more toxic than the combination of cisplatin (75 mg/m2) and paclitaxel because it used a 100 mg/m2 cisplatin dose per cycle.[
17 ] - The Medical Research Council study (MRC-ICON3) compared carboplatin monotherapy with the combination of carboplatin and paclitaxel. While MRC-ICON3 had fewer early crossovers than GOG-132, it yielded similar outcomes for carboplatin monotherapy, including OS (albeit with less toxicity) compared with the combination treatment.[
18 ]
Since the adoption of the standard combination of platinum plus taxane nearly worldwide, clinical trials have demonstrated the following:
- Noninferiority of carboplatin plus paclitaxel versus cisplatin plus paclitaxel.[
15 ,16 ,19 ] - Noninferiority of carboplatin plus paclitaxel versus carboplatin plus docetaxel.[
20 ] - No advantage but increased toxic effects of adding epirubicin to the carboplatin plus paclitaxel doublet.[
21 ] - Noninferiority of carboplatin plus paclitaxel versus sequential carboplatin-containing doublets with either gemcitabine or topotecan; or, triplets with the addition of gemcitabine or pegylated liposomal doxorubicin to the reference doublet as shown below:[
22 ,23 ]- From 2001 to 2004, 4,312 women with stage III or stage IV ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, or PPC participating in the GOG-0182 trial were randomly assigned to four different experimental arms or to a reference treatment consisting of carboplatin (area under the curve [AUC], 6) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for eight cycles.[
22 ] Stratification factors were residual-disease status and the intention to perform interval debulking surgery.- None of the experimental regimens was inferior.
- Lethal events attributable to treatment occurred in less than 1% of patients without clustering to any one regimen.
- With a median follow-up of 3.7 years, the adjusted relative risk of death ranged from 0.952 to 1.114, with the control arm achieving a PFS of 16.0 months and a median OS of 44.1 months.
Moreover, for the stage III patients who made up 84% to 87% of patients, PFS differences were only noted if surgery achieved R0 resections:[
22 ]- PFS in patients with residuum larger than 1 cm was 13 months, and OS was 33 months.
- With residuum 1 cm or smaller, PFS was 16 months, and OS was 40 months.
- With R0 resection (e.g., no residuum or microscopic residuum only), PFS was 29 months, and OS was 68 months.
- From 2001 to 2004, 4,312 women with stage III or stage IV ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, or PPC participating in the GOG-0182 trial were randomly assigned to four different experimental arms or to a reference treatment consisting of carboplatin (area under the curve [AUC], 6) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for eight cycles.[
In gynecologic cancer, as opposed to breast cancer, weekly paclitaxel was not explored in phase III trials before 2004. The positive results from the
Evidence (dose-dense [weekly] treatment schedule):
- A JGOG trial (JGOG-3016 [NCT00226915]) accrued 637 patients and randomly assigned them to six to nine cycles of weekly (dose-dense) paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) or to the standard every-21-day schedule of paclitaxel at 180 mg/m2. Both regimens were given with carboplatin (AUC, 6) in every-3-week cycles. The primary study end point was PFS with a goal of detecting a PFS increase from 16 months to 21 months in patients receiving the weekly paclitaxel-based regimen.[
24 ,25 ] Although more toxic, the weekly paclitaxel regimen did not adversely affect quality of life when compared with the intermittent schedule.[26 ][Level of evidence B1]Other than ethnicity, this trial population may have differed from GOG and other studies in that patients were younger (average age, 57 years). Twenty percent of patients had stage II disease and 33% of patients had histologies other than high-grade serous or endometrioid cancer. Also, 11% of patients were entered while receiving neoadjuvant treatment, which was an all-inclusive way of assessing treatments other than chemotherapy in first-line settings. The JGOG-3016 study results demonstrated the following results:
- At the 1.5-year follow-up after cessation of treatment, patients who received the weekly regimen had a median PFS of 28.0 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 22.3–35.4), and patients who received the intermittent regimen had a median PFS of 17.2 months (range, 15.7–21.1; hazard ratio [HR], 0.71), favoring the weekly regimen (P = .0015).
- A 2013 update revealed an increase in median survival for patients who received the weekly regimen (median OS, 8.3 years vs. 5.1 years; P = .040); the intermittent regimen results are also noteworthy relative to other clinical trials of weekly dosing schedules.
- In a phase III trial (MITO-7 [NCT00660842]), the outcomes of 406 patients assigned to weekly paclitaxel (60 mg/m2) administered with weekly carboplatin (AUC, 2) were compared with those of 404 patients receiving the conventional every-3-week regimen of paclitaxel and carboplatin.[
27 ][Level of evidence A1]- The results failed to confirm the superiority of this weekly schedule (18.3 months PFS for the weekly arm vs. 17.3 months PFS for the standard arm [HR, 0.96; 95% CI, 0.80–1.16]).
- The treatments did not differ in toxic effects. A decrease in quality of life (assessed by the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy Ovarian Trial Outcome Index questionnaire) was not seen in the weekly arm compared with the every-3-week arm.
- GOG-0262 (NCT01167712) is a phase III study that compared weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) to every-3-week dosing (175 mg/m2), both with the conventional every-3-week carboplatin (AUC, 6) regimen.[
28 ][Level of evidence B1] An option to give bevacizumab every 3 weeks beginning with cycle two and continuing until cycle six and followed by bevacizumab alone for 1 year, as in GOG-0218, was included for both arms. This option was applied in about 84% of all patients.- Overall, the weekly paclitaxel regimen failed to prolong PFS compared with the every-3-week regimen (14.7 months vs. 14.0 months), with an HR for progression or death of 0.89 (95% CI, 0.74–1.06).
- However, among patients not receiving bevacizumab, the weekly paclitaxel arm had significantly prolonged PFS (14.2 months vs. 10.3 months), with an HR of 0.62 (95% CI, 0.40–0.95; P = .03)
- The weekly paclitaxel regimen had a higher rate of grade 3 or 4 anemia (36% vs. 16%) and grade 2 to 4 sensory neuropathy (26% vs. 18%).
- The phase III ICON8 (NCT01654146) trial compared weekly paclitaxel with every-3-week dosing, with another arm that compared weekly paclitaxel with weekly carboplatin (AUC, 2 ˣ 6 cycles).[
29 ]- This large study did not demonstrate any significant differences between the arms.
- A separate quality-of-life study found no difference in global quality of life among the three groups at a 9-month cross-sectional analysis, although the weekly paclitaxel schedules scored significantly lower in longitudinal analyses.[
30 ]
While weekly paclitaxel dosing remains an option for the appropriate patient, several large trials have not been able to replicate the superiority of this treatment, and this regimen is now used less often.[
| Trial | Treatment Regimens | No. of Patients | Progression-Free Survival (mo) | Overall Survival (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC = area under the curve; EORTC = European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer; Est = estimated; GOG = Gynecologic Oncology Group; ICON = International Collaboration on Ovarian Neoplasms; JGOG = Japanese Gynecologic Oncology Group; MITO = Multicentre Italian Trials in Ovarian cancer; MRC = Medical Research Council; No. = number; NR = not reported. | ||||
| a Control arms are bolded. | ||||
| b Statistically inferior result (P < .001–< .05). | ||||
| c Optimally debulked only. | ||||
| d Every 3 weeks for six cycles unless specified. | ||||
| e JGOG-3016 included |
||||
| f Estimated from the curve. | ||||
| GOG-111 (1990–1992)a[ |
Paclitaxel (135 mg/m2, 24 h) and cisplatin (75 mg/m2) | 184 | 18 | 38 |
| Cyclophosphamide (750 mg/m2) and cisplatin (75 mg/m2) | 202 | 13b | 24b | |
| EORTC-55931 | Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2, 3 h) and cisplatin (75 mg/m2) | 162 | 15.5 | 35.6 |
| Cyclophosphamide (750 mg/m2) and cisplatin (75 mg/m2) | 161 | 11.5b | 25.8b | |
| GOG-132 (1992–1994) | Paclitaxel (135 mg/m2, 24 h) and cisplatin (75 mg/m2) | 201 | 14.2 | 26.6 |
| Cisplatin (100 mg/m2) | 200 | 16.4 | 30.2 | |
| Paclitaxel (200 mg/m2, 24 h) | 213 | 11.2b | 26 | |
| MRC-ICON3[ |
Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2, 3 h) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) | 478 | 17.3 | 36.1 |
| Carboplatin (AUC, 6) | 943 | 16.1 | 35.4 | |
| Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2, 3 h) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) | 232 | 17 | 40 | |
| Cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m2) and doxorubicin (50 mg/m2) and cisplatin (50 mg/m2) | 421 | 17 | 40 | |
| GOG-158 (1995–1998)c | Paclitaxel (135 mg/m2, 24 h) and cisplatin (75 mg/m2)d | 425 | 14.5 | 48 |
| Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2, 3 h) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) | 415 | 15.5 | 52 | |
| JGOG-3016 (2002–2004)e | Paclitaxel (180 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 6)d | 319 | 17.5 | 62.2 |
| Paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) | 312 | 28.5 | 100.5 | |
| MITO-7[ |
Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 6)d | 404 | 17.3 | NR |
| Paclitaxel (60 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) | 406 | 18.3 | NR | |
| GOG-0262[ |
Paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) plus optional bevacizumab cycles 2–6, and every 3 wk until progression | 346 | 14.7 | Est 42 |
| Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) (× 6 cycles) plus optional bevacizumab cycles 2–6, and every 3 wk until progression | 346 | 14.0 | Est 42 | |
| GOG-218 | Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) (× 6 cycles) and placebo cycles 2–22 | 625 | 10.3 | 39.3 |
| Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) (× 6 cycles) and bevacizumab cycles 2–6, and placebo cycles 7–22 | 625 | 11.2 | 38.7 | |
| Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 6) (× 6 cycles) and bevacizumab cycles 2–22 | 623 | 14.1 | 39.7 | |
| ICON7[ |
Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 5 or 6) and bevacizumab (7.5 mg/kg) (× 6 cycles) and bevacizumab alone cycles 7–18 | 764 | 19.0 | 45.5 |
| Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 5 or 6) (× 6 cycles) | 764 | 17.3 | 44.6 | |
| ICON8[ |
Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) and carboplatin (AUC, 5 or 6) (× 6 cycles) | 522 | 17.5 | 47.4f |
| Paclitaxel (80 mg/m2 weekly) and carboplatin (AUC, 5 or 4) (× 6 cycles) | 523 | 20.1 | 54.8f | |
| Paclitaxel (80 mg/m2 weekly) and carboplatin (AUC, 2 weekly) (× 6 cycles) | 521 | 20.1 | 53.4f | |
Surgery before or after platinum-based chemotherapy and/or additional consolidation therapy
The pharmacological basis for the delivery of anticancer drugs by the IP route was established in the late 1970s and early 1980s. When several drugs were studied, mostly in the setting of measurable residual disease at reassessment after patients had received their initial chemotherapy, cisplatin alone and in combination received the most attention. Favorable outcomes from IP cisplatin were most often seen when tumors had shown responsiveness to platinum therapy and with small-volume tumors (usually defined as tumors <1 cm).[
In the 1990s, randomized trials were conducted to evaluate whether the IP route would prove superior to the IV route. IP cisplatin was the common denominator of these randomized trials.
Evidence (surgery followed by IP chemotherapy):
- The use of IP cisplatin as part of the initial approach in patients with stage III optimally debulked ovarian cancer is supported principally by the results of three randomized clinical trials (SWOG-8501, GOG-0114, and GOG-0172 [NCT00003322]).[
8 ,36 ,37 ] These studies tested the role of IP drugs (IP cisplatin in all three studies and IP paclitaxel in the last study) against the standard IV regimen.- In the three studies, superior PFS and OS favoring the IP arm were documented.
Specifically, the most recent study, GOG-0172, demonstrated the following results:[
8 ][Level of evidence A1]- A median survival of 66 months for patients on the IP arm versus 50 months for patients who received IV administration of cisplatin and paclitaxel (P = .03).
- Toxic effects were greater in the IP arm because of the cisplatin dose per cycle (100 mg/m2); sensory neuropathy resulted from the additional IP chemotherapy and from the systemic administration of paclitaxel.
- The rate of completion of six cycles of treatment was also less frequent in the IP arm (42% vs. 83%) because of the toxic effects and catheter-related problems.
An updated combined analysis of GOG-0114 and GOG-0172 included 876 patients with a median follow-up of 10.7 years and reported the following results:[
38 ]- Median survival with IP therapy was 61.8 months (95% CI, 55.5–69.5) compared with 51.4 months (95% CI, 46.0–58.2) for IV therapy.
- IP therapy was associated with a 23% decreased risk of death (adjusted hazard ratio [AHR], 0.77; 95% CI, 0.65–0.90; P = .002).
- IP therapy improved the survival of patients with gross residual (≤1 cm) disease (AHR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.62–0.92; P = .006).
- Risk of death decreased by 12% for each cycle of IP chemotherapy completed (AHR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.83–0.94; P < .001).
- Factors associated with poorer survival included clear and mucinous versus serous histology (AHR, 2.79; 95% CI, 1.83–4.24; P < .001), gross residual versus no visible disease (AHR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.48–2.43; P < .001), and fewer versus more cycles of IP chemotherapy (AHR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.83–0.94; P < .001).
- Younger patients were more likely to complete the IP regimen, with a 5% decrease in probability of completion with each year of age (odds ratio, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.93–0.96; P < .001).
- A Cochrane-sponsored meta-analysis of all randomized IP-versus-IV trials showed an HR of 0.79 for disease-free survival and 0.79 for OS, favoring the IP arms.[
39 ] - In another meta-analysis of seven randomized trials assessing IP versus systemic chemotherapy conducted by Cancer Care of Ontario, the relative ratio (RR) of disease progression at 5 years based on the three trials that reported this end point was 0.91 (95% CI, 0.85–0.98), and the RR of death at 5 years based on six trials was 0.88 (95% CI, 0.81–0.95) for the IP route.[
40 ] - In the subsequent IP trial (GOG-252), modifications of the IP regimen used in GOG-0172 were made to improve its tolerability (e.g., to reduce by ≥25% the total 3-hour amount of cisplatin given; and, to shift from the less practical 24-hour IV administration of paclitaxel to a 3-hour IV administration).[
41 ]In this study, 1,560 patients were randomly assigned to receive six cycles of IV paclitaxel (80 mg/m2 once per week with IV carboplatin [AUC, 6] every 3 weeks) versus IV paclitaxel (80 mg/m2 once per week with IP carboplatin [AUC, 6] [the IP carboplatin arm]) versus once-every-3-weeks IV paclitaxel (135 mg/m2 over 3 hours on day 1, IP cisplatin 75 mg/m2 on day 2, and IP paclitaxel 60 mg/m2 on day 8 [the IP cisplatin arm]). The last regimen was the modified IP superior arm of GOG-0172. All participants received bevacizumab (15 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks in cycles 2−22) and bevacizumab (15 mg/kg every 3 weeks) was added to all three arms.
- The median PFS duration was 24.9 months in the IV carboplatin arm, 27.4 months in the IP carboplatin arm, and 26.2 months in the IP cisplatin arm.
- For the subgroup of 1,380 patients with stage II/III and residual disease of 1 cm or less, the median PFS was 26.9 months in the IV carboplatin arm, 28.7 months in the IP carboplatin arm, and 27.8 months in the IP cisplatin arm.
- The median PFS for patients with stage II/III disease and no residual tumor was 35.9, 38.8, and 35.5 months, respectively.
- The median OS for all enrolled patients was 75.5, 78.9, and 72.9 months, respectively; the median OS for patients with stage II/III disease with no gross residual tumor was 98.8 months, 104.8 months, and not reached, respectively.
- This study concluded that, compared with the IV carboplatin reference arm, PFS was not significantly increased with either IP regimen when combined with bevacizumab.[
41 ][Level of evidence B1]
Surgery before or after platinum-based chemotherapy and the addition of bevacizumab to induction and/or consolidation therapy
Two phase III studies compared the outcome of standard primary cytoreductive surgery with that of neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by interval cytoreductive surgery; both studies (described below) demonstrated that PFS and OS were noninferior with the use of primary cytoreductive surgery.[
Evidence (chemotherapy followed by surgery):
- Between 1998 and 2006, a study led by the European Organisation for the Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Gynecological Cancer Group, together with the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (EORTC-55971 [NCT00003636]), included 670 women with stages IIIC and IV ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, and PPC.[
42 ][Level of evidence A1] The women were randomly assigned to undergo primary debulking surgery followed by at least six courses of platinum-based chemotherapy or to receive three courses of neoadjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy followed by interval debulking surgery, and at least three more courses of platinum-based chemotherapy.Methods included efforts to ensure accuracy of diagnosis (e.g., rule out peritoneal carcinomatosis of gastrointestinal origin) and stratification by largest preoperative tumor size (excluding ovaries) (<5 cm, >5 cm–10 cm, >10 cm–20 cm, or >20 cm). Other stratification factors included institution, method of biopsy (i.e., image-guided, laparoscopy, laparotomy, or fine-needle aspiration), and tumor stage (i.e., stage IIIC or IV). The primary end point of the study was OS, with primary debulking surgery considered the standard.[
42 ][Level of evidence A1]- Median OS for primary debulking surgery was 29 months, compared with 30 months for patients assigned to neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
- The HRdeath in the group assigned to neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by interval debulking, as compared with the group assigned to primary debulking surgery followed by chemotherapy, was 0.98 (90% CI, 0.84–1.13; P = .01 for noninferiority).[
42 ][Level of evidence A1] - Perioperative and postoperative morbidity and mortality were higher in the primary debulking surgery group (7.4% severe hemorrhage and 2.5% deaths, compared with 4.1% severe hemorrhage and 0.7% deaths in the neoadjuvant group).
- The strongest independent predictor of prolonged survival was the absence of residual tumor after surgery.
- The subset of patients achieving optimal cytoreduction (≤1 cm residuum), whether after primary debulking surgery or after neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by interval debulking surgery, had the best median OS.
- Between 2004 and 2010, a group of 87 hospitals in the United Kingdom and New Zealand enrolled 550 women with stage III or IV ovarian epithelial cancer and randomly assigned them to undergo primary cytoreductive surgery followed by six cycles of chemotherapy or primary (neoadjuvant) chemotherapy for three cycles, followed by surgery and three additional cycles of chemotherapy. In contrast to the EORTC study, the chemotherapy consisted of conventional carboplatin (AUC, 5 or AUC, 6) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2, in 76% of patients), or carboplatin alone (23% of patients), or nonpaclitaxel chemotherapy (1% of patients).[
43 ][Level of evidence A1]A minimization method was used to randomly assign patients in a 1:1 ratio.[
44 ] Participants were stratified by randomizing center, largest radiological tumor, and prespecified chemotherapy regimen. The primary end point was to establish noninferiority, with the upper bound of a one-sided 90% CI for the HRdeath at less than 1.18.- As of 2014, 451 deaths had occurred, and the HRdeath favored neoadjuvant chemotherapy, with the upper bound of the one-sided 90% CI of 0.98 (95% CI, 0.72‒1.05).
- The most common grade 3 or 4 postoperative adverse event was hemorrhage in both groups, with 8 women (3%) having this problem with primary cytoreductive surgery versus 14 (6%) in the neoadjuvant chemotherapy group. Grade 3 and 4 toxic events from chemotherapy occurred in 110 (49%) of 225 women randomly assigned to primary cytoreductive surgery and in 102 (40%) of the 253 women receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy, with one fatal event of neutropenic sepsis occurring in the primary chemotherapy group.
These studies and additional observational and partially published phase III studies have led to the publication of a Clinical Practice Guideline on behalf of the Society of Gynecologic Oncology and the American Society of Clinical Oncology.[
Two phase III trials (GOG-0218 [NCT00262847] and ICON7 [NCT00483782]) have evaluated the role of bevacizumab in first-line therapy for ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, and PPC after surgical cytoreduction.[
Evidence (surgery followed by chemotherapy and bevacizumab):
- GOG-0218 was a double-blinded, randomized, controlled trial that included 1,873 women with stage III or IV disease, all of whom received chemotherapy—carboplatin (AUC, 6) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 for six cycles). Forty percent of the women had suboptimally resected stage III disease, and 26% had stage IV disease. The primary end point of the study was PFS.[
46 ][Level of evidence B1] Participants were randomly assigned to receive one of the following regimens:- Chemotherapy plus placebo (cycles 2–22) (the control group).
- Chemotherapy plus bevacizumab (15 mg/kg cycles 2–6), followed by placebo (cycles 7–22) (the bevacizumab-initiation group).
- Chemotherapy plus bevacizumab (15 mg/kg cycles 2–22) (the bevacizumab-throughout group).
The trial demonstrated the following results:
- There was no difference in PFS between the control group and the bevacizumab-initiation group.
- There was a statistically significant increase in PFS in the bevacizumab-throughout group when compared with the control group (14.1 months vs. 10.3 months), with an HRdisease progression ordeath of 0.717 in the bevacizumab-throughout group (95% CI, 0.625–0.824; P < .001).
- The median OS was 39.3 months for the control group, 38.7 months for the bevacizumab-initiation group, and 39.7 months for the bevacizumab-throughout group.
- Quality of life was not different between the three groups. Hypertension of grade 2 or higher was more common with bevacizumab than with placebo.
- There were more treatment-related deaths in the bevacizumab-throughout arm (10 of 607, 2.3%) than in the control arm (6 of 601, 1.0%).
- ICON7 randomly assigned 1,528 women after initial surgery to chemotherapy—carboplatin (AUC, 5 or 6) plus paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 for six cycles)—or to chemotherapy plus bevacizumab (7.5 mg/kg for six cycles), followed by bevacizumab alone for an additional 12 cycles. Nine percent of patients had early-stage, high-grade tumors; 70% had stage IIIC or IV disease; and 26% had more than 1 cm of residual tumor before initiating chemotherapy. PFS was the main outcome measure.[
47 ][Level of evidence B1]- The median PFS was 17.3 months in the control group and 19 months in the bevacizumab group. HRdisease progression ordeath in the bevacizumab group was 0.81 (95% CI, 0.70–0.94; P = .004).
- Grade 3 or higher adverse events were more common in the bevacizumab group, with an increase in bleeding, hypertension (grade 2 or higher), thromboembolic events (grade 3 or higher), and gastrointestinal perforations.
- Quality of life was not different between the two groups.
- In 2015, the ICON7 authors reported an updated survival analysis.[
34 ]- There was no significant difference with 44.6 months (95% CI, 43.2–45.9) in patients on standard chemotherapy versus 45.5 months (44.2–46.7) in patients receiving bevacizumab with the chemotherapy induction, and then completing 1 year of bevacizumab maintenance (log-rank P = .85).
Supported by these two studies, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved bevacizumab in the first-line setting, both during induction and as consolidation therapy. Bevacizumab had first gained approval in the platinum-resistant setting (AURELIA trial [NCT00976911]).
Surgery after platinum-based chemotherapy and the addition of HIPEC
Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) is another pharmacological-based modality to enhance the antitumor effects via direct drug delivery to peritoneal surfaces. It was initially tested against mucinous tumors of gastrointestinal origin.[
Experience with HIPEC spans more than two decades after initial publications that have since been summarized.[
Evidence (surgery after platinum-based chemotherapy and the addition of HIPEC):
- The final results of a phase III, open-label, Dutch study (NCT00426257) have been published. The study was performed in eight hospitals and included 245 patients with newly diagnosed ovarian cancer who were at least stable after receiving three cycles of carboplatin (AUC, 5–6) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2), both of which were given by IV every 3 weeks.[
50 ] Randomization took place at the time of surgery, and patients were assigned to undergo either cytoreductive surgery without HIPEC (n = 123) or with HIPEC (n = 122). HIPEC consisted of perfusion of the abdominal cavity with cisplatin (100 mg/m2) in heated saline at 40°C (104°F) that was maintained for 60 minutes. Sodium thiosulfate was given at the start of the perfusion as an IV bolus (9 g/m2 in 200 mL) followed by continuous infusion IV (12 g/m2 in 1L) for 6 hours.[51 ] All patients subsequently received three additional cycles of IV chemotherapy. Only two patients received first-line PARP inhibitors for maintenance. The final survival analysis was reported with a median follow-up of 10 years.[52 ]- The median OS was 33.3 months for patients in the surgery-alone group and 44.9 months for patients in the HIPEC group (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.53–0.92).[
51 ][Level of evidence A1] - The median recurrence-free survival was 10.7 months for patients in the surgery-alone group and 14.3 months for patients in the HIPEC group (HR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.48–0.83).
- An exploratory analysis suggested patients without germline or somatic BRCA pathogenic variants had a better disease response to HIPEC. The effect was most pronounced for patients with BRCA wild-type tumors who were found to be homologous recombination deficient (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.20–0.85).
- The median OS was 33.3 months for patients in the surgery-alone group and 44.9 months for patients in the HIPEC group (HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.53–0.92).[
In institutions that have experience performing HIPEC, adverse events were comparable between women who did and did not receive HIPEC during interval debulking surgery. Patients in the HIPEC group had higher incidences of ileus (3% vs. 8%), fever (8% vs. 12%), and thromboembolic events (2% vs. 6%), but the rates of electrolyte changes (5% vs. 6%) and neuropathy (27% vs. 31%) were similar between the HIPEC and the surgery-only groups. The use of sodium thiosulfate was mandatory as part of HIPEC protocol in a published phase I trial.[
Surgery before or after platinum-based chemotherapy and the addition of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors to induction and/or consolidation therapy
PARP is a family of enzymes involved in base-excision repair of DNA single-strand breaks. In patients with homologous recombination deficiency, including patients with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 pathogenic variants or with nongermline homologous recombination deficiency–positive tumors, the inhibition of PARP results in the production of double-strand breaks of DNA. Human DNA repair mechanisms largely rely on one intact copy of the gene. Cells with a double-strand break are usually targeted for cell death. This susceptibility of BRCA-deficient or BRCA-altered cells to PARP inhibition,[
Evidence (surgery before or after chemotherapy and PARP inhibitors):
- A double-blind phase III trial (SOLO-1) (NCT01844986) compared maintenance olaparib (300 mg tablets bid) with a placebo. Enrolled patients had newly diagnosed, high-grade serous or endometrioid advanced ovarian cancer with variants of BRCA1, BRCA2, or both, who had a complete or partial clinical response after platinum-based chemotherapy.[
56 ] The study of 391 randomly assigned patients ran from 2013 to 2015. Of those patients, 260 were assigned to receive olaparib, and 131 patients were assigned to receive a placebo. All but three patients had germline pathogenic variants in BRCA1 (n = 191) or BRCA2 (n = 66). The analysis of the primary end point was stopped after 2 years if there was no evidence of disease or was continued until investigator-assessed disease progression. Patients with partial responses at 2 years were permitted to receive the intervention in a blinded manner. Crossover was not specified, but after discontinuation, patients could receive treatments at the discretion of the investigator. The primary end point was PFS, which was defined as from the time of randomization to objective disease progression on imaging (q 12 weeks up to 3 years), or death from any cause.- After a median follow-up of 41 months, the risk of disease progression or death was 70% lower with olaparib than with a placebo (Kaplan-Meier estimates of PFS at 3 years, 60% vs. 27%; HR, 0.3; 95% CI, 0.23–0.41; P < .001).
- Grades 3 and 4 adverse events were present in 39% of the patients who received olaparib versus 18% who received a placebo. The most common events with olaparib were fatigue, vomiting, and anemia. Drug discontinuation occurred in 12% of the patients who received olaparib versus 2% who received a placebo.
- No significant changes in quality of life occurred in either group.[
56 ][Level of evidence B1] - The results of an updated analysis indicated that the risk of disease progression or death was reduced as follows:[
57 ]- By 69% with olaparib (HR, 0.31; 95% CI, 0.21–0.46) compared with 63% with placebo (HR, 0.37; 95% CI, 0.24–0.58) in patients undergoing up-front or interval surgery;
- By 56% with olaparib (HR, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.25–0.77) compared with 67% with placebo (HR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.23–0.46) in patients with residual or no residual disease after surgery;
- By 66% with olaparib (HR, 0.34; 95% CI, 0.24–0.47) compared with 69% with placebo (HR, 0.31; 95% CI, 0.18–0.52) in women with clinical complete response or partial response at baseline; and
- By 59% with olaparib (HR, 0.41; 95% CI, 0.30–0.56) compared with 80% with placebo (HR, 0.20; 95% CI, 0.10–0.37) in patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants.
- A double-blind phase III trial (PRIMA [NCT02655016]) compared maintenance niraparib (300 mg tablets once daily and later amended to 200 mg in women <77 kg and/or baseline platelet count <150,000/µL) versus placebo in patients with high-grade serous ovarian cancer before the last cycle of platinum-based chemotherapy.[
58 ] Homologous recombination deficiency as determined by myChoice (Myriad) was present in 50.9% of patients. In a 2:1 randomization (niraparib, n = 487; placebo, n = 246), patients were assigned for comparison of primary end points of PFS for homologous recombination deficiency (50.9%) and for the overall population.- At a median follow-up of 13.8 months, the risk of progression in the homologous recombination deficiency population had an HR of 0.43 (95% CI, 0.31−0.59; P < .001) corresponding to a median PFS of 21.9 months versus 10.4 months favoring the drug compared with the placebo. In the overall population selected for this trial, the HR was 0.62, which corresponded to a median PFS of 13.8 months versus 8.2 months (95% CI, 0.50−0.76; P < .001).
- Grade 3 or higher adverse events, none fatal, consisted of anemia in 31% of patients, thrombocytopenia in 28.7% of patients, and neutropenia in 12.8% of patients; 58 of 307 discontinuations of niraparib were caused by adverse events versus 5 of 175 discontinuations of the placebo.
- VELIA/GOG-3005 (NCT02470585), a phase III placebo-controlled study, assessed the efficacy of oral veliparib added to first-line induction chemotherapy with carboplatin/paclitaxel and continued as maintenance chemotherapy.[
59 ] The study randomly assigned 1,140 patients in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive chemotherapy plus placebo followed by placebo maintenance, chemotherapy plus veliparib followed by placebo maintenance, and chemotherapy plus veliparib induction and maintenance (labeled as ‘veliparib throughout'). Doses of veliparib were 150 mg twice daily during induction, and patients who completed six cycles without progression received single-agent veliparib (or matching placebo) at 300 mg twice daily for 2 weeks (labeled as the transition period), and if no dose-limiting side effects were noted, escalated to 400 mg twice daily for an additional 30 cycles of 3 weeks of oral drug. The study accrued patients from 2015 to 2017, and the data was analyzed at a median follow-up of 28 months. As in the PRIMA study above, efficacy analyses were performed in three sequential inclusive populations: 1) the BRCA variant cohort, 2) the homologous recombination deficiency cohort (that included the preceding cohort), and 3) the intention-to-treat population.- At a median follow-up of 28 months, the BRCA variant cohort experienced a PFS of 34.7 months with veliparib throughout versus 22.0 months in the chemotherapy-only arm (induction veliparib added without veliparib maintenance was not compared). This corresponded to an HR of 0.44 (95% CI, 0.28−0.68; P < .001).
- For the homologous recombination deficiency population, PFS occurred at a median of 31.9 months for the veliparib throughout arm versus 20.5 months for the chemotherapy-alone arm, with an HR of 0.57 (95% CI, 0.43−0.76; P < .001).
- In the overall population selected, the median PFS was 23.5 months for the veliparib throughout arm versus 17.3 months for the chemotherapy-alone arm, corresponding to an HR of 0.68 (95% CI, 0.56−0.83; P < .001).
- Veliparib contributed to a higher rate of anemia and thrombocytopenia when combined with chemotherapy, and contributed overall to nausea and fatigue. Adverse events unrelated to progression during the maintenance phase led to drug discontinuation in 82 patients. Forty of 377 patients going onto maintenance therapy in the veliparib throughout cohort withdrew consent for the trial drug, 22 patients in the chemotherapy-plus-placebo cohort of 371 patients withdrew consent for the trial drug, and 24 patients in the veliparib only as maintenance (not further analyzed in the comparisons) cohort of 383 patients withdrew consent for the trial drug.
- PAOLA1 (NCT02477644), a placebo-controlled trial, compared first-line chemotherapy with carboplatin/paclitaxel followed by bevacizumab maintenance for 2 years, to the inclusion of olaparib versus placebo in the maintenance phase.[
60 ] This study included 537 patients who were assessed for BRCA variants (including somatic variants) and a nonhomologous recombination deficiency cohort.- PFS in the 29% of patients with BRCA variants was 37.2 months for bevacizumab-plus-olaparib group versus 21.7 months for the bevacizumab-alone maintenance group, which corresponded to an HR of 0.31.
- For the non-BRCA population, the HR was 0.71, which corresponded to a median PFS of 18.9 months versus 16.0 months.
- For the overall population, the HR was 0.59, which corresponded to a PFS of 22.1 months for the bevacizumab-plus-olaparib group versus 16.6 months for the bevacizumab-alone maintenance group.
Other consolidation and/or maintenance therapy trials
Phase III trials of consolidation and/or maintenance therapy have been carried out with cytotoxic drugs, small molecules,[
Evidence (other consolidation and/or maintenance therapy):
- The JAVELIN OVARIAN 100 study (NCT02718417) was the first published randomized trial of a checkpoint inhibitor (avelumab, an anti–programmed death-ligand 1 [PD-L1] antibody) in patients with previously untreated epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or peritoneal cancer.[
66 ] Between May 2016 and January 2018, 998 patients were randomly assigned to receive either chemotherapy plus avelumab induction followed by avelumab maintenance (n = 331); chemotherapy followed by avelumab maintenance (n = 332); or chemotherapy followed by observation (n = 335).- The study was terminated at interim analysis for futility of reaching the primary end point of improved PFS.
- More patients in the avelumab arms discontinued study treatment and experienced grade 3 to 5 serious adverse events than patients in the chemotherapy-alone arm.
- IMagyn050 (NCT03038100) was a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized phase III trial of platinum-based chemotherapy and bevacizumab with or without atezolizumab, an anti–PD-L1 antibody. The study reported negative results in the first-line arms for patients who received atezolizumab.[
67 ]
Treatment options under clinical evaluation
Trials are ongoing with antiangiogenic drugs (other than bevacizumab) and with PARP inhibitors. PARP is a family of enzymes involved in base-excision repair of DNA single-strand breaks. In patients with homologous recombination deficiency, including patients with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 pathogenic variants or with nongermline homologous recombination deficiency–positive tumors, inhibition of PARP results in production of double-strand breaks of DNA. Human DNA repair mechanisms largely rely on one intact copy of the gene; cells with a double-strand break are usually targeted for cell death. This susceptibility of BRCA-deficient or BRCA-altered cells to PARP inhibition [
Information about ongoing clinical trials is available from the
Current Clinical Trials
Use our
References:
- Paoletti X, Lewsley LA, Daniele G, et al.: Assessment of Progression-Free Survival as a Surrogate End Point of Overall Survival in First-Line Treatment of Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 3 (1): e1918939, 2020.
- Hoskins WJ: Surgical staging and cytoreductive surgery of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer 71 (4 Suppl): 1534-40, 1993.
- Hoskins WJ, Bundy BN, Thigpen JT, et al.: The influence of cytoreductive surgery on recurrence-free interval and survival in small-volume stage III epithelial ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Gynecol Oncol 47 (2): 159-66, 1992.
- Hoskins WJ, McGuire WP, Brady MF, et al.: The effect of diameter of largest residual disease on survival after primary cytoreductive surgery in patients with suboptimal residual epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol 170 (4): 974-9; discussion 979-80, 1994.
- Bristow RE, Tomacruz RS, Armstrong DK, et al.: Survival effect of maximal cytoreductive surgery for advanced ovarian carcinoma during the platinum era: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 20 (5): 1248-59, 2002.
- Horowitz NS, Miller A, Rungruang B, et al.: Does aggressive surgery improve outcomes? Interaction between preoperative disease burden and complex surgery in patients with advanced-stage ovarian cancer: an analysis of GOG 182. J Clin Oncol 33 (8): 937-43, 2015.
- Omura GA, Brady MF, Homesley HD, et al.: Long-term follow-up and prognostic factor analysis in advanced ovarian carcinoma: the Gynecologic Oncology Group experience. J Clin Oncol 9 (7): 1138-50, 1991.
- Armstrong DK, Bundy B, Wenzel L, et al.: Intraperitoneal cisplatin and paclitaxel in ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 354 (1): 34-43, 2006.
- Markman M, Reichman B, Hakes T, et al.: Impact on survival of surgically defined favorable responses to salvage intraperitoneal chemotherapy in small-volume residual ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 10 (9): 1479-84, 1992.
- Markman M: Intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Semin Oncol 18 (3): 248-54, 1991.
- Levin L, Simon R, Hryniuk W: Importance of multiagent chemotherapy regimens in ovarian carcinoma: dose intensity analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 85 (21): 1732-42, 1993.
- McGuire WP, Hoskins WJ, Brady MF, et al.: Assessment of dose-intensive therapy in suboptimally debulked ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 13 (7): 1589-99, 1995.
- Bolis G, Favalli G, Danese S, et al.: Weekly cisplatin given for 2 months versus cisplatin plus cyclophosphamide given for 5 months after cytoreductive surgery for advanced ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 15 (5): 1938-44, 1997.
- Alberts DS, Green S, Hannigan EV, et al.: Improved therapeutic index of carboplatin plus cyclophosphamide versus cisplatin plus cyclophosphamide: final report by the Southwest Oncology Group of a phase III randomized trial in stages III and IV ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 10 (5): 706-17, 1992.
- du Bois A, Lück HJ, Meier W, et al.: A randomized clinical trial of cisplatin/paclitaxel versus carboplatin/paclitaxel as first-line treatment of ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95 (17): 1320-9, 2003.
- Neijt JP, Engelholm SA, Tuxen MK, et al.: Exploratory phase III study of paclitaxel and cisplatin versus paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 18 (17): 3084-92, 2000.
- Muggia FM, Braly PS, Brady MF, et al.: Phase III randomized study of cisplatin versus paclitaxel versus cisplatin and paclitaxel in patients with suboptimal stage III or IV ovarian cancer: a gynecologic oncology group study. J Clin Oncol 18 (1): 106-15, 2000.
- The International Collaborative Ovarian Neoplasm Group: Paclitaxel plus carboplatin versus standard chemotherapy with either single-agent carboplatin or cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in women with ovarian cancer: the ICON3 randomised trial. Lancet 360 (9332): 505-15, 2002.
- Ozols RF, Bundy BN, Greer BE, et al.: Phase III trial of carboplatin and paclitaxel compared with cisplatin and paclitaxel in patients with optimally resected stage III ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 21 (17): 3194-200, 2003.
- Vasey PA, Jayson GC, Gordon A, et al.: Phase III randomized trial of docetaxel-carboplatin versus paclitaxel-carboplatin as first-line chemotherapy for ovarian carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 96 (22): 1682-91, 2004.
- Kristensen GB, Vergote I, Stuart G, et al.: First-line treatment of ovarian cancer FIGO stages IIb-IV with paclitaxel/epirubicin/carboplatin versus paclitaxel/carboplatin. Int J Gynecol Cancer 13 (Suppl 2): 172-7, 2003 Nov-Dec.
- Bookman MA, Brady MF, McGuire WP, et al.: Evaluation of new platinum-based treatment regimens in advanced-stage ovarian cancer: a Phase III Trial of the Gynecologic Cancer Intergroup. J Clin Oncol 27 (9): 1419-25, 2009.
- Hoskins PJ: Triple cytotoxic therapy for advanced ovarian cancer: a failed application, not a failed strategy. J Clin Oncol 27 (9): 1355-8, 2009.
- Katsumata N, Yasuda M, Takahashi F, et al.: Dose-dense paclitaxel once a week in combination with carboplatin every 3 weeks for advanced ovarian cancer: a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 374 (9698): 1331-8, 2009.
- Katsumata N, Yasuda M, Isonishi S, et al.: Long-term results of dose-dense paclitaxel and carboplatin versus conventional paclitaxel and carboplatin for treatment of advanced epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer (JGOG 3016): a randomised, controlled, open-label trial. Lancet Oncol 14 (10): 1020-6, 2013.
- Harano K, Terauchi F, Katsumata N, et al.: Quality-of-life outcomes from a randomized phase III trial of dose-dense weekly paclitaxel and carboplatin compared with conventional paclitaxel and carboplatin as a first-line treatment for stage II-IV ovarian cancer: Japanese Gynecologic Oncology Group Trial (JGOG3016). Ann Oncol 25 (1): 251-7, 2014.
- Pignata S, Scambia G, Katsaros D, et al.: Carboplatin plus paclitaxel once a week versus every 3 weeks in patients with advanced ovarian cancer (MITO-7): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 15 (4): 396-405, 2014.
- Chan JK, Brady MF, Penson RT, et al.: Weekly vs. Every-3-Week Paclitaxel and Carboplatin for Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med 374 (8): 738-48, 2016.
- Clamp AR, James EC, McNeish IA, et al.: Weekly dose-dense chemotherapy in first-line epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal carcinoma treatment (ICON8): primary progression free survival analysis results from a GCIG phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 394 (10214): 2084-2095, 2019.
- Blagden SP, Cook AD, Poole C, et al.: Weekly platinum-based chemotherapy versus 3-weekly platinum-based chemotherapy for newly diagnosed ovarian cancer (ICON8): quality-of-life results of a phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 21 (7): 969-977, 2020.
- Clamp AR, James EC, McNeish IA, et al.: Weekly dose-dense chemotherapy in first-line epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer treatment (ICON8): overall survival results from an open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 23 (7): 919-930, 2022.
- McGuire WP, Hoskins WJ, Brady MF, et al.: Cyclophosphamide and cisplatin compared with paclitaxel and cisplatin in patients with stage III and stage IV ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 334 (1): 1-6, 1996.
- Mahner S, Burges A: Quality of life as a primary endpoint in ovarian cancer trials. Lancet Oncol 15 (4): 363-4, 2014.
- Oza AM, Cook AD, Pfisterer J, et al.: Standard chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for women with newly diagnosed ovarian cancer (ICON7): overall survival results of a phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 16 (8): 928-36, 2015.
- Howell SB, Zimm S, Markman M, et al.: Long-term survival of advanced refractory ovarian carcinoma patients with small-volume disease treated with intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 5 (10): 1607-12, 1987.
- Alberts DS, Liu PY, Hannigan EV, et al.: Intraperitoneal cisplatin plus intravenous cyclophosphamide versus intravenous cisplatin plus intravenous cyclophosphamide for stage III ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 335 (26): 1950-5, 1996.
- Markman M, Bundy BN, Alberts DS, et al.: Phase III trial of standard-dose intravenous cisplatin plus paclitaxel versus moderately high-dose carboplatin followed by intravenous paclitaxel and intraperitoneal cisplatin in small-volume stage III ovarian carcinoma: an intergroup study of the Gynecologic Oncology Group, Southwestern Oncology Group, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 19 (4): 1001-7, 2001.
- Tewari D, Java JJ, Salani R, et al.: Long-term survival advantage and prognostic factors associated with intraperitoneal chemotherapy treatment in advanced ovarian cancer: a gynecologic oncology group study. J Clin Oncol 33 (13): 1460-6, 2015.
- Jaaback K, Johnson N: Intraperitoneal chemotherapy for the initial management of primary epithelial ovarian cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1): CD005340, 2006.
- Elit L, Oliver TK, Covens A, et al.: Intraperitoneal chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of women with stage III epithelial ovarian cancer: a systematic review with metaanalyses. Cancer 109 (4): 692-702, 2007.
- Walker JL, Brady MF, Wenzel L, et al.: Randomized Trial of Intravenous Versus Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy Plus Bevacizumab in Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma: An NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol 37 (16): 1380-1390, 2019.
- Vergote I, Tropé CG, Amant F, et al.: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy or primary surgery in stage IIIC or IV ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 363 (10): 943-53, 2010.
- Kehoe S, Hook J, Nankivell M, et al.: Primary chemotherapy versus primary surgery for newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer (CHORUS): an open-label, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 386 (9990): 249-57, 2015.
- Fagotti A, Ferrandina G, Vizzielli G, et al.: Phase III randomised clinical trial comparing primary surgery versus neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer with high tumour load (SCORPION trial): Final analysis of peri-operative outcome. Eur J Cancer 59: 22-33, 2016.
- Wright AA, Bohlke K, Armstrong DK, et al.: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for newly diagnosed, advanced ovarian cancer: Society of Gynecologic Oncology and American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. Gynecol Oncol 143 (1): 3-15, 2016.
- Burger RA, Brady MF, Bookman MA, et al.: Incorporation of bevacizumab in the primary treatment of ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 365 (26): 2473-83, 2011.
- Perren TJ, Swart AM, Pfisterer J, et al.: A phase 3 trial of bevacizumab in ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 365 (26): 2484-96, 2011.
- Sugarbaker PH: Laboratory and clinical basis for hyperthermia as a component of intracavitary chemotherapy. Int J Hyperthermia 23 (5): 431-42, 2007.
- Koopman M, Antonini NF, Douma J, et al.: Sequential versus combination chemotherapy with capecitabine, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin in advanced colorectal cancer (CAIRO): a phase III randomised controlled trial. Lancet 370 (9582): 135-42, 2007.
- van Driel WJ, Koole SN, Sikorska K, et al.: Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med 378 (3): 230-240, 2018.
- Howell SB, Kirmani S, Lucas WE, et al.: A phase II trial of intraperitoneal cisplatin and etoposide for primary treatment of ovarian epithelial cancer. J Clin Oncol 8 (1): 137-45, 1990.
- Aronson SL, Lopez-Yurda M, Koole SN, et al.: Cytoreductive surgery with or without hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in patients with advanced ovarian cancer (OVHIPEC-1): final survival analysis of a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 24 (10): 1109-1118, 2023.
- Zivanovic O, Abramian A, Kullmann M, et al.: HIPEC ROC I: a phase I study of cisplatin administered as hyperthermic intraoperative intraperitoneal chemoperfusion followed by postoperative intravenous platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with platinum-sensitive recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer 136 (3): 699-708, 2015.
- Bryant HE, Schultz N, Thomas HD, et al.: Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 434 (7035): 913-7, 2005.
- Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, et al.: Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 434 (7035): 917-21, 2005.
- Moore K, Colombo N, Scambia G, et al.: Maintenance Olaparib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med 379 (26): 2495-2505, 2018.
- DiSilvestro P, Colombo N, Scambia G, et al.: Efficacy of Maintenance Olaparib for Patients With Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer With a BRCA Mutation: Subgroup Analysis Findings From the SOLO1 Trial. J Clin Oncol 38 (30): 3528-3537, 2020.
- González-Martín A, Pothuri B, Vergote I, et al.: Niraparib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med 381 (25): 2391-2402, 2019.
- Coleman RL, Fleming GF, Brady MF, et al.: Veliparib with First-Line Chemotherapy and as Maintenance Therapy in Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med 381 (25): 2403-2415, 2019.
- Ray-Coquard I, Pautier P, Pignata S, et al.: Olaparib plus Bevacizumab as First-Line Maintenance in Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med 381 (25): 2416-2428, 2019.
- Vergote IB, Jimeno A, Joly F, et al.: Randomized phase III study of erlotinib versus observation in patients with no evidence of disease progression after first-line platin-based chemotherapy for ovarian carcinoma: a European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Gynaecological Cancer Group, and Gynecologic Cancer Intergroup study. J Clin Oncol 32 (4): 320-6, 2014.
- Berek JS, Taylor PT, Gordon A, et al.: Randomized, placebo-controlled study of oregovomab for consolidation of clinical remission in patients with advanced ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 22 (17): 3507-16, 2004.
- Verheijen RH, Massuger LF, Benigno BB, et al.: Phase III trial of intraperitoneal therapy with yttrium-90-labeled HMFG1 murine monoclonal antibody in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer after a surgically defined complete remission. J Clin Oncol 24 (4): 571-8, 2006.
- Markman M, Liu PY, Wilczynski S, et al.: Phase III randomized trial of 12 versus 3 months of maintenance paclitaxel in patients with advanced ovarian cancer after complete response to platinum and paclitaxel-based chemotherapy: a Southwest Oncology Group and Gynecologic Oncology Group trial. J Clin Oncol 21 (13): 2460-5, 2003.
- Pecorelli S, Favalli G, Gadducci A, et al.: Phase III trial of observation versus six courses of paclitaxel in patients with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer in complete response after six courses of paclitaxel/platinum-based chemotherapy: final results of the After-6 protocol 1. J Clin Oncol 27 (28): 4642-8, 2009.
- Monk BJ, Colombo N, Oza AM, et al.: Chemotherapy with or without avelumab followed by avelumab maintenance versus chemotherapy alone in patients with previously untreated epithelial ovarian cancer (JAVELIN Ovarian 100): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 22 (9): 1275-1289, 2021.
- Moore KN, Bookman M, Sehouli J, et al.: Atezolizumab, Bevacizumab, and Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Stage III or IV Ovarian Cancer: Placebo-Controlled Randomized Phase III Trial (IMagyn050/GOG 3015/ENGOT-OV39). J Clin Oncol 39 (17): 1842-1855, 2021.
Treatment of Recurrent or Persistent Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer
Approximately 80% of patients diagnosed with ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer (FTC), and primary peritoneal cancer (PPC) relapse after first-line platinum-based and taxane-based chemotherapy. These patients may benefit from subsequent therapies. Early detection of persistent disease by second-look laparotomies after completion of first-line treatment is no longer practiced. When the outcomes in institutions practicing such procedures (50% of institutions) were informally compared with the outcomes in institutions not using such procedures, support for second-look laparotomies decreased. This was confirmed in the Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) GOG-0158 trial.[
However, the practice of close follow-up of patients completing treatment by measuring cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) levels at intervals of 1 to 3 months was nearly universally adopted. In patients who are in clinical complete remission, increases in CA-125 from their initial treatment represent the most common method to detect disease that will eventually relapse clinically.
Treatment based on abnormal increases in CA-125 levels in the absence of symptoms or imaging evidence of disease has been addressed in a clinical trial.
Evidence (early vs. delayed initiation of treatment):
- A trial by the Medical Research Council (MRC) (MRC-OV05) and the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer examined the consequences of early treatment for an elevated CA-125 level versus treatment delayed until clinical symptoms appeared.[
2 ] Patients in clinical complete remission after platinum-based chemotherapy were registered and followed with CA-125 levels and clinical visits only. Upon detection of a twofold elevation over the normal range, patients were randomly assigned to disclosure of the result and early treatment for recurrence versus continued blinding and treatment upon development of signs and symptoms indicative of clinical relapse. The number of randomly assigned patients was to exceed 500 to yield a superior survival outcome at 2 years with early institution of therapy; this required 1,400 registrations, which were accrued between 1996 and 2005.- Among 1,442 patients, 29% continued to show no evidence of relapse; however, in 19% of patients, the CA-125 level was noninformative at clinical relapse, or a doubling occurred concurrently with clinical relapse.
- Patients had stage III and stage IV disease in 67% of the cases; however, these stages represented 80% of the patients with a twofold or higher increase in CA-125 level who subsequently were randomly assigned.
- The median survival of all patients registered was 70.8 months.
- Median survival for patients randomly assigned to early treatment (n = 265) was 25.7 months compared with 27.1 months for patients in the delayed-treatment group (n = 264) (hazard ratio [HR], 0.98; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.8–1.2).
- The median delay in instituting second-line chemotherapy was 4.8 months, and the median delay in instituting third-line chemotherapy was 4.6 months. Second-line chemotherapy treatments were comparable among the two groups (mostly platinum- and taxane-based), whereas third-line treatments were less often applied to the delayed-treatment group.
- The study concluded that there was no benefit in the detection of early presence of disease by CA-125. This finding is consistent with the failure of second-look surgeries to provide improved outcomes after early detection of persistent disease.
A quality-of-life assessment accompanying this study found a detrimental effect in the early treatment when it was compared with waiting for the development of signs and symptoms.[
The impact of these findings on CA-125 surveillance patterns over a decade in five U.S. Cancer Centers was disappointingly low.[
Treatment Options for Patients with Recurrent or Persistent Ovarian Epithelial Cancer, FTC, and PPC
Drug treatment options for patients with recurrent disease are subdivided as follows:
-
Platinum-sensitive recurrence : For patients whose disease recurs more than 6 months after cessation of the induction therapy, re-treatment with a platinum or platinum-containing combination, such as carboplatin, should be considered (seeTable 8 ). -
Platinum-refractory or platinum-resistant recurrence : For patients who progress before cessation of induction therapy (platinum refractory) or within 6 months after cessation of induction therapy (platinum resistant), platinum therapy is generally not useful as part of the treatment plan. Clinical trials should be considered.
Other agents that have shown activity in phase II trials are listed in
Cytoreduction may be used;[
The role of radiation therapy in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer has not been defined.
Platinum-sensitive recurrence
Platinum-containing chemotherapy regimens
| Eligibility (mo since end of initial therapy) | Regimen | No. of Patients | Comparator | Comments on Outcome (mo) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR = hazard ratio; No. = number; OS = overall survival; PFS = progression-free survival; PLD = pegylated liposomal doxorubicin. | ||||
| a Trabectedin has been approved for use in treating recurrent ovarian cancer in Europe and Canada. | ||||
| b OS data were not mature at the time the manuscript was published.[ |
||||
| c P< .0001. | ||||
| d P = .012. | ||||
| e HR, 0.51;P = .0001. | ||||
| Most Commonly Used | ||||
| Platinum sensitive (>6) | Cisplatin or carboplatin + paclitaxel | 802 | Single-agent nontaxane + platinum agents | PFS 11 vs. 9; OS 24 vs. 19[ |
| Platinum sensitive (>6) | Carboplatin + gemcitabine | 356 | Carboplatin | PFS 8.6 vs. 5.8; OS 18 vs. 17[ |
| Platinum sensitive (>6) | Carboplatin + PLD | 976 | Carboplatin + paclitaxel | PFS 11.3 vs. 9.4; OS 30.7 vs. 33.0[ |
| Other Regimens | ||||
| Platinum sensitive (>6) | Carboplatin + epirubicin | 190 | Carboplatin | Powered for response differences; OS 17 vs. 15[ |
| Platinum sensitive (≥12) | Cisplatin + doxorubicin + cyclophosphamide | 97 | Paclitaxel | PFS 15.7 vs. 9; OS 34.7 vs. 25.8[ |
| Platinum sensitive + resistant | PLD + trabectedina | 672 | PLD | PFS 7.3 vs. 5.8; OS 20.5 vs. 19.4b |
| Platinum sensitive | Paclitaxel + carboplatin | 674 | Paclitaxel + carboplatin + bevacizumab | PFS 10.4 vs. 13.8c; OS 37.4 vs. 42.2[ |
| Platinum sensitive | Carboplatin + PLD + bevacizumab | 682 | Carboplatin + gemcitabine + bevacizumab | PFS 12.4 vs. 11.3d, OS 31.9 vs. 27.8[ |
| Platinum sensitive | Carboplatin + paclitaxelor gemcitabineor PLD | 406 | Same doublets + bevacizumab | PFS 8.8 vs. 11.8e, deaths 68 vs. 79, OS 27.1 vs. 26.7[ |
Based on improved survival with etoposide or fluorouracil, carboplatin was approved in 1987 for the treatment of patients with ovarian cancer whose disease recurred after treatment with cisplatin.[
Oxaliplatin, initially introduced with the hope that it would overcome platinum resistance, has activity mostly in platinum-sensitive patients [
With all platinum agents, outcome is generally better the longer the initial interval without recurrence from the initial platinum-containing regimens.[
Several randomized trials have addressed whether the use of a platinum in combination with other chemotherapy agents is superior to single agents (see
Evidence (platinum in combination with other chemotherapy agents):
- In an analysis of data examining jointly the results of trials performed by the MRC/Arbeitsgemeinschaft Gynaekologische Onkologie (MRC/AGO) and the International Collaborative Ovarian Neoplasm (ICON) investigators (ICON4), the following results were observed:[
5 ,14 ][Level of evidence A1]- A platinum-plus-paclitaxel combination yielded superior response rates, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS), compared with carboplatin as a single agent or other platinum-containing combinations as controls.
- Platinum plus paclitaxel was compared with several control regimens, although 71% used carboplatin as a single agent in the control, and 80% used carboplatin plus paclitaxel. Prolonged PFS (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.66–0.89; P = .004) and OS (HR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.69–0.97; P = .023) were improved in the platinum-plus-paclitaxel arm.[
14 ]; [5 ][Level of evidence A1] - The AGO had previously compared the combination of epirubicin plus carboplatin with carboplatin alone and had not found significant differences in outcome.
- A meta-analysis of five trials (three of which are in
Table 8 ), with four reviewing independent patient data, supports the use of platinum agents in combination with other active agents rather than carboplatin alone for patients with platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer.[22 ]
- Another trial by European and Canadian groups compared gemcitabine plus carboplatin with carboplatin.
- The PFS of 8.6 months with the combination was significantly superior to 5.8 months for the carboplatin alone (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.58–0.90; P = .003).[
12 ][Level of evidence B1] - The study was not powered to detect significant differences in OS, and the median survival for both arms was 18 months (HR, 0.96; CI, 0.75–1.23; P = .73).
- The PFS of 8.6 months with the combination was significantly superior to 5.8 months for the carboplatin alone (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.58–0.90; P = .003).[
- In a phase III trial, carboplatin plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin was compared with carboplatin plus paclitaxel in patients with platinum-sensitive recurrence (>6 months). The primary end point was PFS.
- The median PFS for the carboplatin-plus-pegylated-liposomal-doxorubicin arm was 11.3 months versus 9.4 months for the carboplatin-plus-paclitaxel arm (HR, 0.823; 95% CI, 0.72–0.94; P = .005).[
23 ][Level of evidence B1] - Long-term follow-up revealed no difference in OS rates between the two arms (30.7 months for carboplatin plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin vs. 33.0 months for carboplatin plus paclitaxel).[
13 ] - The carboplatin-plus-paclitaxel arm was associated with increased severe neutropenia, alopecia, neuropathy, and allergic reaction. The carboplatin-plus-pegylated-liposomal-doxorubicin arm was associated with increased severe thrombocytopenia, nausea, and hand-foot syndrome.
Given its toxicity profile and noninferiority to the standard regimen, carboplatin plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin is an important option for patients with platinum-sensitive recurrence.
- The median PFS for the carboplatin-plus-pegylated-liposomal-doxorubicin arm was 11.3 months versus 9.4 months for the carboplatin-plus-paclitaxel arm (HR, 0.823; 95% CI, 0.72–0.94; P = .005).[
Carboplatin plus paclitaxel has been considered the standard regimen for platinum-sensitive recurrence in the absence of residual neurological toxic effects. The GOG-0213 trial is comparing this regimen with the experimental arm that adds bevacizumab to carboplatin plus paclitaxel.
Bevacizumab, other targeted drugs, and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors with or without chemotherapy
Evidence (bevacizumab with gemcitabine/carboplatin):
- The Ovarian Cancer Study Comparing Efficacy and Safety of Chemotherapy and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Platinum-Sensitive Recurrent Diseases (OCEANS [NCT00434642]) assessed the role of bevacizumab in the treatment of platinum-sensitive recurrence (see
Table 8 for other trials in this setting). In this double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial of chemotherapy (gemcitabine plus carboplatin) with or without bevacizumab for recurrent ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, or PPC, 242 patients were randomly assigned to each arm. In contrast to the first-line studies, treatment was allowed to continue beyond six cycles to ten cycles in responding patients, but there was no maintenance therapy.[24 ]- A subsequent analysis will appear when additional survival data become mature; however, at the time of publication, differences in median OS were not apparent, and crossover from a placebo to bevacizumab had occurred in 31% of the patients.
- Median PFS for patients receiving bevacizumab was 12.4 months versus 8.4 months for those receiving a placebo.
- The HR for the effect of bevacizumab on disease progression in patients assigned to the bevacizumab arm compared with placebo was 0.484 (95% CI, 0.388–0.605; P < .0001).
- Objective responses to chemotherapy were increased when combined with bevacizumab (78.5% vs. 57.4%; P < .0001).
- Bevacizumab-associated toxicities such as hypertension and proteinuria were more prominent than in the first-line trials, but feared safety issues such as gastrointestinal perforations did not occur during the study.
- Treatment discontinuation because of adverse events was more common for patients who received bevacizumab than placebo (55 vs. 12), but fewer patients discontinued treatment because of disease progression (104 vs. 160).
Evidence (bevacizumab added to carboplatin or carboplatin doublets):
- NRG Oncology Group, or National Clinical Trials Network group, a combined research effort of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project, the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group, and the GOG (GOG-0213 [NCT00565851]) assessed both the role of surgical debulking and the addition of bevacizumab induction and maintenance in women with platinum-sensitive recurrences of ovarian cancer.[
7 ][Level of evidence A1] The nonsurgical portion of GOG-0213 had 81% power for a true HR of 0.75; it enrolled 674 women from 2007 to 2011, and the published analysis took place after a median follow-up exceeding 4 years.- OS was not significantly different: 37.3 months (95% CI, 32.6–39.7) versus 42.2 months (95% CI, 37.7–46.2).
- The secondary end point of median PFS was significantly in favor of the addition of bevacizumab: 10.4 months (95% CI, 9.7–11) for chemotherapy alone versus 13.8 months (95% CI, 13.0–14.7).
- Bevacizumab (15 mg/kg q 3 weeks) with chemotherapy and its use in maintenance led to an excess of grade 3 and 4 adverse events (8% for chemotherapy alone vs. 30%), any bleeding (12% vs. 42%), and any hypertension (3% vs. 41%).
- In an open-label, randomized, phase III trial (MITO16b/MANGO-OV2/ENGOT-ov17 [NCT01802749]), investigators enrolled 406 patients at first recurrence or progression at least 6 months after receiving first-line platinum-based treatment, including bevacizumab during induction or maintenance.[
17 ] The trial compared carboplatin doublets with or without bevacizumab as standard treatment for patients with platinum-sensitive recurrence. Dosing schedules varied with each doublet and all bevacizumab was given at a dose rate of 5 mg/kg/week. Twenty-one patients received carboplatin/paclitaxel, and 22 patients received carboplatin/paclitaxel plus bevacizumab; 99 patients received cisplatin/gemcitabine, and 98 patients received cisplatin/gemcitabine plus bevacizumab; and 83 patients received pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, and 83 patients received pegylated liposomal doxorubicin plus bevacizumab. The primary end point was investigator-assessed PFS, seeking to reduce the HR for recurrence to 0.67 (90% power and two-tailed test at alpha = .05). Secondary end points were OS (from time of randomization to death from any cause) and objective response rates according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST).- Median PFS was 8.8 months (95% CI, 8.4–9.3) for patients in the standard chemotherapy arm versus 11.8 months (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 10.8–12.9) for patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm.[
17 ][Level of evidence B1] - OS was not different between the two groups: median OS was 27.1 months for patients in the standard arm versus 26.7 months for patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm.
- Objective response rate analysis determined that 71 of 143 patients in the standard arm and 90 of 130 patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm had either complete or partial responses.
- The safety population included 200 patients in the standard arm and 201 patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm. Numerous serious adverse events were recorded in both arms: 61 events for 41 patients in the standard arm and 76 events for 52 patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm.
- Hypertension was a major adverse event. In the standard arm, 93% of patients experienced hypertension: 166 patients experienced grade 1 or 2 hypertension and 20 patients experienced grade 3 hypertension. In the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm, 98% of patients experienced hypertension: 139 patients experienced grade 1 or 2 hypertension and 58 patients experienced grade 3 hypertension.
- Proteinuria and epistaxis were also prominent grade 1 or 2 adverse events for patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm.
The study demonstrated that the addition of bevacizumab improved PFS but did not result in any OS benefit and was associated with increased toxicity. This study preceded incorporation of PARP inhibitors in phase III trials for patients with platinum-sensitive recurrence. In a subset analysis of patients with BRCA variants in this study, only 23 patients in the standard arm and 30 patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm had documented deleterious variants. These details underscore the evolution of targeted treatment that has occurred during and after this study.
- Median PFS was 8.8 months (95% CI, 8.4–9.3) for patients in the standard chemotherapy arm versus 11.8 months (HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 10.8–12.9) for patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm.[
Evidence (bevacizumab plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin/carboplatin vs. bevacizumab plus gemcitabine/carboplatin):
For the results of clinical trials that used gemcitabine/carboplatin, see
Evidence (PARP inhibitors with or without antiangiogenic agents):
PARP is a family of enzymes involved in base-excision repair of DNA single-strand breaks. In patients with homologous recombination deficiency, including patients with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 pathogenic variants or with nongermline homologous recombination deficiency–positive tumors, inhibition of PARP results in production of double-strand breaks of DNA. Human DNA repair mechanisms largely rely on one intact copy of the gene; cells with a double-strand break are usually targeted for cell death. This susceptibility of BRCA-deficient or BRCA-altered cells to PARP inhibition [
| Drug | PARP−Trapping Potency | FDA-Approved Indications | Dose | Key Trials | Toxicities | Other Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AML = acute myeloid leukemia; CR = complete response; bid = twice a day; FDA = U.S. Food and Drug Administration; FTC = fallopian tube cancer; HRD = homologous recombination deficiency; MDS = myelodysplastic syndrome; PARP = poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; PO = by mouth; PPC = primary peritoneal cancer; PR = partial response. | ||||||
| Olaparib | Intermediate | Maintenance of recurrent ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, or PPC in patients with CR or PR to platinum-based chemotherapy, regardless ofBRCAstatus | 300 mg tablet bid (replacing the 400 mg capsules) | Study 19, Study 42,SOLO2(NCT01874353),SOLO1(NCT01844986) (updated October 2018), others ongoing | Nausea, fatigue, myelosuppression (especially anemia), abdominal pain; rare cases of MDS/AML | Companion diagnostic evaluating for deleterious germlineBRCAvariants when olaparib is used in treatment (not maintenance) |
| Rucaparib | Low-intermediate | Maintenance of recurrent ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, or PPC in patients with CR or PR to platinum-based chemotherapy, regardless ofBRCAstatus | 600 mg PO bid | Study 10,ARIEL2(NCT01891344),ARIEL3(NCT01968213),ARIEL4(NCT02855944) (ongoing), many others ongoing | Nausea, fatigue, elevated liver enzymes, myelosuppression (especially anemia), abdominal pain; rare cases of MDS/AML | Companion diagnostic evaluating for deleteriousBRCAvariants when rucaparib is used in treatment (not maintenance); HRD assays used, but are not yet approved for use |
| Niraparib | Intermediate-high | Maintenance of recurrent ovarian epithelial cancer, FTC, or PPC in patients with CR or PR to platinum-based chemotherapy, regardless ofBRCAstatus | 300 mg PO once daily | |
Nausea, fatigue, constipation, hypertension, myelosuppression (especially ↓ platelets); rare cases of MDS/AML | HRD assays were used in the key clinical trials, but are not yet approved for use |
| Veliparib | Low | None yet | Ongoing trials combining veliparib with chemotherapy | |||
| Talazoparib | High | None yet | Ongoing trials, some with immunotherapy | |||
- In a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled phase II trial of olaparib maintenance therapy, eligible patients had platinum-sensitive, high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Patients were randomly assigned to receive olaparib (400 mg bid) or placebo. Having germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants was not required for eligibility; however, 23% of patients in the experimental group and 22% of patients in the placebo group had known BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants. The primary end point was PFS.[
27 ][Level of evidence B1]- Median PFS was 8.4 months for patients in the olaparib arm versus 4.8 months for patients in the placebo arm (HR, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.25–0.49; P < .001).
- OS was not different between the two groups, as noted in an updated report.[
28 ] - The more common adverse events in the olaparib group were nausea, fatigue, vomiting, and anemia.
- Olaparib tablets (as opposed to the previous capsule formulation) underwent evaluation in SOLO2 (NCT01874353), a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase III trial in patients with high-grade serous or endometrioid cancer, PPC, or FTC. Patients had platinum-sensitive relapses and were preselected for BRCA1/BRCA2 variants.[
29 ][Level of evidence B1] Stratification for response (complete vs. partial) to previous platinum and platinum-free intervals (>6–12 vs. >12 months) and 2:1 random allocation to olaparib in two 150-mg twice-daily or matching placebo tablets took place. Of 295 eligible patients enrolled, 196 were assigned to olaparib, and 99 were assigned to a placebo.- The primary end point was PFS and significantly favored olaparib (19.1 months [95% CI, 16.3–25.7]) more than placebo (5.5 months [range, 5.2–5.8 months]; HR, 0.30 [95% CI, 0.22–0.41]; P < .0001).
- Serious adverse events were experienced by 18% of patients who received olaparib and by 8% who received placebo. The adverse events consisted mostly of anemia, abdominal pain, and intestinal obstruction.
- In this trial, a comprehensive assessment of health-related quality-of-life measurements was carried out in patients who received olaparib compared with patients who received placebo.[
30 ] The Trial Outcome Index score was used in a prespecified analysis of changes, showing that several measurements were met. In addition, time without significant symptoms of toxicity and quality-adjusted PFS were longer in patients who were treated with olaparib. These assessments supplement other measurements such as time to first treatment and time to subsequent therapy or death that have been sought to supplement PFS as a primary end point for drug approval.
- The SOLO3 trial [NCT00628251], a phase III study that employed 2:1 randomization, compared olaparib tablets with physicians' choice of nonplatinum chemotherapy (pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, weekly paclitaxel, gemcitabine, or topotecan) for the treatment of recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer and germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants.[
31 ] A previous randomized phase II study of dose levels of olaparib capsules at either 200 or 400 mg twice daily versus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin had failed to show an advantage over chemotherapy.[32 ] In SOLO3, 178 patients were allocated to receive olaparib and 88 patients received physicians' choice chemotherapy. The primary end point was overall response rate.- Of 151 patients assessed, 109 had objective responses to olaparib (14 complete responses), whereas of 72 patients assessed, 37 had objective responses to chemotherapy (2 complete responses).
- At final analysis, there was no significant difference in OS. The median OS was 34.9 months for patients who received olaparib and 32.9 months for patients who received chemotherapy (HR, 1.07; P = .71).[
33 ] - A subgroup analysis of patients treated with at least three lines of chemotherapy showed a survival detriment. Among these patients, the median OS was 29.9 months in the olaparib group and 39.4 months in the chemotherapy group (HR, 1.33; 95% CI, 0.84–2.18).
- Adverse events were consistent with established safety profiles of olaparib and the chemotherapy comparators, but in this pretreated population, four patients assigned to receive olaparib and three patients assigned to receive chemotherapy developed acute myeloid leukemia (AML)/myelodysplasia; new primary malignancies also occurred in three patients assigned to receive olaparib.[
31 ][Level of evidence B1] - In 2022, AstraZeneca withdrew the indication for olaparib monotherapy for the treatment of patients with deleterious germline BRCA-altered ovarian cancer who have received at least three previous lines of chemotherapy.[
34 ]
- Rucaparib underwent phase II evaluation in ARIEL2 (NCT01891344), an open-label study enrolling 206 patients, 204 of whom were actually receiving the drug (192 were actually in classifiable subgroups) and had high-grade platinum-sensitive recurrences between October 2013 and November 2014.[
35 ][Level of evidence C2] The following three predefined homologous recombination deficiency subgroups on the basis of tumor mutational analysis were studied:- BRCA variant (deleterious genetic or somatic) (n = 40).
- BRCA wild type and high loss of heterozygosity (LOH) quantified by next-generation sequencing analysis (LOH high) (n = 82).
- BRCA wild type and low LOH (LOH low) (n = 70).
- Median PFS after the start of rucaparib treatment for patients with deleterious BRCA variants was 12.8 months (95% CI, 9.0–14.7); for those with LOH, high was 5.7 months (range, 5.3–7.6 months), and low was 5.2 months (range, 3.6–5.5 months).
- The study also showed that variant and methylation status of BRCA and other homologous recombination-related genes, such as RAD51C, can be associated with high genomic LOH in BRCA wild-type tumors, conferring higher rates of response to rucaparib than are seen in patients with low genomic LOH.
- Rucaparib was later assessed as maintenance therapy after response to platinum therapy in a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial (ARIEL3 [NCT01968213]).[
36 ] To be eligible, patients had high-grade carcinomas that were previously treated with at least two platinum-containing regimens and had achieved complete or partial responses to the last platinum-containing regimen. In a 2:1 treatment allocation, 375 patients received rucaparib, and 189 patients received placebo.- PFS, as determined by the investigator, was the primary end point using a step-down procedure for the following three determined, nested treatment cohorts:
- Patients known to have deleterious germline or somatic BRCA variants: PFS of 16.6 months in the rucaparib group (95% CI, 13.4–22.9) versus 5.4 months in the placebo group (95% CI, 3.4–6.7; HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.16–0.34; P < .0001).
- Patients with homologous recombination deficiencies: PFS of 13.6 months in the rucaparib group (95% CI, 10.9–16.2) versus 5.4 months in the placebo group (95% CI, 5.1–5.6; HR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.24–0.42; P < .00011).
- The intention-to-treat population: PFS of 10.8 months in the rucaparib group (95% CI, 8.3–11.4) versus 5.4 months in the placebo group (95% CI, 5.3–5.5; HR, 0.24–0.42; P < .0001.
- Treatment-emergent adverse events of grade 3 or higher in the rucaparib group versus the placebo group consisted primarily of anemia (19% vs. 1%) and increased alanine aminotransferase or aspartate aminotransferase (10% vs. 0%).
- In an updated outcomes, intention-to-treat, and safety analysis for all cohorts, at a median follow-up of 28 months, rucaparib had significant persistent advantages in PFS compared with placebo (14.3 months vs. 8.8 months [HR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0,35−0.53]).[
37 ][Level of evidence B1] - Time to first subsequent therapy, time to progression on subsequent therapy, and time to start a second subsequent treatment were also significantly in favor of rucaparib.
- Three occurrences of AML/myelodysplasia treatment-related events had been previously reported, and treatment-emergent serious adverse events were recorded in 22% of patients who received rucaparib versus 11% of patients who received placebo.
- Anemia was the most common toxicity attributed to rucaparib (in 22% of patients).
- In an analysis from this trial of quality-adjusted PFS and quality-adjusted time without symptoms or toxicity, both determinations confirmed that rucaparib was beneficial compared with placebo in all predefined cohorts.[
38 ]
- PFS, as determined by the investigator, was the primary end point using a step-down procedure for the following three determined, nested treatment cohorts:
- The ARIEL4 trial (NCT02855944) evaluated rucaparib versus chemotherapy in patients with high-grade ovarian epithelial cancer and BRCA variants who had been treated with at least two previous lines of chemotherapy.[
39 ]- In the intent-to-treat population, the median OS was 19.4 months in the rucaparib group and 25.4 months in the chemotherapy group (HR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.00–1.73; P = .0507).
- In 2022, Clovis Oncology withdrew the indication for rucaparib monotherapy for the treatment of patients with BRCA-altered cancer who had been treated with at least two previous lines of chemotherapy.
- QUADRA (NCT02354586) was a multicenter, open-label, single-arm phase II trial that studied niraparib as late-line treatment for patients with ovarian cancer.[
40 ] It enrolled 463 women who had received a median of four (range, 3−5) previous regimens (151 patients were platinum resistant and 161 patients were platinum refractory).- In the primary efficacy measurable population, 13 of 47 patients responded according to RECIST.[
40 ][Level of evidence C2] - Homologous recombination deficiency was a predictor of response.
- Because the makers of olaparib and rucaparib found decreased survival in patients who had received previous chemotherapy when a PARP inhibitor was used as monotherapy, in 2022, GSK withdrew the indication for niraparib as monotherapy for fourth-line treatment in patients with ovarian epithelial tumors associated with homologous recombination deficiency.[
41 ]
- In the primary efficacy measurable population, 13 of 47 patients responded according to RECIST.[
- Niraparib was evaluated further in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial of 533 patients with platinum-sensitive, predominantly high-grade serous ovarian cancer, who were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to maintenance with oral niraparib or placebo and followed for the primary end point of PFS.[
42 ] Patients were categorized according to the presence or absence of germline BRCA or non-BRCA homologous recombination deficiency–positive ovarian cancer or non-BRCA homologous recombination deficiency–negative ovarian cancer, based on BRCAAnalysis testing (Myriad Genetics) from tumor and blood samples.- Patients who received niraparib had significantly longer median PFS duration compared with a placebo.[
42 ][Level of evidence B1] Comparisons across categories ranged from HR, 0.27 for germline BRCA cancer (21.0 months vs. 5.5 months), HR, 0.38 for non-BRCA cancer, homologous recombination deficiency-positive cancer (12.9 months vs. 3.8 months), and HR, 0.45 for non-BRCA, homologous recombination deficiency-negative cancer (9.3 months vs. 3.9 months). - A total of 16.1% of patients who received niraparib and 19.3% of patients who received placebo died during the study.
- One-third to nearly one-half of the patients had received at least three previous lines of therapy that included:
- Grade 3 or 4 adverse events that were managed with dose modifications while patients received niraparib included thrombocytopenia (in 33.8% of patients), anemia (in 25.3%), and neutropenia (in 19.6%).
- Other excess severe toxicities in patients who received niraparib occurred at starting doses of 300 mg once daily and included fatigue (in 30 patients vs. 1 patient on the placebo), hypertension (in 30 patients vs. 4 on the placebo), nausea (in 11 patients vs. 2 on the placebo), and vomiting (in 7 patients vs. 1 on the placebo).
- A subsequent analysis of the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA trial (NCT01847274) updates PFS after maintenance niraparib or placebo according to the best response (partial response [PR] or complete response [CR]) from the last platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with germline BRCA variants and in non-germline BRCA variant cohorts.[
43 ]- The HR was significant for niraparib versus placebo, and the effect was seen in both cohorts.
- No meaningful differences in patient-reported outcomes were observed.
- A phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of niraparib maintenance in patients with homologous recombination deficiency–positive advanced ovarian cancer following response to front-line platinum-based chemotherapy (NCT01847274) is closed to patient accrual and results are pending.
- Other PARP inhibitor trials have been exploring their role in platinum-resistant disease and their role in combination with other agents.
- Patients who received niraparib had significantly longer median PFS duration compared with a placebo.[
- Olaparib was also evaluated as a single agent in a multicenter phase II trial for patients with documented germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants.[
44 ][Level of evidence C3] This trial was open to patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, breast cancer treated with three or more previous regimens, pancreatic cancer with previously administered gemcitabine, or prostate cancer previously treated with hormonal therapy and one systemic therapy. Olaparib was given at 400 mg twice a day. The primary end point was response rate. A total of 298 patients were included.- The overall response rate was 26.2%; the response rate was 31.1% in patients with ovarian cancer.[
44 ][Level of evidence C3]
The data from this trial were used by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to approve olaparib for patients with ovarian cancer who have known BRCA1 or BRCA2 variants and have failed three previous regimens.
- The overall response rate was 26.2%; the response rate was 31.1% in patients with ovarian cancer.[
- Several other trials have combined olaparib with either cytotoxic chemotherapy or other biological therapy.[
45 ,46 ]- Extension in PFS, but not in OS, has been noted.
Platinum-refractory or platinum-resistant recurrence
Chemotherapy
Clinical recurrences that take place within 6 months of completion of a platinum-containing regimen are considered platinum-refractory or platinum-resistant recurrences. Anthracyclines (particularly when formulated as pegylated liposomal doxorubicin), taxanes, topotecan, and gemcitabine are used as single agents for these recurrences on the basis of activity and their favorable therapeutic indices relative to agents listed in
Drugs used to treat platinum-refractory or platinum-resistant recurrences include:
- Paclitaxel.
Treatment with paclitaxel historically provided the first agent with consistent activity in patients with platinum-refractory or platinum-resistant recurrences.[
47 ,48 ,49 ,50 ,51 ] Patients generally received paclitaxel in front-line induction regimens. Re-treatment with paclitaxel, particularly in weekly schedules, had activity comparable with that of other drugs. Residual neuropathy upon recurrence may shift the choice of treatment towards other agents. - Topotecan.
Randomized studies have indicated that the use of topotecan achieved results that were comparable with those achieved with paclitaxel.[
52 ]Evidence (topotecan):
- Topotecan was compared with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in a randomized trial of 474 patients and demonstrated similar response rates, PFS, and OS at the time of the initial report. Responses occurred primarily in the platinum-resistant subsets.[
53 ] - In phase II studies, topotecan administered intravenously (IV) on days 1 to 5 of a 21-day cycle yielded objective response rates ranging from 13% to 16.3% and other outcomes that were equivalent or superior to paclitaxel.[
54 ,55 ,56 ]- Objective responses were reported in patients with platinum-refractory disease.
- Substantial myelosuppression followed administration. Other toxic effects included nausea, vomiting, alopecia, and asthenia. Some schedules and oral formulations to reduce toxicity are under evaluation.
- In a phase III study, 235 patients who did not respond to initial treatment with a platinum-based regimen, but who had not previously received paclitaxel or topotecan, were randomly assigned to receive either topotecan as a 30-minute infusion daily for 5 days every 21 days or paclitaxel as a 3-hour infusion every 21 days.[
52 ][Level of evidence B1]- The overall objective response rate was 20.5% for patients who were randomly assigned to treatment with topotecan and 13.2% for patients who were randomly assigned to treatment with paclitaxel (P = .138).
- Both groups experienced myelosuppression and gastrointestinal (GI) toxic effects. Nausea and vomiting, fatigue, and infection were observed more commonly after treatment with topotecan, whereas alopecia, arthralgia, myalgia, and neuropathy were observed more commonly after treatment with paclitaxel.[
52 ]
- The combination of weekly topotecan and biweekly bevacizumab was evaluated in a phase II study.
- Results showed an objective response rate of 25% (all partial responses) in a platinum-resistant patient population.[
57 ] - The most common grade 3 and grade 4 toxicities were hypertension, neutropenia, and GI toxicity, although no bowel perforations occurred.
- Results showed an objective response rate of 25% (all partial responses) in a platinum-resistant patient population.[
- Topotecan was compared with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in a randomized trial of 474 patients and demonstrated similar response rates, PFS, and OS at the time of the initial report. Responses occurred primarily in the platinum-resistant subsets.[
- Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin.
Evidence (pegylated liposomal doxorubicin):
- In a phase II study encapsulated doxorubicin was given IV once every 21 to 28 days.[
58 ]- Results demonstrated one complete response and eight partial responses in 35 patients with platinum-refractory or paclitaxel-refractory disease (response rate, 25.7%).
- In general, liposomal doxorubicin has few acute side effects other than hypersensitivity. The most frequent toxic effects (stomatitis and hand-foot syndrome) were usually observed after the first cycle and were more pronounced after dose rates exceeded 10 mg/m2 per week. Neutropenia and nausea were minimal, and alopecia rarely occurred.
- Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and topotecan have been compared in a randomized trial of 474 patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.[
53 ][Level of evidence A1]- Response rates (19.7% vs. 17.0%; P = .390), PFS (16.1 weeks vs. 17.0 weeks; P = .095), and OS (60 weeks vs. 56.7 weeks; P = .341) did not differ significantly between the pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and topotecan arms.[
53 ][Level of evidence A1] - Survival was longer for the patients with platinum-sensitive disease who received pegylated liposomal doxorubicin.[
21 ]
- Response rates (19.7% vs. 17.0%; P = .390), PFS (16.1 weeks vs. 17.0 weeks; P = .095), and OS (60 weeks vs. 56.7 weeks; P = .341) did not differ significantly between the pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and topotecan arms.[
- In a phase II study encapsulated doxorubicin was given IV once every 21 to 28 days.[
- Docetaxel.
This drug has shown activity in paclitaxel-pretreated patients and is a reasonable alternative to weekly paclitaxel in the recurrent setting.[
59 ] - Gemcitabine.
Gemcitabine is an antimetabolite that was developed and approved in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy drugs and has shown activity as a single agent. Gemcitabine combined with cell cycle−targeted drugs and other drug combinations used in indications such as pancreatic and lung cancers are being explored.[
60 ,61 ,62 ,63 ]Evidence (gemcitabine):
- Several phase II trials of gemcitabine as a single-agent–administered IV on days 1, 8, and 15 of a 28-day cycle have been reported.[
60 ,61 ,62 ]- The response rate ranged from 13% to 19% in evaluable patients.
- Responses have been observed in patients whose disease was platinum refractory and/or paclitaxel refractory as well as in patients with bulky disease.
- Leukopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia were the most common toxic effects. Many patients reported transient flu-like symptoms and a rash after drug administration. Other toxic effects, including nausea, were usually mild.
- A randomized trial of gemcitabine versus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin showed noninferiority and no advantage in therapeutic index of one drug over the other.[
63 ]
- Several phase II trials of gemcitabine as a single-agent–administered IV on days 1, 8, and 15 of a 28-day cycle have been reported.[
- Pemetrexed.
Pemetrexed combined with gemcitabine has had unconvincing results compared with either agent alone.[
64 ,65 ] More studies are forthcoming that target cell cycle derangements common in certain genomic subtypes of ovarian cancer. Specifically, gemcitabine is presumed to be more active when there is loss of G1/S checkpoint from TP53 variants, CCNE1 amplification, RB1 loss, or CDKN2A mRNA downregulation.Evidence (pemetrexed):
- A randomized, double-blinded phase II European trial with 102 patients evaluated pemetrexed at two doses: standard-dose (500 mg/m2) versus high-dose (900 mg/m2) IV every 3 weeks.[
66 ]- The response rate was 9.3% for the standard dose and 10.4% for the high dose.
- The toxicity profile favored the standard dose, with fatigue, nausea, and vomiting as the most common severe toxicities.
- A phase II study by the GOG utilized pemetrexed (900 mg/m2) IV every 3 weeks in 51 patients with platinum-resistant recurrent disease.[
67 ]- The response rate was 21% in a heavily pretreated population in which 39% of the patients had received five or more regimens previously.
- Myelosuppression and fatigue were the most common severe toxicities.
- A randomized, double-blinded phase II European trial with 102 patients evaluated pemetrexed at two doses: standard-dose (500 mg/m2) versus high-dose (900 mg/m2) IV every 3 weeks.[
Chemotherapy and/or bevacizumab
- Chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab.
The
FDA has approved the use of bevacizumab in combination with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, paclitaxel, or topotecan as a result of the OCEANS and AURELIA trials.OCEANS (NCT00434642) assessed the role of bevacizumab in the treatment of platinum-sensitive recurrences. For more information, see the
Bevacizumab, other targeted drugs, and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors with or without chemotherapy section.Evidence (bevacizumab with chemotherapy):
- The Avastin Use in Platinum-Resistant Epithelial Ovarian Cancer (AURELIA [NCT00976911]) trial was an open-label, randomized trial designed to evaluate the effect of adding bevacizumab to standard chemotherapy in patients with platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer.[
68 ] Eligible patients had platinum-resistant disease (progression within 6 months of finishing a regimen) and no more than two previous regimens. Patients with platinum-refractory disease (those with progression during receipt of a platinum-containing regimen) and those with clinical or radiological signs of bowel involvement were ineligible. Patients were prescribed one of the following three chemotherapy regimens, on the basis of physician preference:- Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin 40 mg/m2 by IV on day 1 every 4 weeks.
- Paclitaxel 80 mg/m2 by IV on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 every 4 weeks.
- Topotecan 4 mg/m2 by IV on days 1, 8, and 15 every 4 weeks; or 1.25 mg/m2 by IV on days 1 through 5 every 3 weeks.
Patients were then randomly assigned to receive either chemotherapy alone or chemotherapy with bevacizumab (10 mg/kg every 2 weeks, or 15 mg/kg every 3 weeks if on the 3-week-dosing schedule). Crossover to a bevacizumab-containing regimen was allowed at progression for those patients in the chemotherapy-only arm. PFS was the primary outcome, with response rate, OS, safety, and quality of life used as secondary end points. The enrollment included 361 patients with a median follow-up of 13.9 months in the chemotherapy-only arm and 13.0 months in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm.
- Patients in the bevacizumab arm exhibited longer PFS (HR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.38 to 0.60); median PFS was 3.4 months in the chemotherapy-alone arm versus 6.7 months in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm.
- The objective response rate was 12.6% in the chemotherapy-alone arm versus 30.9% in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm.
- There was no statistically significant difference in OS between the regimens (13.3 months chemotherapy alone vs. 16.6 months chemotherapy plus bevacizumab).
- Patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm had an increased incidence of hypertension and proteinuria, when compared with patients in the chemotherapy-only arm.
- GI perforation occurred in 2% of those receiving chemotherapy plus bevacizumab, which reflects the study's stringent exclusion criteria.
- The primary end point for the quality-of-life portion of the study was a 15% or greater absolute improvement in the abdominal and GI symptom portion of the assessment modules at week 8 to week 9 of the protocol for patients in the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm.[
69 ][Level of evidence A3] The study used patient-reported outcomes from the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Ovarian Cancer Module 28 and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Ovarian Cancer symptom index at baseline and every 8 to 9 weeks until disease progression.
Although there were some limitations in study design,[
70 ] more patients on the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm had 15% or greater improvement in their GI scores when compared with baseline. For the chemotherapy-plus-bevacizumab arm, 34 of 115 patients (29.6%) showed improvement versus 15 of 118 (12.7%) patients who showed improvement on the chemotherapy-alone arm (difference, 16.9%; 95% CI, 6.1%–27.6%; P = .002).These studies confirm the effect of improving PFS when bevacizumab is added to chemotherapy for ovarian cancer. In the OCEANS trial, the HR for progression was even more prominent than in the first-line trials, and a significant effect was seen when the bevacizumab-chemotherapy combination was extended beyond six cycles until progression.
In summary, the improvement achieved by bevacizumab in relative risk and PFS rates in platinum-sensitive and platinum-resistant recurrences has been consistently more than the improvement achieved with chemotherapy alone; however, bevacizumab-related toxic effects must be considered.
- The Avastin Use in Platinum-Resistant Epithelial Ovarian Cancer (AURELIA [NCT00976911]) trial was an open-label, randomized trial designed to evaluate the effect of adding bevacizumab to standard chemotherapy in patients with platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer.[
- Bevacizumab alone.
Three phase II studies have shown activity for this antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor.
- The first study (GOG-0170D) included 62 patients who had received only one or two previous treatments. These last patients had received one additional platinum-based regimen because of an initial interval of 12 months or longer after first-line regimens and also had to have a performance status of 0 or 1.[
71 ] Patients received a dose of 15 mg/kg every 21 days.- There were two complete responses and 11 partial responses, a median PFS of 4.7 months, and an OS of 17 months. This activity was noted in both platinum-sensitive and platinum-resistant subsets.
- The second study included only patients with platinum-resistant disease using an identical dose schedule.
- The study was stopped because 5 of 44 patients experienced bowel perforations, one of them fatal; seven partial responses had been observed.[
72 ] This increased risk of bowel perforations was associated with three or more previous treatments.[73 ,74 ,75 ][Level of evidence C2]
- The study was stopped because 5 of 44 patients experienced bowel perforations, one of them fatal; seven partial responses had been observed.[
- The third study (CCC-PHII-45) included 70 patients who received 50 mg of oral cyclophosphamide daily, in addition to bevacizumab (10 mg/kg q 2 weeks).
- Partial responses were observed in 17 patients, and 4 patients had intestinal perforations.[
76 ]
- Partial responses were observed in 17 patients, and 4 patients had intestinal perforations.[
- The first study (GOG-0170D) included 62 patients who had received only one or two previous treatments. These last patients had received one additional platinum-based regimen because of an initial interval of 12 months or longer after first-line regimens and also had to have a performance status of 0 or 1.[
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
- Avelumab.
Avelumab, an antibody targeting programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), was studied alone or in combination with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin chemotherapy followed by chemotherapy alone in patients with platinum-resistant or refractory ovarian cancer.[
77 ]Evidence (avelumab):
- The JAVELIN Ovarian 200 trial (NCT02580058) accrued 556 patients between January 2016 and March 2016. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either avelumab plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin alone, or avelumab alone.[
77 ] This study began before the FDA approved the combination of bevacizumab and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin from the AURELIA trial.[68 ]- The PFS and OS results failed to show superiority for avelumab over pegylated liposomal doxorubicin. The median PFS was 3.7 months (95% CI, 3.3–5.1) for patients who received the combination therapy, 3.5 months (2.1–4.0) for patients who received pegylated liposomal doxorubicin alone, and 1.9 months (1.8–1.9) for patients who received avelumab alone. The median OS was 15.7 months (95% CI, 12.7–18.7) for patients who received the combination therapy, 13.1 months (11.8–15.5) for patients who received pegylated liposomal doxorubicin alone, and 11.8 months (8.9–14.1) for patients who received avelumab alone.
- The JAVELIN Ovarian 200 trial (NCT02580058) accrued 556 patients between January 2016 and March 2016. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either avelumab plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin alone, or avelumab alone.[
- Durvalumab.
Early phase studies have evaluated the use of other immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., durvalumab) with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in patients with platinum-resistant recurrent disease.[
78 ]Evidence (durvalumab):
- In a phase I/II trial (NCT02431559), published in abstract form, 40 patients scheduled to receive pegylated liposomal doxorubicin also received durvalumab.[
78 ]- At 6 months, the PFS rate was 47.7% (when assessed per protocol).
- The OS response rate was 22.5%, with four patients achieving a complete response and five patients achieving a partial response. The median PFS was 5.5 months (0.3–28.8+) and the median OS was 17.6 months (1.7–23.5+).
- In a phase I/II trial (NCT02431559), published in abstract form, 40 patients scheduled to receive pegylated liposomal doxorubicin also received durvalumab.[
Antibody-drug conjugates
- Mirvetuximab soravtansine.
Evidence (mirvetuximab soravtansine):
- The international, phase III, randomized controlled MIRASOL trial (NCT04209855) enrolled 453 women with platinum-resistant, high-grade, serous ovarian cancer. Patients had received one to three prior lines of chemotherapy. Women were randomly assigned to receive either mirvetuximab soravtansine (6 mg/kg every 3 weeks) or the investigator's choice chemotherapy (paclitaxel, liposomal doxorubicin, or topotecan). All patients were required to have high tumor expression of folate receptor alpha (defined as ≥75% of cells ≥2+ by immunohistochemistry). The primary end point was PFS.[
79 ]- Patients who received mirvetuximab soravtansine had a longer median PFS (5.62 months; 95% CI, 4.34–5.95) than those who received the investigator's choice of chemotherapy (3.98 months; 95% CI, 2.86–4.47).[
79 ][Level of evidence B1] - Ocular examinations were mandatory, and 56% of patients who received mirvetuximab soravtansine developed an ocular adverse event.
- Patients who received mirvetuximab soravtansine had a longer median PFS (5.62 months; 95% CI, 4.34–5.95) than those who received the investigator's choice of chemotherapy (3.98 months; 95% CI, 2.86–4.47).[
- The international, phase III, randomized controlled MIRASOL trial (NCT04209855) enrolled 453 women with platinum-resistant, high-grade, serous ovarian cancer. Patients had received one to three prior lines of chemotherapy. Women were randomly assigned to receive either mirvetuximab soravtansine (6 mg/kg every 3 weeks) or the investigator's choice chemotherapy (paclitaxel, liposomal doxorubicin, or topotecan). All patients were required to have high tumor expression of folate receptor alpha (defined as ≥75% of cells ≥2+ by immunohistochemistry). The primary end point was PFS.[
Other drugs used to treat platinum-refractory or platinum-resistant recurrence (efficacy not well defined)
The drugs shown in
| Drugs | Drug Class | Major Toxicities | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Etoposide | Topoisomerase II inhibitor | Myelosuppression; alopecia | Oral administration; rare leukemia lessens acceptability and dampens interest |
| Cyclophosphamide and several other bis chloroethyl amines | Alkylating agents | Myelosuppression; alopecia (only the oxazaphosphorines) | Leukemia and cystitis; uncertain activity after platinum agents |
| Hexamethylmelamine (Altretamine) | Unknown but probably alkylating prodrugs | Emesis and neurological toxic effects | Oral administration; uncertain activity after platinum agents |
| Irinotecan | Topoisomerase I inhibitor | Diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms | Cross-resistant to topotecan |
| Oxaliplatin | Platinum | Neuropathy, emesis, myelosuppression | Cross-resistant to usual platinum agents, but less so |
| Vinorelbine | Mitotic inhibitor | Myelosuppression | Erratic activity |
| Fluorouracil and capecitabine | Fluoropyrimidine antimetabolites | Gastrointestinal symptoms and myelosuppression | Capecitabine is oral; may be useful in mucinous tumors |
| Tamoxifen | Antiestrogen | Thromboembolism | Oral administration; minimal activity, perhaps more in subsets |
Current Clinical Trials
Use our
References:
- Ozols RF, Bundy BN, Greer BE, et al.: Phase III trial of carboplatin and paclitaxel compared with cisplatin and paclitaxel in patients with optimally resected stage III ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 21 (17): 3194-200, 2003.
- Rustin GJ, van der Burg ME, Griffin CL, et al.: Early versus delayed treatment of relapsed ovarian cancer (MRC OV05/EORTC 55955): a randomised trial. Lancet 376 (9747): 1155-63, 2010.
- Stark DP, Cook A, Brown JM, et al.: Quality of life with cediranib in relapsed ovarian cancer: The ICON6 phase 3 randomized clinical trial. Cancer 123 (14): 2752-2761, 2017.
- Hoskins WJ, Rubin SC, Dulaney E, et al.: Influence of secondary cytoreduction at the time of second-look laparotomy on the survival of patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 34 (3): 365-71, 1989.
- Parmar MK, Ledermann JA, Colombo N, et al.: Paclitaxel plus platinum-based chemotherapy versus conventional platinum-based chemotherapy in women with relapsed ovarian cancer: the ICON4/AGO-OVAR-2.2 trial. Lancet 361 (9375): 2099-106, 2003.
- Shi T, Zhu J, Feng Y, et al.: Secondary cytoreduction followed by chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer (SOC-1): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 22 (4): 439-449, 2021.
- Coleman RL, Brady MF, Herzog TJ, et al.: Bevacizumab and paclitaxel-carboplatin chemotherapy and secondary cytoreduction in recurrent, platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer (NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group study GOG-0213): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18 (6): 779-791, 2017.
- Du Bois A, Sehouli J, Vergote I, et al.: Randomized phase III study to evaluate the impact of secondary cytoreductive surgery in recurrent ovarian cancer: final analysis of AGO DESKTOP III/ENGOT-ov20. [Abstract] J Clin Oncol 2020; 38(15)(suppl): 6000. doi:10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.6000.
Available online . Last accessed February 10, 2025. - van de Laar R, Zusterzeel PL, Van Gorp T, et al.: Cytoreductive surgery followed by chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for recurrent platinum-sensitive epithelial ovarian cancer (SOCceR trial): a multicenter randomised controlled study. BMC Cancer 14: 22, 2014.
- van de Laar R, Kruitwagen RF, Zusterzeel PL, et al.: Correspondence: Premature Stop of the SOCceR Trial, a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial on Secondary Cytoreductive Surgery: Netherlands Trial Register Number: NTR3337. Int J Gynecol Cancer 27 (1): 2, 2017.
- Monk BJ, Herzog TJ, Kaye SB, et al.: Trabectedin plus pegylated liposomal Doxorubicin in recurrent ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 28 (19): 3107-14, 2010.
- Pfisterer J, Plante M, Vergote I, et al.: Gemcitabine plus carboplatin compared with carboplatin in patients with platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer: an intergroup trial of the AGO-OVAR, the NCIC CTG, and the EORTC GCG. J Clin Oncol 24 (29): 4699-707, 2006.
- Wagner U, Marth C, Largillier R, et al.: Final overall survival results of phase III GCIG CALYPSO trial of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and carboplatin vs paclitaxel and carboplatin in platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer patients. Br J Cancer 107 (4): 588-91, 2012.
- Bolis G, Scarfone G, Giardina G, et al.: Carboplatin alone vs carboplatin plus epidoxorubicin as second-line therapy for cisplatin- or carboplatin-sensitive ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 81 (1): 3-9, 2001.
- Cantù MG, Buda A, Parma G, et al.: Randomized controlled trial of single-agent paclitaxel versus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and cisplatin in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer who responded to first-line platinum-based regimens. J Clin Oncol 20 (5): 1232-7, 2002.
- Pfisterer J, Shannon CM, Baumann K, et al.: Bevacizumab and platinum-based combinations for recurrent ovarian cancer: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 21 (5): 699-709, 2020.
- Pignata S, Lorusso D, Joly F, et al.: Carboplatin-based doublet plus bevacizumab beyond progression versus carboplatin-based doublet alone in patients with platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer: a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 22 (2): 267-276, 2021.
- Muggia FM: Overview of carboplatin: replacing, complementing, and extending the therapeutic horizons of cisplatin. Semin Oncol 16 (2 Suppl 5): 7-13, 1989.
- Piccart MJ, Green JA, Lacave AJ, et al.: Oxaliplatin or paclitaxel in patients with platinum-pretreated advanced ovarian cancer: A randomized phase II study of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Gynecology Group. J Clin Oncol 18 (6): 1193-202, 2000.
- Markman M, Markman J, Webster K, et al.: Duration of response to second-line, platinum-based chemotherapy for ovarian cancer: implications for patient management and clinical trial design. J Clin Oncol 22 (15): 3120-5, 2004.
- Gordon AN, Tonda M, Sun S, et al.: Long-term survival advantage for women treated with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin compared with topotecan in a phase 3 randomized study of recurrent and refractory epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 95 (1): 1-8, 2004.
- Raja FA, Counsell N, Colombo N, et al.: Platinum versus platinum-combination chemotherapy in platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis using individual patient data. Ann Oncol 24 (12): 3028-34, 2013.
- Pujade-Lauraine E, Wagner U, Aavall-Lundqvist E, et al.: Pegylated liposomal Doxorubicin and Carboplatin compared with Paclitaxel and Carboplatin for patients with platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer in late relapse. J Clin Oncol 28 (20): 3323-9, 2010.
- Aghajanian C, Blank SV, Goff BA, et al.: OCEANS: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial of chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab in patients with platinum-sensitive recurrent epithelial ovarian, primary peritoneal, or fallopian tube cancer. J Clin Oncol 30 (17): 2039-45, 2012.
- Bryant HE, Schultz N, Thomas HD, et al.: Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 434 (7035): 913-7, 2005.
- Farmer H, McCabe N, Lord CJ, et al.: Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 434 (7035): 917-21, 2005.
- Ledermann J, Harter P, Gourley C, et al.: Olaparib maintenance therapy in platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med 366 (15): 1382-92, 2012.
- Ledermann J, Harter P, Gourley C, et al.: Olaparib maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive relapsed serous ovarian cancer: a preplanned retrospective analysis of outcomes by BRCA status in a randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 15 (8): 852-61, 2014.
- Pujade-Lauraine E, Ledermann JA, Selle F, et al.: Olaparib tablets as maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive, relapsed ovarian cancer and a BRCA1/2 mutation (SOLO2/ENGOT-Ov21): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18 (9): 1274-1284, 2017.
- Friedlander M, Gebski V, Gibbs E, et al.: Health-related quality of life and patient-centred outcomes with olaparib maintenance after chemotherapy in patients with platinum-sensitive, relapsed ovarian cancer and a BRCA1/2 mutation (SOLO2/ENGOT Ov-21): a placebo-controlled, phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 19 (8): 1126-1134, 2018.
- Penson RT, Valencia RV, Cibula D, et al.: Olaparib Versus Nonplatinum Chemotherapy in Patients With Platinum-Sensitive Relapsed Ovarian Cancer and a Germline BRCA1/2 Mutation (SOLO3): A Randomized Phase III Trial. J Clin Oncol 38 (11): 1164-1174, 2020.
- Kaye SB, Lubinski J, Matulonis U, et al.: Phase II, open-label, randomized, multicenter study comparing the efficacy and safety of olaparib, a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations and recurrent ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 30 (4): 372-9, 2012.
- Penson R, Valencia RV, Colombo N, et al.: Final overall survival results from SOLO3: Phase III trial assessing olaparib monotherapy versus non-platinum chemotherapy in heavily pretreated patients with germline BRCA1- and/or BRCA2-mutated platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer. [Abstract] Gynecol Oncol 166 (Suppl 1) A-026, S19-20, 2022.
- LYNPARZA (olaparib): Important Prescribing Information. AstraZeneca, 2022.
Available online . Last accessed February 10, 2025. - Swisher EM, Lin KK, Oza AM, et al.: Rucaparib in relapsed, platinum-sensitive high-grade ovarian carcinoma (ARIEL2 Part 1): an international, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 18 (1): 75-87, 2017.
- Coleman RL, Oza AM, Lorusso D, et al.: Rucaparib maintenance treatment for recurrent ovarian carcinoma after response to platinum therapy (ARIEL3): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 390 (10106): 1949-1961, 2017.
- Ledermann JA, Oza AM, Lorusso D, et al.: Rucaparib for patients with platinum-sensitive, recurrent ovarian carcinoma (ARIEL3): post-progression outcomes and updated safety results from a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 21 (5): 710-722, 2020.
- Oza AM, Lorusso D, Aghajanian C, et al.: Patient-Centered Outcomes in ARIEL3, a Phase III, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Rucaparib Maintenance Treatment in Patients With Recurrent Ovarian Carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 38 (30): 3494-3505, 2020.
- Oza AM, Lisyanskaya AS, Fedenko AA, et al.: Overall survival results from ARIEL4: A phase III study assessing rucaparib vs chemotherapy in patients with advanced, relapsed ovarian carcinoma and a deleterious BRCA1/2 mutation. [Abstract] Ann Oncol 33 (Suppl 7) A-5180, S780, 2022.
- Moore KN, Secord AA, Geller MA, et al.: Niraparib monotherapy for late-line treatment of ovarian cancer (QUADRA): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 20 (5): 636-648, 2019.
- ZEJULA (niraparib): Important Prescribing Information. GSK, 2022.
Available online . Last accessed February 10, 2025. - Mirza MR, Monk BJ, Herrstedt J, et al.: Niraparib Maintenance Therapy in Platinum-Sensitive, Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med 375 (22): 2154-2164, 2016.
- Del Campo JM, Matulonis UA, Malander S, et al.: Niraparib Maintenance Therapy in Patients With Recurrent Ovarian Cancer After a Partial Response to the Last Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA Trial. J Clin Oncol 37 (32): 2968-2973, 2019.
- Kaufman B, Shapira-Frommer R, Schmutzler RK, et al.: Olaparib monotherapy in patients with advanced cancer and a germline BRCA1/2 mutation. J Clin Oncol 33 (3): 244-50, 2015.
- Liu JF, Barry WT, Birrer M, et al.: Combination cediranib and olaparib versus olaparib alone for women with recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer: a randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 15 (11): 1207-14, 2014.
- Oza AM, Cibula D, Benzaquen AO, et al.: Olaparib combined with chemotherapy for recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer: a randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 16 (1): 87-97, 2015.
- Kohn EC, Sarosy G, Bicher A, et al.: Dose-intense taxol: high response rate in patients with platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 86 (1): 18-24, 1994.
- McGuire WP, Rowinsky EK, Rosenshein NB, et al.: Taxol: a unique antineoplastic agent with significant activity in advanced ovarian epithelial neoplasms. Ann Intern Med 111 (4): 273-9, 1989.
- Einzig AI, Wiernik PH, Sasloff J, et al.: Phase II study and long-term follow-up of patients treated with taxol for advanced ovarian adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 10 (11): 1748-53, 1992.
- Thigpen JT, Blessing JA, Ball H, et al.: Phase II trial of paclitaxel in patients with progressive ovarian carcinoma after platinum-based chemotherapy: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 12 (9): 1748-53, 1994.
- Trimble EL, Adams JD, Vena D, et al.: Paclitaxel for platinum-refractory ovarian cancer: results from the first 1,000 patients registered to National Cancer Institute Treatment Referral Center 9103. J Clin Oncol 11 (12): 2405-10, 1993.
- ten Bokkel Huinink W, Gore M, Carmichael J, et al.: Topotecan versus paclitaxel for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 15 (6): 2183-93, 1997.
- Gordon AN, Fleagle JT, Guthrie D, et al.: Recurrent epithelial ovarian carcinoma: a randomized phase III study of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin versus topotecan. J Clin Oncol 19 (14): 3312-22, 2001.
- Kudelka AP, Tresukosol D, Edwards CL, et al.: Phase II study of intravenous topotecan as a 5-day infusion for refractory epithelial ovarian carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 14 (5): 1552-7, 1996.
- Creemers GJ, Bolis G, Gore M, et al.: Topotecan, an active drug in the second-line treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer: results of a large European phase II study. J Clin Oncol 14 (12): 3056-61, 1996.
- Bookman MA, Malmström H, Bolis G, et al.: Topotecan for the treatment of advanced epithelial ovarian cancer: an open-label phase II study in patients treated after prior chemotherapy that contained cisplatin or carboplatin and paclitaxel. J Clin Oncol 16 (10): 3345-52, 1998.
- McGonigle KF, Muntz HG, Vuky J, et al.: Combined weekly topotecan and biweekly bevacizumab in women with platinum-resistant ovarian, peritoneal, or fallopian tube cancer: results of a phase 2 study. Cancer 117 (16): 3731-40, 2011.
- Muggia FM, Hainsworth JD, Jeffers S, et al.: Phase II study of liposomal doxorubicin in refractory ovarian cancer: antitumor activity and toxicity modification by liposomal encapsulation. J Clin Oncol 15 (3): 987-93, 1997.
- Berkenblit A, Seiden MV, Matulonis UA, et al.: A phase II trial of weekly docetaxel in patients with platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian, primary peritoneal serous cancer, or fallopian tube cancer. Gynecol Oncol 95 (3): 624-31, 2004.
- Friedlander M, Millward MJ, Bell D, et al.: A phase II study of gemcitabine in platinum pre-treated patients with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol 9 (12): 1343-5, 1998.
- Lund B, Hansen OP, Theilade K, et al.: Phase II study of gemcitabine (2',2'-difluorodeoxycytidine) in previously treated ovarian cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 86 (20): 1530-3, 1994.
- Shapiro JD, Millward MJ, Rischin D, et al.: Activity of gemcitabine in patients with advanced ovarian cancer: responses seen following platinum and paclitaxel. Gynecol Oncol 63 (1): 89-93, 1996.
- Mutch DG, Orlando M, Goss T, et al.: Randomized phase III trial of gemcitabine compared with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 25 (19): 2811-8, 2007.
- Yuan Y, Cohen DJ, Love E, et al.: Phase I dose-escalating study of biweekly fixed-dose rate gemcitabine plus pemetrexed in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68 (2): 371-8, 2011.
- Hensley ML, Larkin J, Fury M, et al.: A phase I trial of pemetrexed plus gemcitabine given biweekly with B-vitamin support in solid tumor malignancies or advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14 (19): 6310-6, 2008.
- Vergote I, Calvert H, Kania M, et al.: A randomised, double-blind, phase II study of two doses of pemetrexed in the treatment of platinum-resistant, epithelial ovarian or primary peritoneal cancer. Eur J Cancer 45 (8): 1415-23, 2009.
- Miller DS, Blessing JA, Krasner CN, et al.: Phase II evaluation of pemetrexed in the treatment of recurrent or persistent platinum-resistant ovarian or primary peritoneal carcinoma: a study of the Gynecologic Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 27 (16): 2686-91, 2009.
- Pujade-Lauraine E, Hilpert F, Weber B, et al.: Bevacizumab combined with chemotherapy for platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer: The AURELIA open-label randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 32 (13): 1302-8, 2014.
- Stockler MR, Hilpert F, Friedlander M, et al.: Patient-reported outcome results from the open-label phase III AURELIA trial evaluating bevacizumab-containing therapy for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 32 (13): 1309-16, 2014.
- Liu JF, Cannistra SA: Emerging role for bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy for patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 32 (13): 1287-9, 2014.
- Burger RA, Sill MW, Monk BJ, et al.: Phase II trial of bevacizumab in persistent or recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer or primary peritoneal cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol 25 (33): 5165-71, 2007.
- Cannistra SA, Matulonis UA, Penson RT, et al.: Phase II study of bevacizumab in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer or peritoneal serous cancer. J Clin Oncol 25 (33): 5180-6, 2007.
- Vasey PA, McMahon L, Paul J, et al.: A phase II trial of capecitabine (Xeloda) in recurrent ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 89 (10): 1843-8, 2003.
- Monk BJ, Han E, Josephs-Cowan CA, et al.: Salvage bevacizumab (rhuMAB VEGF)-based therapy after multiple prior cytotoxic regimens in advanced refractory epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 102 (2): 140-4, 2006.
- Kaye SB: Bevacizumab for the treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer: will this be its finest hour? J Clin Oncol 25 (33): 5150-2, 2007.
- Garcia AA, Hirte H, Fleming G, et al.: Phase II clinical trial of bevacizumab and low-dose metronomic oral cyclophosphamide in recurrent ovarian cancer: a trial of the California, Chicago, and Princess Margaret Hospital phase II consortia. J Clin Oncol 26 (1): 76-82, 2008.
- Pujade-Lauraine E, Fujiwara K, Ledermann JA, et al.: Avelumab alone or in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in platinum-resistant or platinum-refractory ovarian cancer (JAVELIN Ovarian 200): an open-label, three-arm, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 22 (7): 1034-1046, 2021.
- O'Cearbhaill RE, Wolfer A, Disilvestro P: A phase I/II study of chemo-immunotherapy with durvalumab (durva) and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) in platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer (PROC). [Abstract] Ann Oncol 29 (suppl 8): A-945P, viii337, 2018.
Also available online . Last accessed February 10, 2025. - Moore KN, Angelergues A, Konecny GE, et al.: Mirvetuximab Soravtansine in FRα-Positive, Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med 389 (23): 2162-2174, 2023.
Latest Updates to This Summary (02 / 12 / 2025)
The PDQ cancer information summaries are reviewed regularly and updated as new information becomes available. This section describes the latest changes made to this summary as of the date above.
Updated
Added this new section.
Added
This summary is written and maintained by the
About This PDQ Summary
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary for health professionals provides comprehensive, peer-reviewed, evidence-based information about the treatment of ovarian epithelial, fallopian tube, and primary peritoneal cancer. It is intended as a resource to inform and assist clinicians in the care of their patients. It does not provide formal guidelines or recommendations for making health care decisions.
Reviewers and Updates
This summary is reviewed regularly and updated as necessary by the
Board members review recently published articles each month to determine whether an article should:
- be discussed at a meeting,
- be cited with text, or
- replace or update an existing article that is already cited.
Changes to the summaries are made through a consensus process in which Board members evaluate the strength of the evidence in the published articles and determine how the article should be included in the summary.
The lead reviewer for Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Treatment is:
- Olga T. Filippova, MD (Lenox Hill Hospital)
Any comments or questions about the summary content should be submitted to Cancer.gov through the NCI website's
Levels of Evidence
Some of the reference citations in this summary are accompanied by a level-of-evidence designation. These designations are intended to help readers assess the strength of the evidence supporting the use of specific interventions or approaches. The PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board uses a
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. Although the content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text, it cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless it is presented in its entirety and is regularly updated. However, an author would be permitted to write a sentence such as "NCI's PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks succinctly: [include excerpt from the summary]."
The preferred citation for this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Ovarian Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at:
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use within the PDQ summaries only. Permission to use images outside the context of PDQ information must be obtained from the owner(s) and cannot be granted by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the illustrations in this summary, along with many other cancer-related images, is available in
Disclaimer
Based on the strength of the available evidence, treatment options may be described as either "standard" or "under clinical evaluation." These classifications should not be used as a basis for insurance reimbursement determinations. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our
Last Revised: 2025-02-12
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the
Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Ignite Healthwise, LLC.
Page Footer
I want to...
Audiences
Secure Member Sites
The Cigna Group Information
Disclaimer
Individual and family medical and dental insurance plans are insured by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (CHLIC), Cigna HealthCare of Arizona, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Illinois, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Georgia, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of North Carolina, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of South Carolina, Inc., and Cigna HealthCare of Texas, Inc. Group health insurance and health benefit plans are insured or administered by CHLIC, Connecticut General Life Insurance Company (CGLIC), or their affiliates (see
All insurance policies and group benefit plans contain exclusions and limitations. For availability, costs and complete details of coverage, contact a licensed agent or Cigna sales representative. This website is not intended for residents of New Mexico.